Engineering:Vacuum insulated evaporator
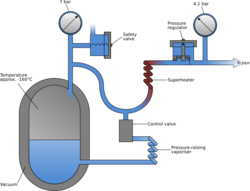
A vacuum insulated evaporator (VIE) is a form of pressure vessel that allows the bulk storage of cryogenic liquids including oxygen, nitrogen and argon for industrial processes and medical applications.
The purpose of the vacuum insulation is to prevent heat transfer between the inner shell, which holds the liquid, and surrounding atmosphere. Without functioning insulation, the stored liquid will rapidly warm and undergo a phase transition to gas, increasing significantly in volume and potentially causing a catastrophic failure to the vessel due to an increase in pressure. To combat such an event, VIEs are installed with a pressure safety valve.
To remain a liquid, the vessel contents must be kept at or below its critical temperature. The critical temperature of oxygen is −118 °C; above this temperature, applying more pressure will not result in a liquid, but rather a supercritical fluid.
This article does not cite any external source. HandWiki requires at least one external source. See citing external sources. (2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
 |