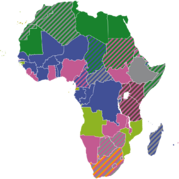
Place:List of regions of Africa
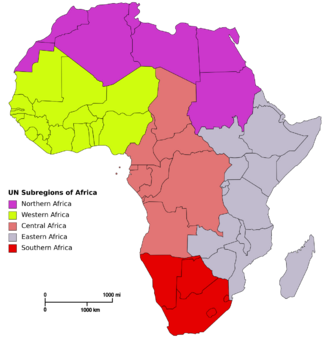
The continent of Africa is commonly divided into five regions or subregions, four of which are in sub-Saharan Africa.
List of subregions in Africa
The five UN subregions:[1]
| Subregion | Country / Territory |
|---|---|
| Northern Africa | |
| Template:Country data Ceuta (Spain) | |
| Template:Country data Melilla (Spain) | |
| Eastern Africa | |
| Template:Country data French Southern and Antarctic Lands (France ) | |
| Template:Country data Reunion (France) | |
| Middle Africa | |
| Template:Country data Congo, Democratic Republic of the | |
| Southern Africa | |
| Western Africa | |
Directional approach
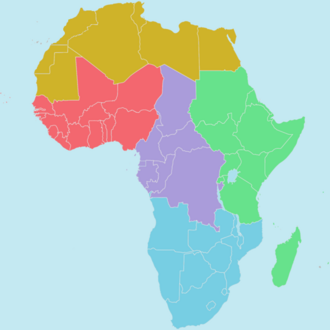
One common approach categorizes Africa directionally, e.g., by cardinal direction (compass direction):
- North Africa lies north of the Sahara and runs along the Mediterranean coast.
- West Africa is the portion roughly west of 10° east longitude, excluding Northern Africa and the Maghreb. West Africa contains large portions of the Sahara Desert and the Adamawa Mountains.
- East Africa stretches from the Red Sea and the Horn of Africa to Mozambique, including Madagascar .
- Central Africa is the large mass at the center of Africa which either does not fall squarely into any other region or only partially does so.
- Southern Africa consists of the portion generally south of -10° latitude and the great rainforests of Congo.
This approach is taken, for example, in the United Nations geoscheme for Africa and the regions of the African Union.
Physiographic approach
Another common approach divides Africa by using features such as landforms, climatic regions, or vegetation types:
- Nubia (Lower Nubia) (Upper Nubia)
- Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt
- The Maghreb is a region of northwest Africa encompassing the coastlands and Atlas Mountains of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
- The Sahara Desert is the massive but largely empty region in North Africa that contains the world's largest hot deserts
- Sub-Saharan Africa is the area of the African continent which lies south of the Sahara.
- The Sahel region covers a belt of grasslands south of the Sahara stretching from Senegal to Sudan.
- The Sudan, slightly more humid and arable region lying below the Sahel.
- Sudanian Savanna
- Sudd
- The Horn of Africa is a peninsula in East Africa that juts for hundreds of kilometers into the Arabian Sea, and lies along the southern side of the Gulf of Aden. It encompasses Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia and Djibouti.
- Ethiopian Highlands (Roof of Africa)
- Nigritia or Negroland
- The Guinea region is distinguished from the neighboring Sudan region by its rainforests and runs along the Atlantic coast from Guinea to Nigeria.
- Upper, Middle, Lower and Forest
- Gold Coast, Slave Coast, Ivory Coast and Pepper Coast
- Rhodesia (region) (Northern Rhodesia, Southern Rhodesia)
- Mayombe
- The Congo Basin is the rainforest region
- The Chad Basin The Chad Basin is the largest endorheic drainage basin in Africa, centered on Lake Chad.
- East African Rift. The region contains Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda.
