Biology:par stability determinant
| FstAT | |
|---|---|
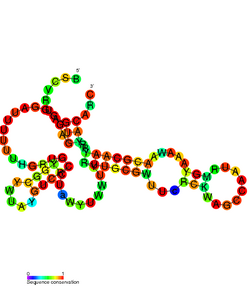 Secondary structure of FstAT | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | fstAT |
| Rfam | RF01797 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; antitoxin |
| Domain(s) | Enterococcus faecalis |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
| Fst Type I toxin-antitoxin system | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Fst_toxin | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF13955 | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.C.64 | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 225 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 2kv5 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The par stability determinant is a 400 bp locus of the pAD1 plasmid which encodes a type I toxin-antitoxin system in Enterococcus faecalis.[1][2] It was the first such plasmid addiction module to be found in gram-positive bacteria.[3]
The par locus contains two genes: fst which encodes a 33-amino acid toxic protein and a gene for RNAII, the small RNA anti-toxin which inhibits fst translation.[4] The two genes are found on opposite DNA strands and share a 5' region which is where they are thought to have an antisense interaction.[4] Their RNA secondary structures have been predicted computationally, the complementary regions appear to be presented on exposed loops for interaction.[4]
par maintains pAD1 by means of post-segregational killing (PSK). If a daughter cell does not inherit the par locus, the unstable RNAII will quickly degrade leaving the long-lived fst toxin to damage or kill the daughter cell.[5]
See also
- Hok/sok system
References
- ↑ "Isolation of a derivative of Escherichia coli-Enterococcus faecalis shuttle vector pAM401 temperature sensitive for maintenance in E. faecalis and its use in evaluating the mechanism of pAD1 par-dependent plasmid stabilization". Plasmid 40 (3): 225–232. November 1998. doi:10.1006/plas.1998.1368. PMID 9806859.
- ↑ "Functional analysis of the Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pAD1-encoded stability determinant par". Mol. Microbiol. 20 (1): 53–63. April 1996. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02488.x. PMID 8861204.
- ↑ "An intramolecular upstream helix ensures the stability of a toxin-encoding RNA in Enterococcus faecalis". J. Bacteriol. 191 (5): 1528–1536. March 2009. doi:10.1128/JB.01316-08. PMID 19103923.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "The antisense RNA of the par locus of pAD1 regulates the expression of a 33-amino-acid toxic peptide by an unusual mechanism". Mol. Microbiol. 37 (3): 652–660. August 2000. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02035.x. PMID 10931358.
- ↑ "Antisense RNA-regulated programmed cell death". Annu. Rev. Genet. 31: 1–31. 1997. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.31.1.1. PMID 9442888.
Further reading
- "Antisense RNA-regulated programmed cell death". Annu. Rev. Genet. 31: 1–31. 1997. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.31.1.1. PMID 9442888.
- "A family of genes encoding a cell-killing function may be conserved in all gram-negative bacteria". Mol. Microbiol. 3 (11): 1463–1472. November 1989. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00131.x. PMID 2693900.
- Hayes F (September 2003). "Toxins-antitoxins: plasmid maintenance, programmed cell death, and cell cycle arrest". Science 301 (5639): 1496–1499. doi:10.1126/science.1088157. PMID 12970556. Bibcode: 2003Sci...301.1496H.
- "Unique type of plasmid maintenance function: postsegregational killing of plasmid-free cells". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83 (10): 3116–3120. May 1986. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.10.3116. PMID 3517851. Bibcode: 1986PNAS...83.3116G.
External links
 |

