Astronomy:Margaritifer Terra
Margaritifer Terra (/ˌmɑːrɡəˈrɪtəfər ˈtɛrə/) is an ancient, heavily cratered region of Mars. It is centered just south of the Martian equator at [ ⚑ ] : 4°54′S 25°00′W / 4.9°S 25°W and covers 2600 km at its widest extent.[1] The area reveals "chaos terrain", outflow channels, and alluvial plains that are indicative of massive flooding. Wind erosion patterns are also in evidence. A region within the terra shows some of the highest valley network densities on the planet. Ares Vallis is another notable feature, where the flood and flow patterns are in evidence; it was the landing site of the Soviet Mars 6 lander[2] and NASA's Mars Pathfinder.[3] It is also one of several proposed landing sites for the Mars 2020 Rover.[4]
Holden and Eberswalde, craters in Margaritifer Terra, are thought to have formerly held lakes because they contain deltas and iron/magnesium smectite minerals which need water to form.[5] The Uzboi-Landon-Morava (ULM) system of paths for water flow is found in Margaritifer Terra. Researchers think that great flood channels in this region were carved quickly in just weeks or months by catastrophic outflows of groundwater.[6] Because forming hematite requires liquid water, which could not long exist without a thick atmosphere, Mars must have had a much thicker atmosphere at some time in the past.[7]
Margaritifer Terra was named in 1979, after the Pearl Coast, south India . Part of it is found in the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle and part in the Oxia Palus quadrangle.
Layers
Some of the images from this region display layers. Many places on Mars show rocks arranged in layers. Rock can form layers in a variety of ways. Volcanoes, wind, or water can produce layers.[8] A detailed discussion of layering with many Martian examples can be found in Sedimentary Geology of Mars.[9]
Layers can be hardened by the action of groundwater. Martian ground water probably moved hundreds of kilometers, and in the process it dissolved many minerals from the rock it passed through. When ground water surfaces in low areas containing sediments, water evaporates in the thin atmosphere and leaves behind minerals as deposits and/or cementing agents. Consequently, layers of dust could not later easily erode away since they were cemented together.
-
Butte in Arsinoes Chaos with some light-toned layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
-
Light-toned deposit in Arsinoes Chaos, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
-
Light-toned deposit in Arsinoes Chaos, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Note: this field can be found in the previous wide image of Arsinoes Chaos, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
-
Layered butte, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
-
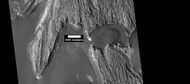
Light toned butte on floor of crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Arrows show outcrops of light toned material. Light toned material is probably sulfate-rich and similar to material examined by Spirit Rover, and it once probably covered the whole floor. Other images below show enlargements of the butte.
-
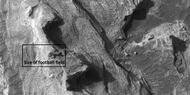
Enlargement of white butte, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Box shows size of a football field.
-
Closer view towards top of white butte, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Box shows size of a football field.
-
Top of white butte, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Box shows size of a football field.
-
THEMIS image of wide view of following HiRISE images. Black box shows approximate location of HiRISE images. This image is just a part of the vast area known as Aureum Chaos. Click on image to see more details.
-
Aureum Chaos, as seen by HiRISE, under the HiWish program.
-
Close up view of previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Small round dots are boulders.
-
Huge canyons in Aureum Chaos. Gullies are rare at this latitude. Picture taken by THEMIS.
-
Aureum Chaos, as seen from THEMIS.
On April 1, 2010, NASA released the first images under the HiWish program, with the public suggesting places for HiRISE to photograph. One of the eight locations was Aureum Chaos.[10] The first image below gives a wide view of the area. The next two images are from the HiRISE image.[11]
-
THEMIS image of wide view of following HiRISE images. Black box shows approximate location of HiRISE images. This image is just a part of the vast area known as Aureum Chaos. Click on image to see more details.
-
Aureum Chaos, as seen by HiRISE, under the HiWish program.
-
Close up view of previous image, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Small round dots are boulders.
-
Close up of layers in Lotto Crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Yardangs
-
Yardangs formed in light-toned material and surrounded by dark, volcanic basalt sand, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program.
-
Close-up image of yardangs, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Arrows point to transverse aeolian ridges, TAR's, a type of dune. Note this is an enlargement of the previous image from HiRISE.
-
Yardangs and layers, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program Arrows point to some yardangs.
Other images of Margaritifer Terra
-
Channel, as seen by HiRISE, under HiWish program
-
Hanging valleys in Aram Chaos, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
See also
- Areas of chaos terrain on Mars
- Geography of Mars
- Groundwater on Mars
- Lakes on Mars
- Uzboi-Landon-Morava (ULM)
- Dartmouth
- Astrobio.net
- J.A. Grant, 'Valley Evolution in Margaritifer Sinus, Mars'
- Geologic Map of MTM -15027, -20027, -25027, and -25032 Quadrangles, Margaritifer Terra Region of Mars United States Geological Survey
References
- ↑ "Margaritifer Terra". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- ↑ "Mars 6". US National Space Science Data Centre. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft/display.action?id=1973-052A.
- ↑ "Mars Pathfinder Science Results". NASA. http://mpfwww.jpl.nasa.gov/MPF/science/geology.html.
- ↑ "Choosing a place to land NASA's next Mars rover". Arizona State University News. 16 May 2014. https://asunews.asu.edu/20140516-mars-2020.
- ↑ Murchie, S. et al. 2009. A synthesis of Martian aqueous mineralogy after 1 Mars year of observations from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Journal of Geophysical Research: 114.
- ↑ "HiRISE | Uplifted Blocks of Light-Toned Layered Deposits (ESP_054753_1825)". https://www.uahirise.org/ESP_054753_1825.
- ↑ "Mars Odyssey Mission THEMIS: Discoveries". http://themis.asu.edu/discoveries-aramchaos.
- ↑ "HiRISE | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment". University of Arizona. http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu?PSP_008437_1750.
- ↑ Grotzinger, J. and R. Milliken (eds.). 2012. Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM.
- ↑ Captioned Images Inspired by HiWish Suggestions (HiRISE)
- ↑ Okubo, Chris (31 March 2010). "Mesas in Aureum Chaos". University of Arizona. https://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/ESP_016869_1775.
External links
- Lakes on Mars - Nathalie Cabrol (SETI Talks)
 |