Biology:Guam kingfisher
| Guam kingfisher | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Coraciiformes |
| Family: | Alcedinidae |
| Subfamily: | Halcyoninae |
| Genus: | Todiramphus |
| Species: | T. cinnamominus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Todiramphus cinnamominus (Swainson, 1821)
| |
The Guam kingfisher (Todiramphus cinnamominus) is a species of kingfisher from the United States Territory of Guam. It is restricted to a captive breeding program following its extinction in the wild due primarily to predation by the introduced brown tree snake.
Taxonomy and description
In the indigenous Chamorro language, it is referred to as sihek.[2]
The mysterious extinct Ryūkyū kingfisher, known from a single specimen, is sometimes placed as a subspecies (T. c. miyakoensis; Fry et al. 1992), but was declared invalid by the International Ornithological Congress in 2022, rendering the species monotypic.[3] Among-island differences in morphological, behavioral, and ecological characteristics have been determined sufficient that Micronesian kingfisher populations, of which the Guam kingfisher was considered a subspecies, should be split into separate species.[4]
This is a brilliantly colored, medium-sized kingfisher, 20–24 cm in length. They have iridescent blue backs and rusty-cinnamon heads. Adult male Guam kingfishers have cinnamon underparts while females and juveniles are white below. They have large laterally-flattened bills and dark legs. The calls of Micronesian kingfishers are generally raspy chattering.[5]
Behavior
Guam kingfishers were terrestrial forest generalists that tended to be somewhat secretive. The birds nested in cavities excavated from soft-wooded trees and arboreal termitaria, on Guam.[6] Micronesian kingfishers defended permanent territories as breeding pairs and family groups.[7] Both sexes care for young, and some offspring remain with parents for extended periods. Research suggests that thermal environment has the potential to influence reproduction.[7]
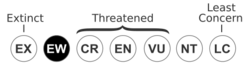
Conservation status
The Guam kingfisher population was extirpated from its native habitat after the introduction of brown tree snakes.[8] It was last seen in the wild in 1986, and the birds are now U.S. listed as endangered.[5] The Guam kingfisher persists as a captive population of fewer than two hundred individuals (as of 2017) in US mainland and Guam breeding facilities. However, there are plans to reintroduce the Guam birds to Palmyra Atoll by May 4th 2023, and potentially also back to their native range on Guam if protected areas can be established and the threat of the brown tree snakes is eliminated or better controlled.[2][5] Unfortunately, however, three decades of research and management have yielded little hope for safe habitats on Guam.[citation needed]
In popular culture
In 2023 the Guam kingfisher was featured on a United States Postal Service Forever stamp as part of the Endangered Species set, based on a photograph from Joel Sartore's Photo Ark. The stamp was dedicated at a ceremony at the National Grasslands Visitor Center in Wall, South Dakota.[9]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2017). "Todiramphus cinnamominus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2017: e.T22725862A117372355. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T22725862A117372355.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22725862/117372355. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Magazine, Smithsonian. "Scientists Are Using 3-D-Printing Technology to Ready Guam Kingfishers for Reintroduction to the Wild" (in en). http://www.smithsonianmag.com/blogs/national-zoo/2022/03/02/scientists-using-3d-printing-tech-ready-guam-kingfishers-for-reintroduction-to-wild/.
- ↑ "IOC World Bird List 12.1" (in en-US). doi:10.14344/ioc.ml.12.1. https://doi.org/10.14344/IOC.ML.12.1.
- ↑ Andersen, Michael J.; Shult, Hannah T.; Cibois, Alice; Thibault, Jean-Claude; Filardi, Christopher E.; Moyle, Robert G. (2015). "Rapid diversification and secondary sympatry in Australo-Pacific kingfishers (Aves: Alcedinidae: Todiramphus)". Royal Society Open Science 2 (2): 140375. doi:10.1098/rsos.140375. PMID 26064600. Bibcode: 2015RSOS....240375A.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "ECOS: Species Profile". https://ecos.fws.gov/ecp/species/6.
- ↑ Marshall, Samuel D. (1989). "Nest Sites of the Micronesian Kingfisher on Guam". The Wilson Bulletin 101 (3): 472–477. ISSN 0043-5643. https://www.jstor.org/stable/4162756.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Kesler, Dylan C.; Lopes, Iara F.; Haig, Susan M. (March 2006). "Sex determination of Pohnpei Micronesian Kingfishers using morphological and molecular genetic techniques" (in en). Journal of Field Ornithology 77 (2): 229–232. doi:10.1111/j.1557-9263.2006.00045.x. ISSN 0273-8570. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1557-9263.2006.00045.x.
