Biology:DUF3268 RNA motif
| DUF3268 | |
|---|---|
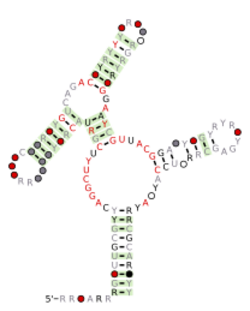 Consensus secondary structure and sequence conservation of DUF3268 RNA | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | DUF3268 |
| Rfam | RF02966 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; sRNA |
| SO | 0001263 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
The DUF3268 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics.[1] DUF3268 motifs are found in Bacillota and Clostridia.
DUF3268 RNAs are consistently found in the 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) of operons that include genes which encode the conserved protein domain DUF3268, sigma factors and signal peptidases. This genetic location could suggest that DUF3268 are cis-regulatory elements. However, it is unusually for cis regulators to be present in 3′ UTRs in bacteria. Therefore, it is also possible that DUF3268 RNAs function as small RNAs.
Predicted Rho-independent transcription terminators are often located nearby to (10–40) and downstream of DUF3268 RNAs. These transcription terminators are consistent with both the hypothesis of cis-regulatory function and function as a small RNA.
The DUF3268 motif contains an experimentally validated kink turn that provided insight into the biochemistry of kink turns.[2]
References
- ↑ "Detection of 224 candidate structured RNAs by comparative analysis of specific subsets of intergenic regions". Nucleic Acids Res. 45 (18): 10811–10823. October 2017. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx699. PMID 28977401.
- ↑ "Structure and ion-dependent folding of k-junctions". RNA. June 2023. doi:10.1261/rna.079678.123. PMID 37311599.
 |

