Astronomy:GR Muscae
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox (celestial coordinates) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Musca |
| Right ascension | 12h 57m 37.153s[1] |
| Declination | −69° 17′ 18.98″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 19.1[1] |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
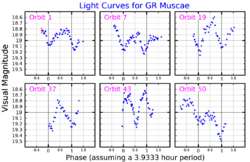
GR Muscae, also known as 2S 1254-690 is a binary star system in the constellation Musca composed of a neutron star of between 1.2 and 1.8 times the mass of the Sun and a low-mass star likely to be around the mass of the Sun in close orbit.[2] A magnitude 19 blue star was pinpointed as the optical counterpart of the X-ray source in 1978.[3] Its apparent magnitude varies from 18 to 19.1 over a period of 0.16 days.[4]
While the optical counterpart to the X-ray source was identified in 1978, optical variability was not detected until 1980, when a bright flare was seen that increased the white-light flux by a factor of two in a time interval of about 1.7 seconds.[5] GR Muscae received its variable star designation in 1985.[6]
The neutron star has an accretion disk that takes around 6.74 days to complete a revolution, and is inclined at an angle to the incoming stream of material from the donor star.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "GR Muscae – Low Mass X-ray Binary". SIMBAD Astronomical Database. Centre de Données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?Ident=GR+Mus&NbIdent=1&Radius=2&Radius.unit=arcmin&submit=submit+id. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Cornelisse, R.; Kotze, M.M.; Casares, J.; Charles, P.A.; Hakala, P.J. (2013). "The Origin of the Tilted Disc in the Low-mass X-ray Binary GR Mus (XB 1254-690)". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 436 (1): 910–20. doi:10.1093/mnras/stt1654. Bibcode: 2013MNRAS.436..910C.
- ↑ Griffiths, R.E.; Gursky, H.; Schwartz, D.A.; Schwarz, J.; Bradt, H.; Doxsey, R.E.; Charles, P.A.; Thorstensen, J. R. (1978). "Positions and Identifications for Galactic X-ray Sources 2A1822-371 and 2S1254-690". Nature 276 (16): 247–49. doi:10.1038/276247a0. Bibcode: 1978Natur.276..247G.
- ↑ "VSX : Detail for GR Mus". The International Variable Star Index. AAVSO. http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=19876.
- ↑ Mason, K. O.; Middleditch, J.; Nelson, J. E.; White, N. E. (9 October 1980). "An optical burst from the star identified with the X-ray source 2S1254-690". Nature 287 (5782): 516–518. doi:10.1038/287516a0. Bibcode: 1980Natur.287..516M. https://www.nature.com/articles/287516a0. Retrieved 8 October 2024.
- ↑ Kholopov, P. N.; Samus, N. N.; Kazarovets, E. V.; Perova, N. B. (March 1985). "The 67th Name-List of Variable Stars". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars 2681: 1. Bibcode: 1985IBVS.2681....1K. https://ibvs.konkoly.hu/pub/ibvs/2601/2681.pdf. Retrieved 8 October 2024.
 |
