Biology:FAM180b
Gene
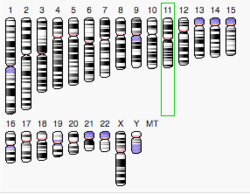
Family with sequence similarity 180 is a Homo sapiens protein that is encoded by the FAM180b gene also known as LOC399888.[1] It is located on the positive DNA strand in Chromosome 11p11.2 (47,586,651 – 47,589,194) and is 1403 nucleotides long. The gene also has 3 exons.[2]
Protein
Composition
The isoelectric point of FAM180b is 4.74 and has a molecular weight of 20KDa.[3] The protein lacks any prominent amino acids, but does have an increase in acidity due to the negatively charged KR-ED.[4]
Paralog
FAM180A is the only paralog to FAM180b. The four different isoforms of FAM180b are listed below.[5]
| Name | Accession number | Length | Amino Acid Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| protein FAM180B isoform 1 | NM_001164379 NP_001157851 | 1403 bp | 183 aa |
| protein FAM180B isoform 2 | NM_001367966 NP_001354895 | 1394 bp | 171 aa |
| protein FAM180B isoform 2 | NM_001367967 NP_001354896 | 1359 bp | 133 aa |
| protein FAM180B isoform 4 | NM_001367968 NP_001354897 | 1465 bp | 121 aa |
Orthologs
FAM180b is found in Primates, Mammalians, and Fungi. But there are no orthologs in plants.[6]
A table indicating the various orthologs:
| Scientific name | Common name | Divergence from Humans (MYA) [7] | NCBI Protein Accession Number | Sequence length (A.A) ! !Sequence similarity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saimiri boliviensis boliviensis | Black- Capped Squirrel Monkey | 43 | XP_010332662.1 | 188 | 91% |
| Carlito syrichta | Philippine Tarsier | 69 | XP_008067959.1 | 181 | 88% |
| Otolemur garnettii | Northern Greater Galago | 74 | XP_012668472.0 | 183 | 89% |
| Microcebus murinus | Gray Mouse Lemur | 74 | XP_020142069.1 | 186 | 88% |
| Propithecus coquereli | Coquerel's Sifaka | 74 | XP_012500556.1 | 182 | 90% |
| Peromscus leucopus | White-footed Mouse | 89 | XP_028734672.1 | 179 | 73% |
| Peromyscus maniculatus bairdii | Deer Mouse | 89 | XP_006999134.1 | 179 | 74% |
| Cricetulus griseus | Chinese Hamster | 89 | XP_027247094.1 | 217 | 65% |
| Octodon degus | Common Degu | 89 | XP_004627338.2 | 181 | 76% |
| Cavia porcellus | Guinea Pig | 89 | XP_005008583.3 | 183 | 79% |
| Chinchilla lanigera | Long-tailed Chincilla | 89 | XP_005384010.1 | 183 | 81% |
| Phoca vitulina | Harbor Seal | 94 | XP_032270037.1 | 232 | 58.6% |
| Podarcis muralis | Common Wall Lizard | 318 | XP_028581862.1 | 204 | 44% |
| Pogona vitticeps | Central Bearded Dragon | 318 | XP_020655822.1 | 207 | 43% |
| Python bivattatus | Burmese Python | 318 | XP_007431575.1 | 201 | 42% |
| Geecko japonicus | Schlegel's Japanese Gecko | 318 | XP_015271160.1 | 177 | 40% |
| Cyprinus carpio | Common Carp | 433 | XP_018978565.1 | 160 | 36% |
| Erpetoichthys calabaricus | Reedfish | 433 | XP_028649020.1 | 171 | 40% |
| Anarrhichthys ocellatus | Wolf Eel | 433 | XP_031713372.1 | 163 | 39% |
| Trichoderma gamsii | N/A | 1017 | XP_018664307.1 | 182 | 27% |
Secondary & Tertiary Structures
FAM180b is composed of 63% alpha-helixes and 54.1% beta sheets.[8] Certain amino acids have an overlap in both, hence the percentage exceeding 100% when totaled. The predicted tertiary structure obtained from Phyre 2 can be seen in Figure 3. on the right.Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
Subcellular Localization
The FAM180b protein is predicted to be located in the extracellular region, with a reliability score of 55.6%.[9] The protein contains a signal peptide, which has a cleavage site between 23 and 24 aa. However, FAM180b does not have any ER retention motif in the C-terminus, nor cleavage sites for mitochondria.Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag FAM180b also has three Threonine residues positioned in aa 4, 22, and 23, and one Glycine residue located in aa 19 that are all predicted to be phosphorylation sites.[10] O-GlcNacylation sites are present in serine residues located in 35 aa, 171 aa and in Threonine residue located in 36 aa.
[11]
Domains & Motifs
FAM180b has one domain listed as Big-1 (bacterial IG-like domain 1) domain at position 1–8. It has an e-value of 1.6 + 0.3. As for the motif, there is an amidation site at position 78–81.[12]
Gene Expression
In human fetal tissues, FAM180b is expressed in the lungs and stomach at 10 weeks. It's also highly expressed in the intestine at 11 weeks. Amongst various different RNA sequenced tissues, FAM180b is highly expressed in fat, skin, and thyroid.[13]
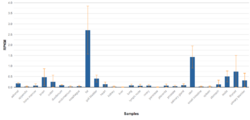
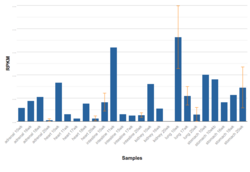
Clinical Significance
Currently there are no clinical significances associated with protein FAM180b [14]
Suggested Readings
Strausberg, Robert L et al. “Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America vol. 99,26 (2002): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899
References
- ↑ "FAM180B (family with sequence similarity 180 member B)". http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/Genes/GC_FAM180B.html.
- ↑ Homo sapiens family with sequence similarity 180 member B (FAM180B), transcript variant 1, mRNA. 9 June 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NM_001164379.3.
- ↑ "Compute pI/Mw". ExPasy. https://web.expasy.org/cgi-bin/compute_pi/pi_tool.
- ↑ "Compositional Analysis". ExPasy. https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/services/web/toolresult.ebi?jobId=saps-I20200503-223015-0706-89272185-p2m.
- ↑ "FAM180b Gene". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=FAM180B. Retrieved 29 April 2020.
- ↑ "NCBI Protein Blast". https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi.
- ↑ Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Hedges, S.B (2017). "TimeTree: a resource for timelines, timetrees, and divergence times". Molecular Biology and Evolution 34 (7): 1812–1819. doi:10.1093/molbev/msx116. PMID 28387841. http://timetree.org/.
- ↑ "CFSSP". http://www.biogem.org/tool/chou-fasman/index.php.
- ↑ "PSORT II Prediction". https://psort.hgc.jp/cgi-bin/runpsort.pl.
- ↑ "GPS Web Server". http://gps.biocuckoo.cn/online.php.
- ↑ "YingoYang 1.2 Server- prediction results". http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/cgi-bin/webface2.fcgi?jobid=5EAF146F00004C18CEE0F0F0&wait=20.
- ↑ "Motif Scan Results". https://myhits.sib.swiss/cgi-bin/motif_scan.
- ↑ "Expression". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/399888.
- ↑ "dsNP". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/rs4486587#clinical_significance. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
 |
