Biology:Aspergillus persii
From HandWiki
Short description: Species of fungus
| Aspergillus persii | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Eurotiales |
| Family: | Aspergillaceae |
| Genus: | Aspergillus |
| Species: | A. persii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aspergillus persii A.M. Corte & Zotti 2002[1]
| |
| Type strain | |
| CBS 112795, IBT 22660, MUCL 41970[2] | |
Aspergillus persii is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus which can cause onychomycosis.[1][2][3] and otomycosis[4]
It is from the Circumdati section.[5] Aspergillus persii produces xanthomegnin and ochratoxin A.[6][7][8]
Growth and morphology
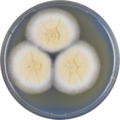
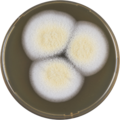
A. persii has been cultivated on both Czapek yeast extract agar (CYA) plates and Malt Extract Agar Oxoid® (MEAOX) plates. The growth morphology of the colonies can be seen in the pictures below.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Aspergillus persii. http://www.mycobank.org/Biolomics.aspx?Table=Mycobank&MycoBankNr_=374215.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 (in en) Aspergillus persii. https://www.uniprot.org/taxonomy/306094.
- ↑ Zotti, M; Machetti, M; Perotti, M; Barabino, G; Persi, A (June 2010). "A new species, Aspergillus persii, as an agent of onychomycosis". Medical Mycology 48 (4): 656–60. doi:10.3109/13693780903420641. PMID 20055738.
- ↑ Merad, Yassine; Adjmi-Hamoudi, Haiat; Cassaing, Sophie; Mehadji, Mohamed; Berry, Antoine (2016-03-01). "Première description d’Aspergillus persii en tant qu’agent d’otomycose : à propos de trois cas, dans deux différentes villes d’Algérie". Journal de Mycologie Médicale 26 (1): 70. doi:10.1016/j.mycmed.2016.02.010. ISSN 1156-5233. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1156523316000214.
- ↑ Visagie, C.M.; Varga, J.; Houbraken, J.; Meijer, M.; Kocsubé, S.; Yilmaz, N.; Fotedar, R.; Seifert, K.A. et al. (2014). "Ochratoxin production and taxonomy of the yellow aspergilli (Aspergillus section Circumdati)". Studies in Mycology 78: 1–61. doi:10.1016/j.simyco.2014.07.001. PMID 25492980.
- ↑ Dijksterhuis, Jan; Samson, Robert A. (2007) (in en). Food Mycology: A Multifaceted Approach to Fungi and Food. CRC Press. ISBN 9781420020984.
- ↑ Saeger, Sarah De (2011) (in en). Determining Mycotoxins and Mycotoxigenic Fungi in Food and Feed. Elsevier. ISBN 9780857090973.
- ↑ Anke, Timm; Weber, Daniela (2009) (in en). Physiology and Genetics: Selected Basic and Applied Aspects. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9783642002861.
Further reading
- Kim, Jung A.; Jeon, Jongbum; Park, Sook-Young; Kim, Ki-Tae; Choi, Gobong; Nguyen, Hoa Thi; Jeon, Sun Jeong; Lee, Hyang Burm et al. (21 September 2017). "Draft Genome Sequence of Aspergillus persii NIBRFGC000004109, Which Has Antibacterial Activity against Plant-Pathogenic Bacteria". Genome Announcements 5 (38): e00932–17. doi:10.1128/genomeA.00932-17. PMID 28935731.
- (in en) Aspergillus persii | Aspergillus & Aspergillosis Website. http://www.aspergillus.org.uk/content/aspergillus-persii-5.
- (in en) Aspergillus persii | Aspergillus & Aspergillosis Website. http://www.aspergillus.org.uk/content/aspergillus-persii-7.
- Lamoth, Frederic; Steinbach, William J. (2016) (in en). Advances in Aspergillus fumigatus pathobiology. Frontiers Media SA. ISBN 9782889197897.
Wikidata ☰ Q10420040 entry
 |