- ↑ Savidge, Julie A. (1987). "Extinction of an Island Forest Avifauna by an Introduced Snake". Ecology 68 (3): 660–668. doi:10.2307/1938471. ISSN 0012-9658. https://www.jstor.org/stable/1938471.
- ↑ "Postal Service Spotlights Endangered Species". United States Postal Service. April 19, 2023. https://about.usps.com/newsroom/national-releases/2023/0419ma-postal-service-spotlights-endangered-species.htm.
- Laws, Rebecca J.; Kesler, Dylan C. (2012). "A Bayesian network approach for selecting translocation sites for endangered island birds". Biological Conservation 155: 178–185. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2012.05.016.
- Kesler, Dylan C.; Haig, Susan M. (2007). "Conservation biology for suites of species: Demographic modeling for Pacific island kingfishers". Biological Conservation 136 (4): 520–530. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2006.12.023. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/usgsstaffpub/669.
- Kesler, Dylan C.; Haig, Susan M. (2007). "Multiscale Habitat Use and Selection in Cooperatively Breeding Micronesian Kingfishers". The Journal of Wildlife Management 71 (3): 765–772. doi:10.2193/2006-011. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/usgsstaffpub/684.
- Kesler, Dylan C.; Haig, Susan M. (2007). "Territoriality, Prospecting, and Dispersal in Cooperatively Breeding Micronesian Kingfishers (Todiramphus Cinnamominus Reichenbachii)". The Auk 124 (2): 381. doi:10.1642/0004-8038(2007)124[381:TPADIC2.0.CO;2]. ISSN 0004-8038. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/usgsstaffpub/664.
- Kesler, Dylan C.; Haig, Susan M. (2005). "Microclimate and Nest-Site Selection in Micronesian Kingfishers". Pacific Science 59 (4): 499–508. doi:10.1353/psc.2005.0045. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1701&context=usgsstaffpub.
- Kesler, D. (2005). Population demography, resource use, and movement in cooperatively breeding Micronesian Kingfishers (Thesis). S2CID 82407115.
- Kesler, Dylan C.; Haig, Susan M. (2004). "Thermal characteristics of wild and captive Micronesian kingfisher nesting habitats". Zoo Biology 23 (4): 301–308. doi:10.1002/zoo.20010. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/usgsstaffpub/697.
- Fry, C. Hilary; Fry, Kathie; Harris, Alan (1992). Kingfishers, Bee-eaters, and Rollers. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0713680287.
- Haig, Susan M.; Ballou, Jonathan D. (1995). "Genetic Diversity in Two Avian Species Formerly Endemic to Guam". The Auk 112 (2): 445–455. doi:10.2307/4088732.
- Haig, S. M.; Ballou, J. D.; Casna, N. J. (1995). "Genetic Identification of Kin in Micronesian Kingfishers". Journal of Heredity 86 (6): 423–431. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a111616.
- Marshall, Samuel D. (1989). "Nest Sites of the Micronesian Kingfisher on Guam". The Wilson Bulletin 101 (3): 472–477.
- Pratt, H.D., P.L. Bruner, and D.G. Berrett. 1987. The Birds of Hawaii and the Tropical Pacific. Princeton University Press. Princeton, NJ.
- Savidge, Julie A. (1987). "Extinction of an Island Forest Avifauna by an Introduced Snake". Ecology 68 (3): 660–668. doi:10.2307/1938471.
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, 2004. Draft Revised Recovery Plan for the Sihek or Guam Micronesian Kingfisher (Halcyon cinnamomina cinnamomina).
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, 1984. Endangered and threatened wildlife and plants: determination of endangered status for seven birds and two bats on Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands. Federal Register 50 CFR Part 17 49(167), 33881–33885.
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, 2004. Draft Revised Recovery Plan for the Sihek or Guam Micronesian Kingfisher (Halcyon cinnamomina cinnamomina). U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Portland, OR.
External links
- BirdLife Species Factsheet.
- Micronesian kingfisher Naturalis The Netherlands
- Philadelphia Zoo - Description of Guam Micronesian kingfisher Conservation efforts
- United States Fish and Wildlife Service - Threatened and Endangered Animals in the Pacific Islands.
- US Geological Survey - USGS Micronesian Avifauna Conservation Projects
- US Geological Survey - The Brown Treesnake on Guam.
Wikidata ☰ Q204140 entry
 |