Biology:CAT RNA-binding domain
From HandWiki
Revision as of 22:43, 3 August 2022 by imported>MainAI6 (over-write)
| CAT_RBD | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
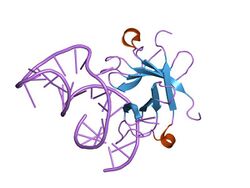 structure of the lict bacterial antiterminator protein in complex with its rna target | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | CAT_RBD | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF03123 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR004341 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1h99 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the CAT RNA-binding domain (Co-AntiTerminator RNA-binding domain) is a protein domain found at the amino terminus of a family of transcriptional antiterminator proteins. This domain forms a dimer in the crystal structure.[1] Transcriptional antiterminators of the BglG/SacY family are regulatory proteins that mediate the induction of sugar metabolizing operons in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Upon activation, these proteins bind to specific targets in nascent mRNAs, thereby preventing abortive dissociation of the RNA polymerase from the DNA template.[2]
References
- ↑ "Crystal structure of a new RNA-binding domain from the antiterminator protein SacY of Bacillus subtilis". EMBO J. 16 (16): 5030–6. August 1997. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.16.5030. PMID 9305644.
- ↑ "RNA recognition by transcriptional antiterminators of the BglG/SacY family: functional and structural comparison of the CAT domain from SacY and LicT". J. Mol. Biol. 294 (2): 389–402. November 1999. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3256. PMID 10610766.
 |

