Biology:Scavenger receptor cysteine-rich protein domain
| SRCR | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
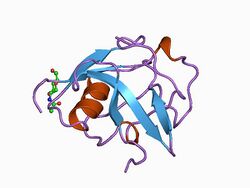 structure of m2bp scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | SRCR | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00530 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001190 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00348 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1by2 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the protein domain SRCR is short for Scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain. They are found solely in eukaryotes. These domains are present on the cell membrane and have a role in binding to specific ligands and are often found to be involved with the immune system.[1]
Function
The function of these endocytic receptors are to mediating non-opsonic phagocytosis in response to foreign ligands. This triggers various processes of host defence and immune response.[2]
Structure
The structure contains a six stranded beta-sheet and one alpha-helix.[1]
Examples
The speract receptor found in egg, is a transmembrane glycoprotein.[3] Other members of this family include the macrophage scavenger receptor type I, an enteropeptidase, and T-cell surface glycoprotein CD5.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hohenester E; Sasaki T; Timpl R (1999). "Crystal structure of a scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domain sheds light on an ancient superfamily.". Nat Struct Biol 6 (3): 228–32. doi:10.1038/6669. PMID 10074941.
- ↑ "A novel scavenger receptor-cysteine-rich (SRCR) domain containing scavenger receptor identified from mollusk mediated PAMP recognition and binding.". Dev Comp Immunol 35 (2): 227–39. 2011. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2010.09.010. PMID 20888856.
- ↑ Resnick D; Pearson A; Krieger M (January 1994). "The SRCR superfamily: a family reminiscent of the Ig superfamily". Trends Biochem. Sci. 19 (1): 5–8. doi:10.1016/0968-0004(94)90165-1. PMID 8140623.
 |

