Biology:Clear-winged woolly bat
| Clear-winged woolly bat | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Vespertilionidae |
| Genus: | Kerivoula |
| Species: | K. pellucida
|
| Binomial name | |
| Kerivoula pellucida (Waterhouse, 1845)
| |
| |
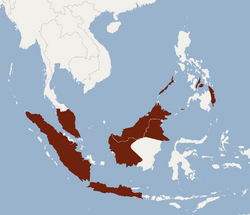
The clear-winged woolly bat (Kerivoula pellucida) is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found in Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines . Members of this species are relatively small, typically weighing about 4.5g and mainly forages in the understory of tropical forests. This species also presents a unique variant of echolocation that is a higher intensity and lower frequency than most other kerivoula calls. The short range calls are distinguishable from the long range orientational echolocation calls by peak frequency and duration.[2]
Appearance
As the name suggests, this bat has relatively translucent wings that are approximately 30-32 millimeters long. Translucent wings are a unique feature for this bat that allow for easy identification. The body length is 44-48 millimeters with a 41-47 millimeter long posterior tail. This is not a traditional tail, as the skin flaps that make up the wings attach behind the animal here. The bats dorsal and ventral fur ranges in color, with the dorsal portion being primarily a range of pale grey to dark brown. No fur is found on the wings of this bat. The fur color exhibits a smooth transition to white on the ventral side of the animal. No nose leaf is present on the muzzle of the bat. The ears are a pinkish-yellow color.[3]
Biology
Clear-winged woolly bats typically inhabit the understory and lower canopy, typically roosting in dead leaves. Mating occurs year-round and the mothers give birth to single pups at a time that generally weigh about a quarter of the mothers weight. Until they are able to fly, the pups cling to their mothers belly as she forages. Once they are able to fly, they will forage alongside the mother. Sexual maturity is reached at one year of age. As with many other species, habitat destruction is the primary threat to this species.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Nor Zalipah, M. (2020). "Kerivoula pellucida". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T10983A22021330. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T10983A22021330.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/10983/22021330. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- ↑ Kingston, T. (2000). "Social Calls in Clear-Winged Wooly Bats Kerivoula pellucida from Malaysia". Bioacoustics 11 (1): 1–16. doi:10.1080/09524622.2000.9753446. Bibcode: 2000Bioac..11....1K. http://www.bioacoustics.info/article/social-calls-clear-winged-woolly-bats-kerivoula-pellucida-malaysia.
- ↑ Kingston, T., Liat, L.B. and Akbar, Z. (2006) Bats of Krau Wildlife Reserve. Penerbit UKM, Bangi.
Wikidata ☰ Q304292 entry
 |