Astronomy:SN 1998aq
| Event type | Supernova |
|---|---|
| Spectral class | Type Ia[1] |
| Date | April 13, 1998[2] |
| Constellation | Ursa Major |
| Right ascension | 11h 56m 25.87s[1] |
| Declination | +55° 07′ 43.2″[1] |
| Distance | 70.38 ± 0.23 Mly (21.58 ± 0.07 Mpc)[3] |
| Host | NGC 3982[1] |
| Colour (B-V) | −0.18[4] (peak) |
| Peak apparent magnitude | 12.36[1] |
SN 1998aq is a nearby supernova located in the intermediate spiral galaxy NGC 3982, offset 18″ west and 7″ of the galactic nucleus. It was discovered April 13, 1998 by amateur astronomer Mark Armstrong[2] and was confirmed by fellow British amateur Ron Arbour; both members of the U.K. Supernova/Nova Patrol.[4] The event was not visible on a prior check by Armstrong made April 7.[5] It reached peak brightness on April 27, and 15 days later had declined by 1.14 magnitudes in the B (blue) band.[4]
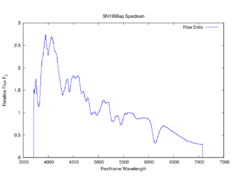
Spectroscopic observations determined this was a Type Ia supernova event, and it became one of the best-studied supernova of its type, at least in the visual band.[4] An absorption feature of singly-ionized carbon was (probably) detected nine days before maximum, an indication of unburned ash left over from the original carbon-oxygen core of the progenitor white dwarf.[7] Brightness calibration using Cepheid variables in NGC 3982 gives a peak absolute magnitude estimate of at least −19.47±0.15 (assuming no extinction in the host galaxy).[8]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Barbon, R. et al. (2008). "Asiago Supernova Catalogue". CDS/ADC Collection of Electronic Catalogues 1. Bibcode: 2008yCat....1.2024B.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hurst, G. M. et al. (April 1998). Green, D. W. E.. ed. "Supernova 1998aq in NGC 3982". IAU Circular 6875: 1. Bibcode: 1998IAUC.6875....1H.
- ↑ Tully, R. Brent et al. (October 2013). "Cosmicflows-2: The Data". The Astronomical Journal 146 (4): 25. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/146/4/86. 86. Bibcode: 2013AJ....146...86T.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Branch, David et al. (September 2003). "Optical Spectra of the Type Ia Supernova 1998aq". The Astronomical Journal 126 (3): 1489–1498. doi:10.1086/377016. Bibcode: 2003AJ....126.1489B.
- ↑ Hewitt, N. (April 2000). "The first seven UK supernova discoveries". Journal of the British Astronomical Association 110 (2): 65–79. Bibcode: 2000JBAA..110...65H.
- ↑ Matheson, T. et al. (2008). "Optical Spectroscopy of Type Ia Supernovae". Astronomical Journal 135 (4): 1598–1615. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/135/4/1598. Bibcode: 2008AJ....135.1598M.
- ↑ Parrent, Jerod T. et al. (May 2011). "A Study of Carbon Features in Type Ia Supernova Spectra". The Astrophysical Journal 732 (1): 15. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/732/1/30. 30. Bibcode: 2011ApJ...732...30P.
- ↑ Saha, A. et al. (November 2001). "Cepheid Calibration of the Peak Brightness of Type Ia Supernovae. XI. SN 1998aq in NGC 3982". The Astrophysical Journal 562 (1): 314–336. doi:10.1086/323529. Bibcode: 2001ApJ...562..314S.
External links
 |
