Biology:Acacia baueri
| tiny wattle | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. baueri
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia baueri Benth.
| |
| |
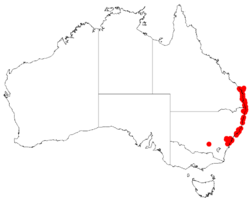
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
Acacia baueri, commonly known as tiny wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Lycopodiifoliae that is native to an area along the coast in eastern Australia.
Description
The small shrub typically grows to a height of 0.1 to 1 m (3.9 in to 3 ft 3.4 in) with a decumbent to spreading habit. Like most species of Acacia it has phyllodes rather than true leaves. They often have a whorled or scattered arrangement and a straight to slightly curved shape with a length 0.5 to 1.6 cm (0.20 to 0.63 in) and a width of 1 mm (0.039 in). The grey-green and terete phyllodes are quite leathery and are glabrous to sparsely hairy and have one longitudinal groove on each surface. It produces yellow flowers between July and September.[1] The simple inflorescences occur singly in the axils and are supported on 2 to 6 mm (0.079 to 0.236 in) long stalks. The spherical flower-heads have a diameter of 3 to 5 mm (0.12 to 0.20 in) and contain 8 to 20 bright yellow coloured flowers. The flat, thinly leathery seed pods that form after flowering are curved just a little and are usually straight-sided or have minimum constriction between the seeds. The pods have a length of 1 to 2.7 cm (0.39 to 1.06 in) and a width of 2.5 to 4 mm (0.098 to 0.157 in) with narrow longitudinal striations. The seeds inside are arranged longitudinally and have a filiform funicle.[1]
Taxonomy
The specific epithet honours the botanical artists Franz and Ferdinand Bauer.[2] Two known subspecies are recognised:
- Acacia baueri subsp. aspera, listed as vulnerable in New South Wales
- Acacia baueri subsp. baueri, listed as vulnerable in Queensland.[2]
Distribution
It is found in coastal regions in central and northern New South Wales extending north from the Illawarra region and into south eastern Queensland. It is usually situated on plateaus made of sandstone in rocky, exposed or damp areas as a part of coastal heathland communities.[1] It is found as far south as the Blue Mountains close to Sydney.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Acacia baueri Benth.". PlantNet. Royal Botanic Garden, Sydney. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/NSWfl.pl?page=nswfl&lvl=sp&name=Acacia~baueri.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Acacia baueri". Australian Native Plants Society. http://anpsa.org.au/a-bau.html.
Wikidata ☰ Q15289650 entry
 |

