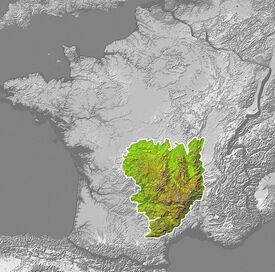
Earth:Massif Central
| Massif Central | |
|---|---|
 View of Puy de Sancy, the highest peak in the Massif Central | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Puy de Sancy |
| Elevation | 1,886 m (6,188 ft) |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] 45°31′42″N 2°48′51″E / 45.52833°N 2.81417°E |
| Naming | |
| Native name | Massís Central (Occitan) |
| Pronunciation | UK: /ˌmæsiːf sɒ̃ˈtrɑːl/, US: /mæˌsiːf -, - sɛnˈ-, məˌsiːf sɑːnˈ-/[1][2][3] French: [masif sɑ̃tʁal] Occitan: [maˈsis senˈtɾal] |
| Geography | |
| Country | France |
| Regions | Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, Bourgogne-Franche-Comté, Nouvelle-Aquitaine and Occitania |
| Range coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 46°N 3°E / 46°N 3°E |
The Massif Central (French pronunciation: [masif sɑ̃tʁal])[4] is a highland region in south-central France, consisting of mountains and plateaus. It covers about 15% of mainland France.
Subject to volcanism that has subsided in the last 10,000 years, these central mountains are separated from the Alps by a deep north–south cleft created by the Rhône river and known in French as the sillon rhodanien (literally "Rhône furrow"). The region was a barrier to transport within France until the opening of the A75 motorway, which not only made north–south travel easier, but also opened access to the massif itself.
Geography and geology
The Massif Central is an old massif, formed during the Variscan orogeny, consisting mostly of granitic and metamorphic rocks. It was powerfully raised and made to look geologically younger in the eastern section by the uplift of the Alps during the Paleogene period and in the southern section by the uplift of the Pyrenees. The massif thus presents a strongly asymmetrical elevation profile with highlands in the south and in the east (Cévennes) dominating the valley of the Rhône and the plains of Languedoc and, by contrast, the less elevated region of Limousin in the northwest.
These tectonic movements created faults and may be at the origin of the volcanism in the massif (but the hypothesis is not proved yet). In fact, above the crystalline foundation, one can observe many volcanoes of many different types and ages: volcanic plateaus (Aubrac, Cézallier), stratovolcanoes (Mounts of Cantal, Monts Dore), and small, very recent monogenic volcanoes (Chaîne des Puys, Vivarais). The entire region contains a large concentration of around 450 extinct volcanoes. The Chaîne des Puys (near Clermont-Ferrand), a range running north to south and less than 160 km2 (60 sq mi) long, contains 115 of them (monogenic volcanoes only).[citation needed] The Auvergne Volcanoes regional natural park is in the massif. The amusement park of Vulcania near Clermont-Ferrand allows visitors to discover this natural heritage and introduces them to volcanology.
In the south, one remarkable region, made up of features called Causses in French, consists of raised limestone plateaus cut by very deep canyons. The most famous of these is the Gorges du Tarn (canyon of the Tarn).
Mountains
Mountain ranges, with notable individual mountains, are (roughly north to south):
- Chaîne des Puys
- Puy de Dôme (1,464 m (4,803 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Puy de Pariou (1,210 m (3,970 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Puy de Lassolas (1,187 m (3,894 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Puy de la Vache (1,167 m (3,829 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Monts Dore
- Puy de Sancy (1,886 m (6,188 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Monts du Lyonnais
- Pilat massif
- Crêt de la Perdrix (1,431 m (4,695 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Mounts of Cantal
- Plomb du Cantal (1,855 m (6,086 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Puy Mary (1,787 m (5,863 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Forez
- Pierre-sur-Haute (1,634 m (5,361 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- L'Aubrac
- Signal de Mailhebiau (1,469 m (4,820 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Margeride
- Signal de Randon (1,551 m (5,089 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Mont Mouchet (1,497 m (4,911 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Vivarais (Ardèche)
- Mont Mézenc (1,753 m (5,751 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Mont Gerbier de Jonc (1,551 m (5,089 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Cévennes
- Mont Lozère (1,699 m (5,574 ft)[convert: invalid option]), the highest non-volcanic summit
- Mont Aigoual (1,567 m (5,141 ft)[convert: invalid option]), near Le Vigan, Florac
- Monts de Lacaune
- Montgrand (1,267 m (4,157 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Monts de l'Espinouse
- Sommet de l'Espinouse (1,124 m (3,688 ft)[convert: invalid option])
- Montagne Noire
- Pic de Nore (1,211 m (3,973 ft)[convert: invalid option])
Chaine des Puys in Auvergne
Puy de Sancy (1,886 m (6,188 ft)[convert: invalid option])
The Cévennes range
Gorges du Tarn canyon
Plateaus
- Causse du Larzac
- Plateau de Millevaches
- Plateau de Lévézou
- Causse du Comtal
- Causse de Sauveterre
- Causse de Sévérac
- Causse Méjean
- Causse Noir
- Causse de Blandas
Administration
The following departments are generally considered as part of the Massif Central: Allier, Ardèche, Aude, Aveyron, Cantal, Corrèze, Creuse, Gard, Haute-Garonne, Haute-Loire, Haute-Vienne, Hérault, Loire, Lot, Lozère, Puy-de-Dôme, Rhône, Saône-et-Loire, Tarn, and Tarn-et-Garonne; these form parts of the regions of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, Bourgogne-Franche-Comté, Nouvelle-Aquitaine and Occitania.
The largest cities in the region are Clermont-Ferrand, Limoges, and Saint-Étienne.
Economy
In the Massif Central, the industry remains little developed except locally (metallurgy in Saint-Étienne, tire industry in Clermont-Ferrand, headquarters of Michelin, world leader in the sector, aeronautics industry in Figeac, etc.). The other industries present are linked to agriculture (Groupe Limagrain, the world's third-largest seed producer, cheese-producing industries that export to the world, such as Cantal and Roquefort).
On the agricultural level, the Limagne plain is dominated by major cereal crops, but in the mountains, it is mainly livestock farming that predominates: cattle farming in the west for meat and milk (Cantal cheese), sheep farming in the south on the limestone plateaus (Roquefort cheese).
Finally, tourism is booming, taking advantage of the UNESCO heritage classification of the volcanoes of the Chaîne des Puys and the Causses and Cévennes region.
The entire economy of the Massif Central has benefited from the opening of roads, in particular the construction of the A75 motorway (on which is located the famous Millau Viaduct).
See also
- Geography of France
- Flora of the Massif central
References
- ↑ "Massif Central" (US) and "Massif Central". Massif Central. Oxford University Press. http://www.lexico.com/definition/Massif+Central.
- ↑ "Massif Central". Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. 2014. https://www.ahdictionary.com/word/search.html?q=Massif+Central.
- ↑ "Massif Central". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/Massif+Central. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ↑ Occitan: Massís Central, pronounced [maˈsis senˈtɾal]; Template:Lang-frp; literally "Central Massif"
External links
 |