Biology:C6orf201
 Generic protein structure example |
Chromosome 6 open reading frame 201, C6orf201, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C6orf201 gene.[1] In humans this gene encodes for a nuclear protein that is primarily expressed in the testis.[2][3]
Gene
In humans, the gene is 51,558 base pairs long. The transcript that produces the longest protein of 140 amino acids is translated from unprocessed mRNA that has six exons and is 1664 nucleotides in length.[4][5]
Aliases
Chromosome 6 open reading frame 201 (C6orf201) is also referred to as: dJ1013A10.5, MGC87625, RP5-1013A10.5, and LOC404220.[6]
Locus
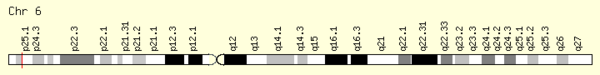
C6orf201 is located on chromosome 6 at 6p25.2 position and is encoded on the plus strand.[7] C6orf201 is located near the FAM217A gene and the ECI2 gene.[8]
Conservation
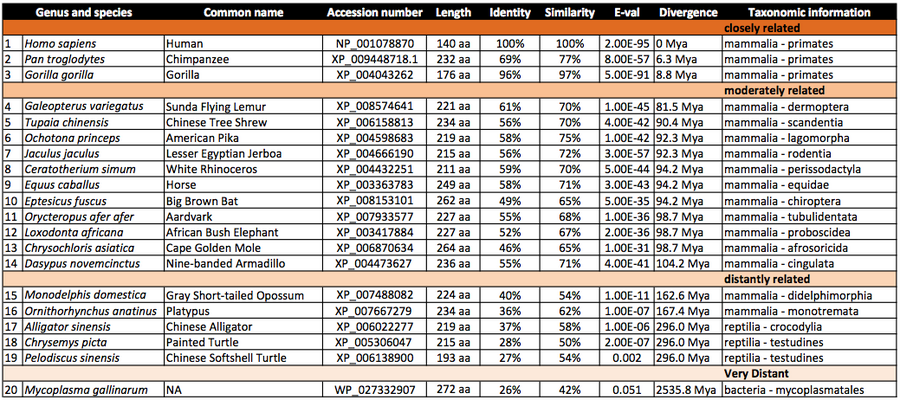
C6orf201 is highly conserved in primates, is moderately conserved in other mammals, and there is also conservation in a few reptiles.[9] There is enough conservation in mycoplasma gallinarum to suggest that there may have been a horizontal gene transfer event sometime during the evolutionary history of C6orf201. There are no paralogs or gene duplication events for C6orf201.
Orthologs
Homologous domains
C6orf201 belongs to DUF4523 (Pfam15023), a functionally uncharacterized family of proteins that is found in mammals.[10]
Protein
Names
Less common names of the C6orf201 protein are: protein MGC87625, hypothetical protein LOC404220, OTTHUMP00000213693, and OTTHUMP00000213725.[6]
General properties/features
In humans the longest protein variant is 140 amino acids long,[11] has a molecular weight of 16.2 kDa,[12] and an isoelectric point of 10.88.[12] C6orf201 is predicted to be a nuclear protein.[3]
Modification and Structure
C6orf201 has multiple predicted PKC and CKII phosphorylation sites in humans.[13] The protein also has a nuclear localization signal.[3] C6orf201 has a conserved alpha helix and a conserved beta strand in the protein.[12]
Protein interactions
C6orf201 interacts with SRPK1,[14] TMEM106B,[15] and APP.[16]
Expression
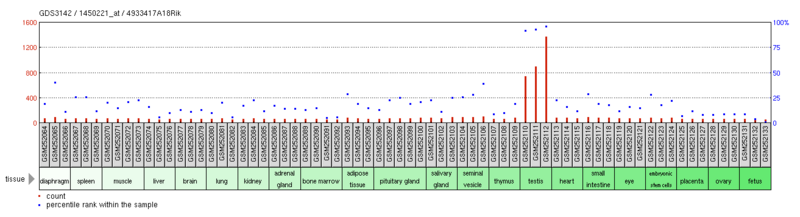
C6orf201 is primarily expressed in the testis of humans and is also expressed in the testis of adult mice and rats.[2] GEO microarray data also supports expression of C6orf201 in the testis of humans and mouse.[17][18]

Clinical relevance
Research Results
A toxicology study revealed that C6orf201 was one of the top 20 deregulated genes in monkeys that had been exposed to welding fumes for an extended period of time.[19] Another study investigated gene expression after the use of a methylation inhibitor, C6orf201 being one of many genes investigated.[20]
References
- ↑ "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6". Nature 425 (6960): 805–11. October 2003. doi:10.1038/nature02055. PMID 14574404. Bibcode: 2003Natur.425..805M.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "EST Profile". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/UniGene/ESTProfileViewer.cgi?uglist=Hs.716731. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Nakai, Kenta. "PSORT II prediction". http://www.genscript.com/psort/psort2.html. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ "GeneCards: The Human Gene Compendium". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=C6orf201. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ↑ "Homo sapiens chromosome 6 open reading frame 201 (C6orf201) mRNA". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NM_001085401.2. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Homo sapiens gene C6orf201, encoding chromosome 6 open reading frame 201.". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ieb/research/acembly/av.cgi?db=human&term=c6orf201&submit=Go. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ "Genomatix". http://www.genomatix.de/. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ "NCBI gene: C6orf201 Gene". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?cmd=Retrieve&dopt=full_report&list_uids=404220. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ↑ "Basic Local Alignment Search Tool". http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi.
- ↑ "Family: DUF4523 (PF15023)". http://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF15023#tabview=tab0. Retrieved 26 April 2015.
- ↑ "uncharacterized protein C6orf201 [Homo sapiens"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_001078870.1. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 "The Biology WorkBench". http://workbench.sdsc.edu/. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ "Motif Scan". http://myhits.isb-sib.ch/cgi-bin/motif_scan/. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ "The protein interaction landscape of the human CMGC kinase group". Cell Reports 3 (4): 1306–20. April 2013. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2013.03.027. PMID 23602568.
- ↑ "A proteome-scale map of the human interactome network". Cell 159 (5): 1212–1226. November 2014. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.050. PMID 25416956.
- ↑ "Interactions of pathological hallmark proteins: tubulin polymerization promoting protein/p25, beta-amyloid, and alpha-synuclein". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 286 (39): 34088–100. September 2011. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.243907. PMID 21832049.
- ↑ "C6orf201 Small cell lung cancers - Homo sapiens". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/tools/profileGraph.cgi?ID=GDS4794:231642_at. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ "C6orf201 Various tissues - Mus musculus". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSM1060762. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ↑ "Gene expression profiling in the lung tissue of cynomolgus monkeys in response to repeated exposure to welding fumes". Archives of Toxicology 84 (3): 191–203. March 2010. doi:10.1007/s00204-009-0486-z. PMID 19936710.
- ↑ "DNA methylation analysis of CD4+ T cells in patients with psoriasis". Archives of Dermatological Research 306 (3): 259–68. April 2014. doi:10.1007/s00403-013-1432-8. PMID 24323136.
 |