- Eastern Rift mountains
- Rift Valley Lakes
- African Great Lakes
- Swahili Coast
- Barbary Coast
- Skeleton Coast
- Great Escarpment
- Karoo
- Bushveld
- Mittelafrika
- Igboland (Mbaise)
- Maputaland
- Azania
- Kalahari
- Borkou
- Ouaddaï
- Agadez
- Azawad
- Kanem
- Darfur
- Bahr el Ghazal
- Equatoria
- Greater Upper Nile
- Kordofan
- The Cape (Dutch Cape colony, Cape colony)
- Bushmanland
- Natal
- Griqualand
- Veld
- For depressions, refer to: Africa
- For mountain ranges, refer to: Africa
- For deserts, refer to: Africa
- Kivu
Linguistic approach
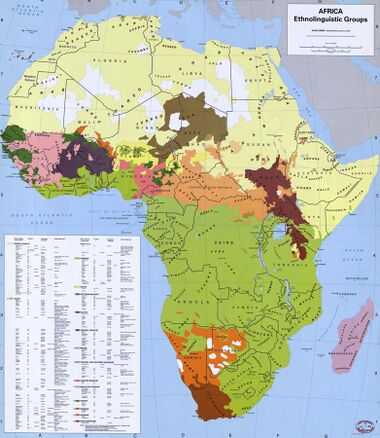
By official language
- Anglophone Africa includes five countries in West Africa (The Gambia, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Ghana, and the most populous African country Nigeria, as well as a part of Cameroon) that are separated by Francophone countries, South Sudan, and a large continuous area in Southern Africa and the African Great Lakes.
- Arabophone Africa includes the four most populous Arabic-speaking countries (Egypt, the Sudan, Morocco, Algeria) as well as Tunisia, Mauritania and Chad, and includes a majority of both the population and the area of the Arabic-speaking countries. French has also kept a strong role in the Maghreb countries, though this has receded somewhat with official Arabization.
- Francophone Africa is a continuous area in West Africa and Central Africa, plus Madagascar and Djibouti.
- Lusophone Africa consists of the widely separated countries of Cabo Verde, Guinea-Bissau, São Tomé and Príncipe, Angola, and Mozambique.
- Equatorial Guinea is the only African country where the Spanish language is official, though French is co-official (but rarely spoken).
- Swahili is widely used as an inter language in East Africa; its use for official and educational functions is greatest in Tanzania.
- Ethiopia and Somalia use the Afro-Asiatic Amharic and Somali languages, respectively, as their official languages, although Arabic also serves as a secondary language in Somalia. Eritrea and some parts of Ethiopia use the Tigrinya language as a working language and Arabic language as a non-indigenous working language within Eritrea.
By indigenous language family
- Niger–Congo languages and Nilo-Saharan languages are spoken in most of Sub-Saharan Africa. Nilo-Saharan occupies a smaller area but is highly diverse, and may be related as a parent or sibling of Niger–Congo.
- Afro-Asiatic languages are spoken in North Africa, the Horn of Africa, as well as parts of the Sahel.
- Khoisan languages are spoken in desert areas of Southern Africa, but were formerly spoken over a larger area, and are thought to include two small languages (Hadza and Sandawe) in the African Great Lakes.
- Austronesian languages originating from Southeast Asia are spoken in Madagascar .
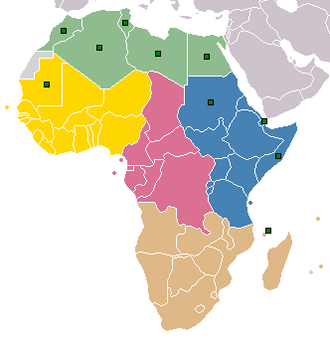
Investment approach
A slightly less common, but equally important method of division of the continent is by investment factors. For the purposes of investing, Africa is not a single destination with a single set of standardized risk factors and homogeneous potential for reward.[2] Although some high-level similarities are evident, digging into the specifics of certain regions and countries shows that Africa comprises a range of distinct investment destinations, each with its own attractions, flaws, cultural differences and business practices.[3][4]
The investment approach was first developed by global, independent financial analytics provider and investment consultant, RisCura.
- Maghreb region
- Otherwise known as the western portion of Northern Africa, these countries form the Arab Maghreb Union,[5] established in 1989. The region was established with the goal of functioning as a unified political and economic grouping. Political unrest in the region[6] has stunted progress since its inception but hope still remains that the Union will fulfill its purpose in years to come. Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco and Tunisia are included in this region.
