Biology:Gray thrasher
| Gray thrasher | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Mimidae |
| Genus: | Toxostoma |
| Species: | T. cinereum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Toxostoma cinereum (Xántus, J, 1860)
| |
| |
The gray thrasher (Toxostoma cinereum) is a medium-sized passerine bird belonging to the family Mimidae. It is endemic to the Baja California peninsula of Mexico.[1]
Taxonomy and systematics
The gray thrasher has two subspecies, the nominate T. c. cinereum and T. c. mearnsi.[1]
Description
The gray thrasher is 21.4 to 25.0 cm (8.4 to 9.8 in) long. Four males weighed 58.6 to 69.8 g (2.07 to 2.46 oz) and a female 54.4 g (1.92 oz). It is gray-brown above with cinnamon tones on the rump. Its underparts are white with arrow-shaped black spots. The outer tail feathers have white tips. Its eyes are golden yellow. The subspecies are similar, with T. c. mearnsi being somewhat darker overall.[2]
Distribution and habitat
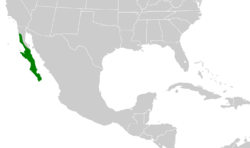
The gray thrasher is found only in Mexico's Baja California, where its range extends from approximately north latitude 31°14' to its southern tip. On the east side of the peninsula, however, it is found only as far north as approximately 28°. There is a record of this species in the Famosa Slough, San Diego County, California.[3] T. c. mearnsi occupies approximately the northern half of the range and the nominate subspecies the southern half.[2]
The gray thrasher inhabits arid and semi-arid landscapes. Most are open to semi-open with cacti, scrub, or scattered bushes and trees. In elevation it ranges from sea level to 1,500 m (4,900 ft).[2]
Behavior
Feeding
The gray thrasher typically forages on the ground or low down in vegetation. Its diet is not well studied but is known to include arthropods and cactus fruits.[2]
Breeding
Subspecies T. c. mearnsi of the gray thrasher breeds in March and April; T. c. cinereum breeds from May to mid-July in the far south. The species' nest is a cup made of twigs and lined with finer materials such as grass. T. c. mearnsi almost always places its nest in cacti, while T. c. cinereum uses cacti, thorny shrubs, and mesquite trees. Nests are typically within 3 m (9.8 ft) of the ground. The clutch size is two to four.[2]
Vocalization
The gray thrasher's song is "a loud, fairly scratchy warbling...repeated two or three times"', and often sung from a high open perch. Its calls include "a rolled, rippling to rough whirr-rr-rr or chirr-rri-rrit, and a gruff chrek".[2]
Status
The IUCN has assessed the gray thrasher as being of Least Concern. It has a very large range and an apparently stable population of at least 20,000 mature individuals.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. (July 2021). "IOC World Bird List (v 11.2)". https://www.worldbirdnames.org/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Soberanes-González, C. A., C. I. Rodríguez-Flores, M. d. C. Arizmendi, G. M. Kirwan, and T. S. Schulenberg (2020). Gray Thrasher (Toxostoma cinereum), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (T. S. Schulenberg, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.grathr1.01 retrieved July 25, 2021
- ↑ https://ebird.org/checklist/S24474588
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedIUCN
Further reading
- Peterson, Roger Tory & Edward L. Chalif (1973) A Field Guide to Mexican Birds, Houghton Mifflin.
- van Perlo, Ber (2006) A Field Guide to the Birds of Mexico and Central America, Collins.
Wikidata ☰ Q2226589 entry
 |


