Biology:Gillbeea
| Gillbeea | |
|---|---|
| |
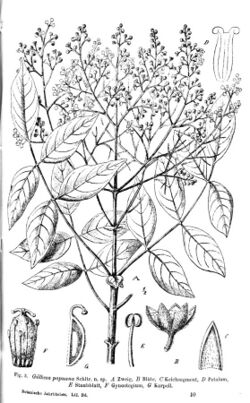
| Gillbeea papuana | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Oxalidales |
| Family: | Cunoniaceae |
| Genus: | Gillbeea F.Muell.[1][2][3] |
| Type species | |
| Gillbeea adenopetala | |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
Gillbeea is a genus of three species of Australasian rainforest trees from the family Cunoniaceae.[2][3][4][5][6]
Botanical science has formally published as of July 2021[update], the names and descriptions of one species endemic to New Guinea and two species endemic to the Wet Tropics rainforests of northeastern Queensland, Australia . These two Wet Tropics, NE. Qld species each only grow naturally in different tablelands rainforest regions, separated from each other for millions of years by a relatively narrow belt of drier non–rainforest landscape.[2][3][5][6][7][8]
Naming and classification
In 1865, European science formally published the name and description of this genus using John Dallachy's northeastern Queensland Gillbeea adenopetala type specimen collection, authored by Melbourne based German–Australian botanist Ferdinand von Mueller.[1] Mueller named this genus after Melbourne medical doctor William Gillbee.[6]
In 1915, the species name Gillbeea papuana and description was formally scientifically published by German botanist Rudolf Schlechter.[9]
In 1960, a revision of this genus and three more related genera of the family Cunoniaceae was published by Dutch botanist Ruurd Dirk Hoogland.[10]
Only in the year 2000, was the species name Gillbeea whypallana and description formally scientifically published by Australian botanists Andrew C. Rozefelds and Belinda Pellow from Tasmania.[3]
In October 2013, a study was published of the molecular phylogenetics and morphologies of the members of the plant tribe Geissoieae of the family Cunoniaceae, including a synopsis of its genera. Evidence was published that Gillbeea was moderately supported as an early relative of the tribe Geissoieae and the authors described the requirement for more evidence, however, before including Gillbeea in an expanded description of the tribe.[8]
Species
- Gillbeea adenopetala F.Muell.[1] Pink Alder – Atherton Tableland endemic, NE. Qld, Australia endemic[2][6][11]
- Gillbeea papuana Schltr.[9] – New Guinea endemic[7]
- Gillbeea whypallana Rozefelds & Pellow[3] – Windsor–Carbine tablelands and Daintree Rainforest restricted endemic, NE Qld, Australia[2][6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Mueller, Ferdinand von (Apr 1865). "Gillbeea F.Muell.; Gillbeea adenopetala F.Muell." (in Latin) (Digitised archive copy, online, from biodiversitylibrary.org). XXXI. 5. Auctoritate Gubern. Coloniæ Victoriæ, Ex Officina Joannis Ferres. p. 17. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/761725. Retrieved 23 Dec 2013.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 "Gillbeea%". Australian Plant Name Index (APNI), Integrated Botanical Information System (IBIS) database. Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research, Australian Government. http://www.anbg.gov.au/cgi-bin/apni?TAXON_NAME=Gillbeea%25. Retrieved 23 Dec 2013.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Rozefelds, Andrew C.; Pellow, Belinda (Aug 2000). "A new species of Gillbeea (Cunoniaceae) from north-eastern Queensland, Australia". Nordic Journal of Botany 20 (4): 435–441. doi:10.1111/j.1756-1051.2000.tb01584.x. ISSN 1756-1051.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Conn, Barry J. (2013). "Gillbeea". Census of Vascular Plants of Papua New Guinea. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/PNGcensus.pl?fam=&gen=Gillbeea&sp=&infr=&group=. Retrieved 23 Dec 2013.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "Cunoniaceae". Centre for Australian National Biodiversity Research (CANBR), Australian Government. 2020. https://apps.lucidcentral.org/rainforest/text/entities/Cunoniaceae.htm.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Cooper, Wendy; Cooper, William T. (June 2004). "Gillbeea F.Muell.". Fruits of the Australian Tropical Rainforest. Clifton Hill, Victoria, Australia: Nokomis Editions. pp. 148. ISBN 9780958174213. https://books.google.com/books?id=s0JFAQAAIAAJ&q=%22Gillbeea%22. Retrieved 23 Dec 2013.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Gillbeea papuana Schltr.". Flora Malesiana. http://dev.e-taxonomy.eu/dataportal/flora-malesiana/cdm_dataportal/taxon/a4ff3c0a-23c4-43c8-b9f2-a39e0fdfaa0d. Retrieved 23 Dec 2013.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Hopkins, H. C. F.; Rozefelds, A. C.; Pillon, Y. (18 Oct 2013). "Karrabina gen. nov. (Cunoniaceae), for the Australian species previously placed in Geissois, and a synopsis of genera in the tribe Geissoieae". Australian Systematic Botany 26 (3): 167–185. doi:10.1071/SB12037.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Schlechter, R. (1915). "33. Die Cunoniaceae Papuasiens" (in German). Botanische Jahrbücher für Systematik, Pflanzengeschichte und Pflanzengeographie. pp. 144–146. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/189668. Retrieved 23 Dec 2013.
- ↑ Hoogland, R. D. (1960). "Studies in the Cunoniaceae. I. The genera Ceratopetalum, Gillbeea, Aistopetalum, and Calycomis". Australian Journal of Botany 8 (3): 318–341. doi:10.1071/bt9600318.
- ↑ "Gillbeea adenopetala". Centre for Australian National Biodiversity Research (CANBR), Australian Government. 2020. https://apps.lucidcentral.org/rainforest/text/entities/Gillbeea_adenopetala.htm.
Wikidata ☰ Q8964068 entry
 |