- Egypt and the Sudan
- Previously united under British rule, these countries still share strong ties,[7] as well as one significant commonality – the trade facilitation through transport on the Nile River. As Egypt does not fall within the Arab Maghreb Union, it is separated from the rest of North Africa. However, Egypt's strong economic and cultural ties with the Middle East bring natural trading partners, and it is often seen grouped with the Middle East for investment purposes.[8]
- Francophone West Africa
- This is a commonly recognized region on the continent,[9] and typically includes Mauritania. However, Mauritania is sometimes allocated to the Maghreb region as it is found to have closer ties to the North African countries. These French-speaking countries share more than just a language. Due to their common history as French colonies, they also share similar legal and socio-political systems. The countries in this group are Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Côte d'Ivoire, Guinea, Mali, Niger, São Tomé and Príncipe, Senegal and Togo.
- Nigeria
- On its own, Nigeria is the size of the entire Maghreb region on an aggregated-GDP basis. While Nigeria is traditionally grouped with the rest of West Africa, its reliance on the rest of the region is less pronounced, likely as a result of its massive standalone GDP, its access to international markets via its six large ports, and its population of over 170 million people.
- East Africa
- This is a combination of the East African Community (Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda and Burundi), the LAPSSET corridor (Kenya, South Sudan and Ethiopia) as well as Djibouti, a crucial link to the Indian Ocean for Ethiopia and South Sudan. Kenya has traditionally headlined this region through consistently generating the largest GDP and acts as the primary route to international trade through the Mombasa port.
- Central Africa
- This market is the same as that defined by the African Development Bank with the exception of Madagascar , which here is classified as Southern Africa (ex-SA). On a GDP basis (United States dollar ) and by population, the Central Africa region is on par with the Francophone West African region. Countries included here are Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad and the Democratic Republic of Congo, as well as Equatorial Guinea and Gabon.
- Southern Africa excluding South Africa (ex-SA)
- This incorporates countries south of central and eastern Africa, and north of the South African border. The region has support from the most developed economy on the continent from the south, and access to capital coming out of South Africa as large companies look to expand into the rest of the continent. The group comprises Angola (which offers substantial oil resources), Botswana, Comoros, Madagascar , Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Reunion, Zambia (substantial supply of copper) and Zimbabwe.
- South Africa
- Like Nigeria, South Africa is a large African economy on a standalone basis. Due to the developed nature of South Africa relative to the rest of the continent, it has not been included in the Southern African region. South Africa boasts the largest GDP per capita of all the regions (double that of Nigeria) and is the most advanced investment destination on the continent. The South African market includes Lesotho and Eswatini due to their reliance and proximity to SA. The Swazi lilangeni is pegged to the South African rand, which is also accepted as currency within the country.
- Other West Africa
- This region includes Ghana, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Guinea-Bissau and The Gambia.
See also
- List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Africa
- Regions of the African Union
- United Nations geoscheme for Africa
Notes
- 1.^ Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic: sovereignty disputed with Morocco
References
- ↑ "Geographic Regions". United Nations Statistics Division. 2021. https://unstats.un.org/unsd/methodology/m49/#geo-regions.
- ↑ "Compelling investment markets in Africa – Inside Riscura's Bright Africa 2015 Report: Debbie O'Hanlon, Senior Analyst, RisCura (Infographics) | African Business News | African Financial & Economic News". http://www.africanbusinesscentral.com/2015/10/12/compelling-investment-markets-in-africa-inside-riscuras-bright-africa-2015-report-debbie-ohanlon-senior-analyst-riscura-infographics/.
- ↑ "Segmenting Africa into meaningful markets | Bright Africa". http://www.riscura.com/brightafrica/segmenting-africa-into-meaningful-markets/.
- ↑ "Meaningful African markets for investment" (in en-US). 22 September 2015. http://www.capitalmarketsinafrica.com/meaningful-african-markets-for-investment/.
- ↑ "UMA". http://www.maghrebarabe.org/en/uma.cfm.
- ↑ "What Is the Arab Spring?". http://middleeast.about.com/od/humanrightsdemocracy/a/Definition-Of-The-Arab-Spring.htm.
- ↑ "Sudan - Egypt Relations". http://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/sudan/forrel-eg.htm.
- ↑ Kessler, Oren (23 August 2015). Trading Peace in Egypt and Israel. https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/israel/2015-08-23/trading-peace-egypt-and-israel. Retrieved 2015-11-11.
- ↑ "What it takes to succeed in Francophone Africa". http://performance.ey.com/wp-content/uploads/downloads/2013/06/130219-SGF-TL-FSSA-email-version.pdf.
 |