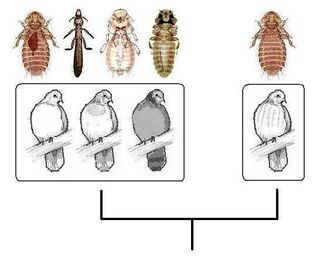
Biology:Eichler's rule
Eichler's rule is one of several coevolutionary rules which states that parasites tend to be highly specific to their hosts, and thus it seems reasonable to expect a positive co-variation between the taxonomic richness of hosts and that of their parasites.
History
A rule to describe the taxonomic relationship between parasites and their hosts was developed in 1942 by Wolfdietrich Eichler (1912–1994), a German authority in zoology and parasitology who served as a professor of parasitology at Leipzig University.[1][2] The principle was later dubbed 'Eichler's rule'. It is one of the first three coevolutionary rules, created in opposition to Heinrich Fahrenholz's anti-Darwinian research into coevolution.[3]
Research
As a part of their 2012 study, Vas and his co-authors tested Eichler's rule, and concluded that exceptionally strong correlational evidence supports the positive co-variation between the species richness of avian and mammalian families and the generic richness of their parasitic lice.[4]
In volume nine of Advances in Parasitology, parasitologist W. Grant Inglis posited that, when studying the co-variation between the taxonomic richness of hosts and parasites, it is easier to study parasites than free-living host organisms.[5]
References
- ↑ Eichler, Wolfdietrich (1966). "Two New Evolutionary Terms for Speciation in Parasitic Animals". Systematic Zoology 15 (3): 216–218. doi:10.2307/2411393. ISSN 0039-7989. PMID 5924358. https://www.jstor.org/stable/2411393.
- ↑ Eichler, W. (1942). "Die Entfaltungsregel und andere Gesetzmäßigkeiten in den parasitogenetischen Beziehungen der Mallophagen und anderer ständiger Parasiten zu ihren Wirten". Zoologischer Anzeiger 136: 77–83. http://phthiraptera.info/sites/phthiraptera.info/files/39548.pdf. Retrieved 2012-12-28.
- ↑ Klassen, G. J. (1992). "Coevolution: a history of the macroevolutionary approach to studying host-parasite associations". The Journal of Parasitology 78 (4): 573–587. doi:10.2307/3283532. ISSN 0022-3395. PMID 1635016. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1635016/.
- ↑ Vas, Z.; Csorba, G.; Rozsa, L. (2012). "Evolutionary co-variation of host and parasite diversity – the first test of Eichler's rule using parasitic lice (Insecta: Phthiraptera)". Parasitology Research 111 (1): 393–401. doi:10.1007/s00436-012-2850-9. PMID 22350674. http://www.zoologia.hu/list/Vas_Csorba_Rozsa_2012.pdf.
- ↑ (in en) Advances in Parasitology. Academic Press. 1971-03-31. ISBN 978-0-08-058055-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=yovuRdSJmWwC&q=eichler%27s+rule&pg=PA201.
 |