Biology:Cucullanorhynchus
| Cucullanorhynchus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Acanthocephala |
| Class: | Archiacanthocephala |
| Order: | Oligacanthorhynchida |
| Family: | Oligacanthorhynchidae |
| Genus: | Cucullanorhynchus Amin, Ha and Heckmann, 2008 |
| Species: | C. constrictruncatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cucullanorhynchus constrictruncatus Amin, Ha and Heckmann, 2008
| |
Cucullanorhynchus is a monotypic genus of acanthocephalans (thorny-headed or spiny-headed parasitic worms). It contains a single species, Cucullanorhynchus constrictruncatus, which infests leopards in Vietnam.
Taxonomy
Description
Distribution
The distribution of C. constrictruncatus is determined by that of its hosts. C. constrictruncatus has been found in Vietnam.
Hosts
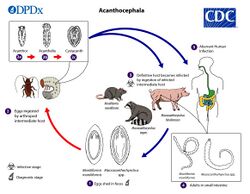
The life cycle of an acanthocephalan consists of three stages beginning when an infective acanthor (development of an egg) is released from the intestines of the definitive host and then ingested by an arthropod, the intermediate host. Although the intermediate hosts of Cucullanorhynchus are not known, without exception for the order Oligacanthorhynchidae, this intermediate host is a lizard or insect. When the acanthor molts, the second stage called the acanthella begins. This stage involves penetrating the wall of the mesenteron or the intestine of the intermediate host and growing. The final stage is the infective cystacanth which is the larval or juvenile state of an Acanthocephalan, differing from the adult only in size and stage of sexual development. The cystacanths within the intermediate hosts are consumed by the definitive host, usually attaching to the walls of the intestines, and as adults they reproduce sexually in the intestines. The acanthor are passed in the feces of the definitive host and the cycle repeats. There are no known paratenic hosts (hosts where parasites infest but do not undergo larval development or sexual reproduction) for Cucullanorhynchus.[3]
Cucullanorhynchus constrictruncatus has been found parasitizing leopards.[4] There are no reported cases of C. constrictruncatus infesting humans in the English language medical literature.[2]
- Hosts for Cucullanorhynchus constrictruncatus
The leopard is a host of C. constrictruncatus
Notes
References
- ↑ CDC’s Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria (April 11, 2019). "Acanthocephaliasis". Center for Disease Control. https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/acanthocephaliasis/index.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Mathison, BA (2021). "Human Acanthocephaliasis: a Thorn in the Side of Parasite Diagnostics". J Clin Microbiol 59 (11): e02691-20. doi:10.1128/JCM.02691-20. PMID 34076470. PMC 8525584. https://doi.org/10.1128%2FJCM.02691-20.
- ↑ Schmidt, G.D. (1985). "Development and life cycles". Biology of the Acanthocephala. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press. pp. 273–305. https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/17218255.pdf. Retrieved 16 July 2023.
- ↑ Amin, Omar; Nguyen, Ha Van; Heckmann, Richard A (March 2008). "New and Already Known Acanthocephalans Mostly from Mammals in Vietnam, withDescriptions of Two New Genera and Species in Archiacanthocephala". The Journal of Parasitology 94 (1): 194-201. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/5479254_New_and_Already_Known_Acanthocephalans_Mostly_from_Mammals_in_Vietnam_with_Descriptions_of_Two_New_Genera_and_Species_in_Archiacanthocephala.
Wikidata ☰ Q122252617 entry
 |