Biology:Boronia deanei
| Deane's boronia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Boronia deanei leaves and flowers | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Rutaceae |
| Genus: | Boronia |
| Species: | B. deanei
|
| Binomial name | |
| Boronia deanei Maiden & Betche[1]
| |
| |
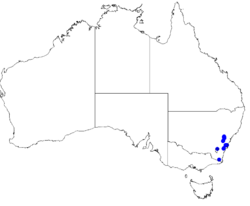
| Occurrence data from Australasian Virtual Herbarium | |
Boronia deanei, commonly known as Deane's boronia,[2] is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to the central and southern highlands of New South Wales. It is an erect shrub with crowded, strongly aromatic leaves and white to bright pink flowers in late winter and spring.
Description
Boronia deanei is an erect, glabrous shrub which grows to a height of 0.2–1.5 m (0.7–5 ft) and has slightly angled branches with scattered small warts. The leaves are divided into narrow, paired leaflets which are thick, strongly aromatic, linear in shape, 4–12 mm (0.2–0.5 in) long and 0.5–2 mm (0.02–0.08 in) wide. They are smooth on the upper surface but glandular-warty on the lower side.[2][3]
The flowers are arranged near the ends of the branches in groups of up to three, each flower on a stalk 1–3 mm (0.04–0.1 in) long. The petals are white to bright pink, 4–5 mm (0.16–0.20 in) long with their edges overlapping. There are eight stamens with glabrous filaments. Flowering occurs between August and November and the fruit is present in December.[2][3]
Taxonomy and naming
Boronia deanei was first formally described in 1907 by Joseph Maiden and Ernst Betche from a specimen collected by Henry Deane in the Blue Mountains. The description was published in Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales.[4][5] The specific epithet (deanei) honours the collector of the type specimen.
In 2002, Marco Duretto described two subspecies and the names have been accepted by the Australian Plant Census:[6]
- Boronia deanei subsp. deanei[7] which has leaflets with a blunt tip;[8]
- Boronia deanei subsp. acutifolia[9] which has leaflets with a pointed tip.[10]
Distribution and habitat
This boronia mainly occurs in the higher Blue Mountains north of Clarence, in the Kanangra-Boyd National Park and south to the South East Forests National Park. It grows near high altitude swamps, in wet heath and in open forest, often in poorly-drained soil.[3]
Conservation
Boronia deanei is listed as "Vulnerable" under the Commonwealth Government Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (EPBC) Act and under the New South Wales Threatened Species Conservation Act 1995. The main threats to its survival are habitat disturbance due to feral pigs (Sus scrofa) and clearing for rural residential developments.[3]
Use in horticulture
Deane's boronia is a reliable and adaptable garden plant which can be grown in poorly-drained soils and is relatively frost-hardy. Its pleasantly scented leaves and pink flowers are attractive features. Specimens have been grown in pots and in the Australian National Botanic Gardens have grown to a height of 2 m (7 ft), needing only tip pruning, occasional fertilising and adequate summer watering.[11]
References
- ↑ "Boronia deanei". https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/59765. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Boronia deanei". Royal Botanic Garden Sydney: plantnet. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/NSWfl.pl?page=nswfl&lvl=sp&name=Boronia~deanei. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Approved Conservation Advice for Boronia deanei (Deane's Boronia)". Australian Government Department of the Environment. http://www.environment.gov.au/biodiversity/threatened/species/pubs/8397-conservation-advice.pdf. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ "Boronia deanei". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/464344. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ Maiden, Joseph; Betche, Ernest (1907). "Notes from the Botanic Gardens, Sydney". Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales 31 (4): 731. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/121639#page/763/mode/1up. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ Duretto, Marco (2003). "Notes on Boronia (Rutaceae) in eastern and northern Australia". Muelleria 17: 109–112. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/244696#page/111/mode/1up. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- ↑ "Boronia deanei subsp. deanei". https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/181124. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- ↑ "Boronia deanei aubsp. deanei". Royal Botanic Garden Sydney: plantnet. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/NSWfl.pl?page=nswfl&lvl=in&name=Boronia~deanei+subsp.~deanei. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ "Boronia deanei subsp. acutifolia". https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/181125. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- ↑ "Boronia deanei subsp. acutifolia". Royal Botanic Garden Sydney: plantnet. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/NSWfl.pl?page=nswfl&lvl=in&name=Boronia~deanei+subsp.~acutifolia. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ Ollerenshaw, Peter J.. "Boronia deanei". Australian National Botanic Gardens. https://www.anbg.gov.au/gnp/gnp9/boronia-deanei.html. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
Wikidata ☰ Q15387767 entry
 |


