ARGUS distribution
|
Probability density function 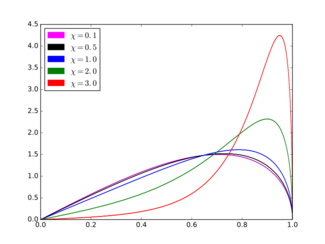 c = 1. | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function 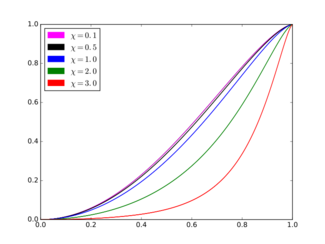 c = 1. | |||
| Parameters |
cut-off (real) curvature (real) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| see text | |||
| CDF | see text | ||
| Mean |
where I1 is the Modified Bessel function of the first kind of order 1, and is given in the text. | ||
| Mode | |||
| Variance | |||
In physics, the ARGUS distribution, named after the particle physics experiment ARGUS,[1] is the probability distribution of the reconstructed invariant mass of a decayed particle candidate in continuum background[clarification needed].
Definition
The probability density function (pdf) of the ARGUS distribution is:
for . Here and are parameters of the distribution and
where and are the cumulative distribution and probability density functions of the standard normal distribution, respectively.
Cumulative distribution function
The cumulative distribution function (cdf) of the ARGUS distribution is
- .
Parameter estimation
Parameter c is assumed to be known (the kinematic limit of the invariant mass distribution), whereas χ can be estimated from the sample X1, …, Xn using the maximum likelihood approach. The estimator is a function of sample second moment, and is given as a solution to the non-linear equation
- .
The solution exists and is unique, provided that the right-hand side is greater than 0.4; the resulting estimator is consistent and asymptotically normal.
Generalized ARGUS distribution
Sometimes a more general form is used to describe a more peaking-like distribution:
where Γ(·) is the gamma function, and Γ(·,·) is the upper incomplete gamma function.
Here parameters c, χ, p represent the cutoff, curvature, and power respectively.
The mode is:
The mean is:
where M(·,·,·) is the Kummer's confluent hypergeometric function.[2][circular reference]
The variance is:
p = 0.5 gives a regular ARGUS, listed above.
References
- ↑ Albrecht, H. (1990). "Search for hadronic b→u decays". Physics Letters B 241 (2): 278–282. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(90)91293-K. Bibcode: 1990PhLB..241..278A. (More formally by the ARGUS Collaboration, H. Albrecht et al.) In this paper, the function has been defined with parameter c representing the beam energy and parameter p set to 0.5. The normalization and the parameter χ have been obtained from data.
- ↑ Confluent hypergeometric function
Further reading
- Albrecht, H. (1994). "Measurement of the polarization in the decay B → J/ψK*". Physics Letters B 340 (3): 217–220. doi:10.1016/0370-2693(94)01302-0. Bibcode: 1994PhLB..340..217A.
- Pedlar, T.; Cronin-Hennessy, D.; Hietala, J.; Dobbs, S.; Metreveli, Z.; Seth, K.; Tomaradze, A.; Xiao, T. et al. (2011). "Observation of the hc(1P) Using e+e− Collisions above the DD Threshold". Physical Review Letters 107 (4): 041803. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.041803. PMID 21866994. Bibcode: 2011PhRvL.107d1803P.
- Lees, J. P.; Poireau, V.; Prencipe, E.; Tisserand, V.; Garra Tico, J.; Grauges, E.; Martinelli, M.; Palano, A. et al. (2010). "Search for Charged Lepton Flavor Violation in Narrow Υ Decays". Physical Review Letters 104 (15): 151802. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.104.151802. PMID 20481982. Bibcode: 2010PhRvL.104o1802L.
 |
