Biology:Ichthyophis sumatranus
| Ichthyophis sumatranus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Gymnophiona |
| Clade: | Apoda |
| Family: | Ichthyophiidae |
| Genus: | Ichthyophis |
| Species: | I. sumatranus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ichthyophis sumatranus Taylor, 1960[2]
| |
| |
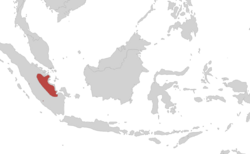
| Sumatran caecilian range | |
Ichthyophis sumatranus, also known as the Sumatra caecilian, is a species of amphibian in the family Ichthyophiidae. It is endemic to Sumatra, Indonesia.[1][3] It is known from western Sumatra, but many records lack precise location data and its exact range is poorly known.[1]
Description
The type series consists of two males and two females: the males measure 176 and 273 mm (6.9 and 10.7 in) and females 205 and 285 mm (8.1 and 11.2 in) in total length. The tail is short, 3–5 mm (0.12–0.20 in) in length. The maximal body width is 6–10 mm (0.24–0.39 in). There are 315–329 body folds and 7 tail folds. The eye is distinct; black iris is surrounding the lens that appears white. There is a white spot in front of the eye and a semicircular row of small cream glandules partly surrounding the eye. Preserved specimens are dark brown above, with slightly lighter grooves. Ventral coloration has a lighter shade of brown. There is a cream mark at the vent and one at the tip of the tail. The lips are cream.[2]
Habitat and conservation
Ichthyophis sumatranus is believed to inhabit tropical moist forest and have subterranean lifestyle as adults. It is presumably oviparous and has terrestrial eggs and aquatic larvae. The main threat to this species is conversion of forest for palm oil plantations. Its presence in protected areas is unknown.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group (2018). "Ichthyophis sumatranus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T59635A96061820. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T59635A96061820.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/59635/96061820. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Taylor, Edward H. (1960). "On the caecilian species Icthyophis glutinosus and Ichthyophis monochrous, with description of related species". University of Kansas Science Bulletin 40 (4): 37–120. doi:10.5962/bhl.part.18735. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/part/18735.
- ↑ Frost, Darrel R. (2020). "Ichthyophis sumatranus Taylor, 1960". Amphibian Species of the World: An Online Reference. Version 6.1. American Museum of Natural History. doi:10.5531/db.vz.0001. https://amphibiansoftheworld.amnh.org/Amphibia/Gymnophiona/Ichthyophiidae/Ichthyophis/Ichthyophis-sumatranus.
Wikidata ☰ Q628541 entry
 |