Biology:Hooded tinamou
| Hooded tinamou | |
|---|---|

| |
| Illustration by Joseph Smit, 1895 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Infraclass: | Palaeognathae |
| Order: | Tinamiformes |
| Family: | Tinamidae |
| Genus: | Nothocercus |
| Species: | N. nigrocapillus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Nothocercus nigrocapillus (G.R. Gray, 1867)[2]
| |
| Subspecies[2] | |
|
N. n. cadwaladeri | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The hooded tinamou (Nothocercus nigrocapillus) is a type of ground bird found in forests of Bolivia and Peru.[3]
Taxonomy
Tinamou are from the family Tinamidae, and in the larger scheme are also ratites. Unlike other ratites, tinamous can fly, although in general, they are not strong fliers. Ratites evolved from prehistoric flying birds, and tinamous are the closest living relative of these birds.[4]
The hooded tinamou has two subspecies:
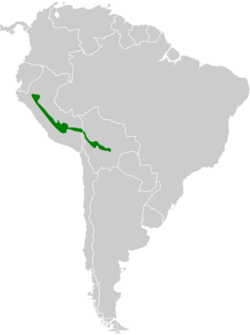
- N. n. cadwaladeri occurs in the Andes of northwestern Peru.[3]
- N. n. nigrocapillus occurs in the Andes of central Peru and Bolivia.[3]
Habitat and range
The hooded tinamou is found in montane moist forest up to 1,550 to 3,000 m (5,090–9,840 ft) altitude.[5] This species is native to the Andes in Bolivia and Peru.[3]
Description
Hooded tinamou is light brown above and narrowly freckled with black in color. It is paler below with dusky bars, belly pale-spotted, and averages 33 cm (13 in) long.
Behavior
Like other tinamous, the hooded tinamou eats fruit off the ground or low-lying bushes. They also eat small amounts of invertebrates, flower buds, tender leaves, seeds, and roots. The male incubates the eggs which may come from as many as 4 different females, and then will raise them until they are ready to be on their own, usually 2–3 weeks. The nest is located on the ground in dense brush or between raised root buttresses.[4]
Conservation
This species has an estimated global extent of occurrence of 35,000 km2 (14,000 sq mi).[5]
Footnotes
- ↑ BirdLife International (2020). "Nothocercus nigrocapillus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T22678160A179743794. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22678160A179743794.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22678160/179743794. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 Brands, S. (2008)
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Clements, J (2007)
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 Davies, S. J. J. F. (2003)
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 BirdLife International (2008)
References
- BirdLife International (2008). "Hooded Tinamou - BirdLife Species Factsheet". Data Zone. http://www.birdlife.org/datazone/species/index.html?action=SpcHTMDetails.asp&sid=18&m=0.
- Brands, Sheila (Aug 14, 2008). "Systema Naturae 2000 / Classification, Nothocercus nigrocapillus". Project: The Taxonomicon. http://www.taxonomy.nl/Main/Classification/51353.htm.
- Clements, James (2007). The Clements Checklist of the Birds of the World (6th ed.). Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-4501-9.
- Davies, S.J.J.F. (2003). "Tinamous". in Hutchins, Michael. Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia. 8 Birds I Tinamous and Ratites to Hoatzins (2nd ed.). Farmington Hills, MI: Gale Group. pp. 57–59. ISBN 0-7876-5784-0.
External links
- Hooded Tinamou videos, photos & sounds on the Internet Bird Collection.
Wikidata ☰ Q971229 entry
 |


