Biology:Cochliomyia hominivorax
| Cochliomyia hominivorax | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Diptera |
| Family: | Calliphoridae |
| Genus: | Cochliomyia |
| Species: | C. hominivorax
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cochliomyia hominivorax (Coquerel, 1858)
| |
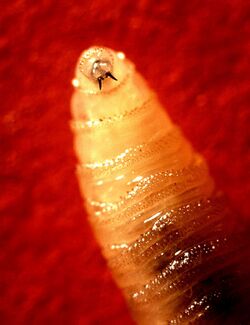
Cochliomyia hominivorax, the New World screw-worm fly, or simply screw-worm, is a species of parasitic fly that is well known for the way in which its larvae (maggots) eat the living tissue of warm-blooded animals. It is present in the New World tropics. There are five species of Cochliomyia but only one species of screw-worm fly in the genus is parasitic; there is also a single Old World species in a different genus (Chrysomya bezziana). Infestation of a live vertebrate animal by a maggot is technically called myiasis. While the maggots of many fly species eat dead flesh, and may occasionally infest an old and putrid wound, screw-worm maggots are unusual because they attack healthy tissue.
Life cycle
Screw-worm females lay 250–500 eggs in the exposed flesh of warm-blooded animals, including humans, such as in wounds and the navels of newborn animals. The larvae hatch and burrow into the surrounding tissue as they feed. Should the wound be disturbed during this time, the larvae burrow or "screw" deeper into the flesh, hence the larva's common name. The maggots are capable of causing severe tissue damage or even death to the host. About three to seven days after hatching, the larvae fall to the ground to pupate. The pupae reach the adult stage about seven days later. Female screw-worm flies mate four to five days after hatching. The entire lifecycle is around 20 days. A female can lay up to 3,000 eggs and fly up to 200 km (120 mi) during her life.
Control
The United States officially eradicated the screw-worm in 1982 using the sterile insect technique. However, a 2016 outbreak occurred in Monroe County, Florida.[1] The screw-worm was eradicated in Guatemala and Belize in 1994, El Salvador in 1995, and Honduras in 1996. Campaigns against the flies continue in Mexico, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panama, and Jamaica with financial assistance from the United States Department of Agriculture, which is trying to push the parasite south of the narrow Isthmus of Panama.
Etymology
From the Greek kochlias (snail with a spiral shell) + myia (fly) and the Latin hominis (man) + vorax (consuming), Cochliomyia hominivorax, or the New World screw-worm fly (formerly Callitroga (Greek kallos, (beautiful), + trogein, (to gnaw), Americana), was first described by France entomologist Charles Coquerel in 1858.[2]
In popular culture
The 1977 science fiction story "The Screwfly Solution" imagines aliens exterminating humans in a similar fashion. In Carmen Mola's detective novel La novia gitana (2018), and in The Dante Club (2003) by Matthew Pearl, Cochliomyia hominivorax is used as a murder weapon by introducing eggs or larvae into the body of an intended victim. In the television series BrainDead (2016), an extraterrestrial version of the screw-worm causes the hosts to become overzealous about their politics and health.
References
- ↑ "Deadly fly larvae infests federally endangered Key deer population, more than 40 are euthanized". FLKeysNews.com. 2016-10-03. http://www.flkeysnews.com/news/local/article105665836.html. Retrieved 2016-10-03.
- ↑ Henry, Ronnie (February 2019). "Etymologia: Cochliomyia hominivorax". Emerg Infect Dis 25 (2): 389–390. doi:10.3201/eid2502.et2502. PMID 30666944. "citing public domain text from the CDC".
Further reading
- John Curran, Veterinary Officer, Broome (2002). "Screw-Worm Fly". Government of Western Australia: Department of Agriculture Farmnotes. http://www.agric.wa.gov.au/pls/portal30/docs/folder/ikmp/pw/ins/ap/fn077_2002.pdf. Retrieved May 6, 2006.
- California Department of Food and Agriculture Animal Health Branch (January 2000). "Fact Sheet: Screwworm". http://www.cdfa.ca.gov/ahfss/Animal_Health/pdfs/Screwworm_Fact_Sheet.pdf. Retrieved Mar 4, 2012.
- James, Maurice T. (1947) The Flies That Cause Myiasis in Man. USDA Miscellaneous Publication No. 631.
External links
- Species Profile - Screwworm (Cochliomyia hominivorax), National Invasive Species Information Center, United States National Agricultural Library.
- Invasive Species Compendium, CAB International
Wikidata ☰ Q526003 entry
 |