Chemistry:Communesin B
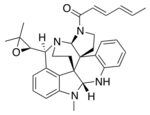
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E,4E)-1-{(3aR,8aR,13bR,16aS,17S)-17-[(2R)-3,3-Dimethyloxiran-2-yl]-9-methyl-2,3,8a,9,14,15-hexahydro-8H-13,16-methanobenzo[c]indolo[3,2-j]pyrrolo[3,2-e][2,6]naphthyridin-1(16aH)-yl}hexa-2,4-dien-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C32H36N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 508.666 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Communesin B is a cytotoxic fungi isolate from Penicillium strains found on the marine alga Ulva intestinalis.[1][2] Out of all naturally-occurring compounds, it exhibited the highest potency on human lung carcinoma, prostate carcinoma, colorectal carcinoma, cervical adenocarcinoma, and breast adenocarcinoma cell lines.[3]
Biosynthesis

Communesin B is a dimeric indole alkaloid with a hexadienoyl moiety originating from polyketide synthesis.[4] Biosynthesis starts with two L-tryptophan molecules processed by different pathways. The first pathway involves a decarboxylation step catalyzed by CnsB to produce tryptamine. The second pathway starts the synthesis of 4-L-dimethylallyl tryptophan by CnsF followed by further processing of CnsA and CnsD to form aurantioclavine.[4] These two indole-containing fragments are combined through a radical oxidative coupling by CnsC, a P450 enzyme, to form the core scaffold of communesin alkaloids.[5] CnsE transfers a methyl group to the indole nitrogen, and CnsJ creates an epoxide ring on the dimethylallyl substituent off the ring structure to form communesin I.[6] Separately, CnsI synthesizes a hexadienoyl group using acetyl-CoA as a starting material and extending it with two malonyl-CoA units.[6] Then, CnsK performs N-acylation with the CnsI-synthesized hexadienoyl chain to form communesin B.[6]
References
- ↑ "A synthetic approach to nomofungin/communesin B". Organic Letters 5 (18): 3169–3171. September 2003. doi:10.1021/ol034407v. PMID 12943379.
- ↑ "Bioactive Compounds Produced by Strains of Penicillium and Talaromyces of Marine Origin". Marine Drugs 14 (2): 37. February 2016. doi:10.3390/md14020037. PMID 26901206.
- ↑ Pompeo, Matthew M.; Cheah, Jaime H.; Movassaghi, Mohammad (2019-09-11). "Total Synthesis and Anti-Cancer Activity of All Known Communesin Alkaloids and Related Derivatives" (in en). Journal of the American Chemical Society 141 (36): 14411–14420. doi:10.1021/jacs.9b07397. ISSN 0002-7863. PMID 31422662.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Branching and converging pathways in fungal natural product biosynthesis". Fungal Biology and Biotechnology 9 (1): 6. March 2022. doi:10.1186/s40694-022-00135-w. PMID 35255990.
- ↑ "Total Synthesis and Anti-Cancer Activity of All Known Communesin Alkaloids and Related Derivatives". Journal of the American Chemical Society 141 (36): 14411–14420. September 2019. doi:10.1021/jacs.9b07397. PMID 31422662.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "Elucidation of the concise biosynthetic pathway of the communesin indole alkaloids". Angewandte Chemie 54 (10): 3004–3007. March 2015. doi:10.1002/anie.201411297. PMID 25571861.
 |

