Biology:GA-cis RNA motif
| GA-cis | |
|---|---|
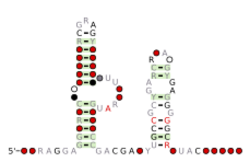 Consensus secondary structure and sequence conservation of GA-cis RNA | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | GA-cis |
| Rfam | RF02987 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Gene; sRNA |
| SO | 0001263 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
The GA-cis RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics.[1] GA-cis motif RNAs are found in one species classified within the phylum Bacillota: specifically, there are 9 predicted copies in Coprocuccus eutactus ATCC 27759.
GA-cis RNAs are generally located in the 5' untranslated regions of protein-coding genes. Indeed, the RNAs are upstream of multiple genes that encode non-homologous proteins. If all examples of the RNA were upstream of homologous genes, there is the possibility that the RNAs were conserved in that position simply by inheritance. The non-homology of the genes downstream of COG2908 RNAs makes this scenario less likely. This evidence suggests that GA-cis RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements. However, due to some cases where a GA-cis RNA is not immediately upstream of a gene makes this hypothesis tentative.
The GA-cis RNA motif is named because of the frequent occurrence of conserved GpA di-nucleotides in its sequence, and its locations that are typical of cis-regulatory elements.
References
- ↑ "Detection of 224 candidate structured RNAs by comparative analysis of specific subsets of intergenic regions". Nucleic Acids Res. 45 (18): 10811–10823. October 2017. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx699. PMID 28977401.
 |

