Biology:Chaenophryne longiceps
| Chaenophryne longiceps | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Lophiiformes |
| Family: | Oneirodidae |
| Genus: | Chaenophryne |
| Species: | C. longiceps
|
| Binomial name | |
| Chaenophryne longiceps (Regan, 1925)
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
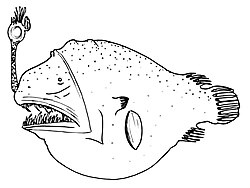
Chaenophryne longiceps, commonly known as the can-opener smoothdream, longhead dreamer or smooth-head dreamer, is a species of anglerfish in the family Oneirodidae (dreamers).[3][4][5][6][7]
Description
Chaenophryne longiceps is known for its monstrous appearance: inky black in colour with sharp pointed teeth (28–40 in upper jaw, 34–57 in lower) and (in females) a pointed lure (esca) protruding from its forehead.[8] The maximum length of females is 28 cm (11 in); the males are about 2 cm (0.79 in) and attach themselves to the female with special denticles, but are not parasitic.[9][10] It has 6–8 dorsal soft rays and 5–6 anal soft rays. Its specific name, longiceps, means "long head."[11]
Habitat
Chaenophryne longiceps is bathypelagic, living at depths of 500–1,000 m (1,600–3,300 ft) in tropical to temperate parts of all the Earth's oceans. In 2010 it was found off Greenland for the first time.[12]
Behaviour
Feeds on fish, cephalopods and crustaceans.[11]
References
- ↑ Project), Nadia Richman (Sampled Red List Index; Collen (SRLI), Ben (February 4, 2009). "IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Chaenophryne longiceps". https://www.iucnredlist.org/en.
- ↑ "WoRMS - World Register of Marine Species - Chaenophryne longiceps Regan, 1925". http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=126560.
- ↑ "Marine Species Identification Portal : Chaenophryne longiceps". http://species-identification.org/species.php?species_group=fnam&id=1527.
- ↑ "Chaenophryne longiceps". https://fishesofaustralia.net.au/home/species/3589.
- ↑ Australia, Atlas of Living. "Species: Chaenophryne longiceps (Longhead Dreamer)". https://bie.ala.org.au/species/urn:lsid:biodiversity.org.au:afd.taxon:72a7ef07-1295-4d58-b983-41e1250ce49c.
- ↑ "NOAA Technical Report NMFS.". U.S. Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Marine Fisheries Service. July 3, 1989. https://books.google.com/books?id=9opRAQAAIAAJ&dq=%22smooth-head+dreamer%22&pg=PA225.
- ↑ Pietsch, Theodore W. (July 3, 2009). Oceanic Anglerfishes: Extraordinary Diversity in the Deep Sea. University of California Press. ISBN 9780520255425. https://books.google.com/books?id=97c44d18TpsC&dq=%22Chaenophryne+longiceps%22&pg=PA386.
- ↑ "Marine Monsters: 8 Sea Creatures That Look Like They From Sci-Fi Movies". March 29, 2021. https://whatdewhat.com/marine-monsters-sea-creatures-sci-fi-movies/.
- ↑ "Longhead Dreamer, Chaenophryne longiceps Regan, 1925". http://australian.museum/learn/animals/fishes/longhead-dreamer-chaenophryne-longiceps-regan-1925/.
- ↑ "Chaenophryne longiceps (Can-opener smoothdream)". https://descna.com/en/speciesrecords/fish/osteichthyes-bony-fish/lophiiformes-anglerfishes/chaenophryne-longiceps-can-opener-smoothdream.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "Chaenophryne longiceps, Can-opener smoothdream". https://www.fishbase.se/summary/Chaenophryne-longiceps.html.
- ↑ "'Longhead dreamer' angler fish". 27 April 2010. https://www.thedailystar.net/news-detail-136029.
Wikidata ☰ Q2222979 entry
 |


