Pentapolis
From HandWiki
Short description: Cluster of five cities
This article may lack focus or may be about more than one topic. In particular, is this article about the word, the concept, or should it be a disambig page?. (October 2010) |
A pentapolis (from Greek πεντα- penta-, 'five' and πόλις polis, 'city') is a geographic and/or institutional grouping of five cities. Cities in the ancient world probably formed such groups for political, commercial and military reasons, as happened later with the Cinque Ports in England.
Significant historical cases
- In the biblical Holy Land, Genesis 14 describes the region where five cities—Sodom, Gomorrah, Zoara, Admah and Zeboim—united to resist the invasion of Chedorlaomer, and of which four were shortly after destroyed.[1]
- The Philistine Pentapolis: Gaza, Ashdod, Ashkelon, Ekron, and Gath, all combined to make Philistia.
- The Doric—or Dorian Pentapolis: Kos, on the island of the same name in the Aegean Sea; Knidos, in Caria on the west coast of Asia Minor; Lindus, Ialysus and Camirus, all three on Rhodes.
- The Phrygian Pentapolis: Eukarpia, Hierapolis, Otrus, Bruzus, and Stectorium.
- The Pontic Pentapolis: Apollonia, Callatis, Mesembria, Odessos, and Tomis, all on the Black Sea.
- The Western Pentapolis of Cyrenaica: five main Greek colonies that came to be in the Roman province of Libya Superior, the western part of Cyrenaica until Diocletian's Tetrarchy reform in AD 296 (now Libya).[2] The most important was Cyrene and its port Apollonia, Ptolemais (the next capital after Cyrene's destruction by an earthquake), port of Barca (the later Arab provincial capital Barka), Teucheira (modern Tocra) and Berenice (modern Benghazi); also known as the Pentapolis inferior ("lower pentapolis"'). This is the Pentapolis that is referenced in the official title of the Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Alexandria and the Pope of the Coptic Orthodox Church.
- In Italy there were:
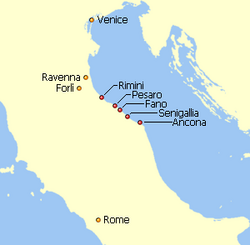
- an early pentapolis including: Ravenna, Forlì, Forlimpopoli, Classe, Caesarea.
- a later, medieval Duchy of the Pentapolis on the Adriatic coast east of Tuscany and north of the duchy of Spoleto, including the port cities (North to South) of Rimini, Pesaro, Fano, Sinigaglia and Ancona.[3] It was part of the core of the Byzantine Exarchate of Ravenna. Later, after the fall of the Exarchate, it was transformed into the March of Ancona
- The Cinque Ports in England—the five being Hastings, New Romney, Hythe, Dover, and Sandwich.
Pentapoleis of the modern world
Italy
- The Cinque Terre are five rustic coastal towns in Liguria that are now organized into the Cinque Terre National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
India
- The National Capital Region (NCR) consists of five cities, namely, Delhi, Gurgaon, Ghaziabad, Noida and Faridabad.
United States
- The Five Towns, on the southwestern shore of New York's Long Island region, is a group of towns comprising the villages of Lawrence and Cedarhurst, the hamlets of Woodmere and Inwood, and "The Hewletts", which consist of the villages of Hewlett Bay Park, Hewlett Harbor and Hewlett Neck and the hamlet of Hewlett.[4]
- The Five Boroughs of New York City, which were separately governed city-counties until the 1874 and 1898 annexations.
- The Quad Cities of Iowa and Illinois (so named before the fifth city, Bettendorf, Iowa, grew in the mid-20th century) that share cultural institutions and infrastructure.
- Locally known as "The Five Cities" in San Luis Obispo County, California are Arroyo Grande, Pismo Beach, Shell Beach, Grover Beach, and Oceano.
Algeria
- There are five qsur "walled villages" (ksour) located on rocky outcrops along the Wəd Mzab collectively known as the Pentapolis, founded between 1012 and 1350.[5] They are: Ghardaïa (Tagherdayt), the principal settlement today; Beni Isguen (At Isjen); Melika (At Mlishet); Bounoura (At Bunur); and El Atteuf (Tajnint), the oldest of the five settlements.[6] Adding the more recent settlements of Bérianne and El Guerrara, the Mzab Heptapolis is completed.
See also
- Pentapolis (North Africa)
- Monopoli (meaning only city)
- Tripolis (meaning three cities)
- Tetrapolis (meaning four cities)
- Doric Hexapolis (meaning six Doric cities in the eastern Aegean)
- Heptapolis (meaning seven cities)
- Decapolis (meaning ten cities)
Notes
- ↑
 Herbermann, Charles, ed (1913). "Pentapolis". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/11646b.htm.
Herbermann, Charles, ed (1913). "Pentapolis". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/11646b.htm.
- ↑ "Pentapolis", Claremont Coptic Encyclopedia
- ↑ Hallenbeck, Jan T. (1982). "Pavia and Rome: The Lombard Monarchy and the Papacy in the Eighth Century". Transactions of the American Philosophical Society (Philadelphia) 72 (4): 1–186. doi:10.2307/1006429.
- ↑ Barron, James. "IF YOU'RE THINKING OF LIVING IN: FIVE TOWNS", The New York Times , July 10, 1983. Accessed May 20, 2008. "The basic five are Lawrence, Cedarhurst, Woodmere, Hewlett and Inwood. But the area also includes some unincorporated communities and two tiny villages, Hewlett Bay Park and Woodsburgh, that are not added to the final total."
- ↑ "M'Zab Valley". WHC. UNESCO. https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/188/.
- ↑ Urwin, Simon (16 April 2021). "The fortified cities on the fringes of the Sahara". BBC Travel. https://www.bbc.com/travel/article/20210415-the-fortified-cities-on-the-fringes-of-the-sahara.
References
- Westermann Großer Atlas zur Weltgeschichte ('Great Atlas of World History', in German)
 |