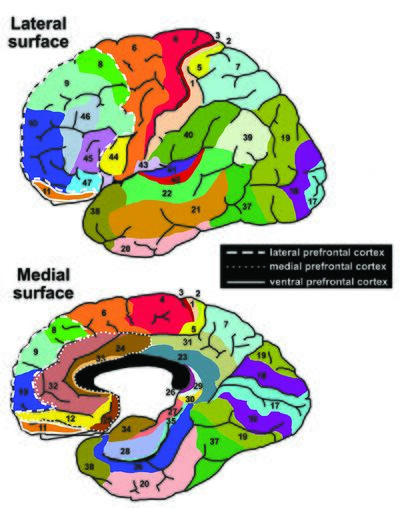
Biology:Lateral prefrontal cortex
In human brain anatomy, the lateral prefrontal cortex (LPFC) is part of the prefrontal cortex (PFC). According to Striedter[1] the PFC of humans can be delineated into two functionally, morphologically, and evolutionarily different regions: the ventromedial PFC (vmPFC) present in all mammals and the LPFC present only in primates. The LPFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA45, BA46, and BA47. Some researchers also include BA44.
The LPFC is often further divided into dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (BA8, BA9, BA10, BA46) and ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (BA45, BA47, BA44).
Function
The vmPFC is primarily concerned with inhibition of urges, motivation, identification of rewarding or otherwise significant stimuli, as well as mood and empathy. The LPFC is primarily involved in working memory, reasoning, planning, and active forms of imagination: Prefrontal Synthesis, mental rotation, and integration of modifiers.
References
- ↑ Striedter, George F. (2005) (in en). Principles of brain evolution. Sinauer Associates. ISBN 978-0878938209. https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2004-21314-000.
 |