Astronomy:NGC 6229
From HandWiki
Short description: Globular cluster in the constellation Hercules
| NGC 6229 | |
|---|---|
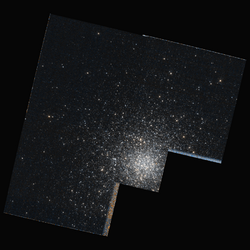 NGC 6229 as seen through the Hubble Space Telescope | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Hercules |
| Right ascension | 16h 46m 58.8s |
| Declination | +47° 31′ 40″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 9.4 |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 4.50' |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Absolute magnitude | -8.06 |
| Metallicity | = -1.13±0.06[1] dex |
| Other designations | GCL 47 |
NGC 6229 is a globular cluster located in the constellation Hercules. It is designated as GC(v)B in the galaxy morphological classification scheme and was discovered by the British astronomer William Herschel on 12 May 1787. NGC 6229 is located at about 100,000 light years away from Earth.[2][3][4][5]
It is an intermediate-metallicity globular cluster with two distinct generations of stars, and may be the remnant core of a spheroidal dwarf galaxy.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Johnson, Christian I.; Caldwell, Nelson; Michael Rich, R.; Walker, Matthew G. (2017), "Light and Heavy Element Abundance Variations in the Outer Halo Globular Cluster NGC 6229", The Astronomical Journal 154 (4): 155, doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa86ac, Bibcode: 2017AJ....154..155J
- ↑ "Object No. 1 - NGC 6229". NASA/IPAC. http://ned.ipac.caltech.edu/cgi-bin/objsearch?objname=NGC+6229&extend=no&hconst=73&omegam=0.27&omegav=0.73&corr_z=1&out_csys=Equatorial&out_equinox=J2000.0&obj_sort=RA+or+Longitude&of=pre_text&zv_breaker=30000.0&list_limit=5&img_stamp=YES.
- ↑ "Revised NGC Data for NGC 6229". http://spider.seds.org/ngc/revngcic.cgi?NGC6229.
- ↑ "NGC NGC 6229 (= GCL 47)". http://cseligman.com/text/atlas/ngc62.htm#6229.
- ↑ "NGC 6229". http://www.ngcicproject.org/ngcicdb.asp.
External links
 |
