Biology:Ichthyosaurus
Ichthyosaurus (derived from Greek ἰχθύς (ichthys) meaning 'fish' and σαῦρος (sauros) meaning 'lizard') is a genus of ichthyosaurs from the Early Jurassic (Hettangian - Pliensbachian[1]) of Europe (Belgium, England, Germany and Portugal[2]). Some specimens of the ichthyosaurid Protoichthyosaurus from England and Switzerland have been erroneously referred to this genus in the past.[3][4] It is among the best known ichthyosaur genera, as it is the type genus of the order Ichthyosauria.[5][6]
History of discovery

Ichthyosaurus was the first complete fossil to be discovered in the early 19th century by Mary Anning in England;[7] the holotype of I. communis, no coll. number given,[8] was a fairly complete specimen discovered by Mary and Joseph Anning around 1814 in Lyme Regis[9] but was reported as lost by McGowan (1974) in his review of the latipinnate ichthyosaurs of England.[10] The name Ichthyosaurus was first used by Charles König in 1818, but it was not used in a formal scientific description, with the earliest described ichthyosaur being Proteosaurus by James Everard Home in 1819 for a skeleton which is now attributed to Temnodontosaurus platyodon. Henry De la Beche and William Conybeare in 1821 considered Ichthyosaurus to have taxonomic priority over Proteosaurus and named the species I. communis based on BMNH 2149 (now NHMUK PV R1158), a now partially lost specimen now assigned to Temnodontosaurus that was discovered and collected between 1811 and 1812.[11][12] One specimen that Home had assigned to Proteosaurus was the first complete ichthyosaur skeleton known, but it was destroyed in WW2. Two casts were rediscovered in 2022, showing that the specimen belonged to Ichthyosaurus, but of uncertain species.[13] During the 19th century, almost all fossil ichthyosaurs were attributed to Ichthyosaurus, resulting in the genus having over 50 species by 1900. These species were subsequently moved to separate genera or synonymised with other species.[14]
I. anningae, described in 2015 from a fossil found in the early 1980s in Dorset, England, was named after Anning.[15][16][14] The fossil was acquired by Doncaster Museum and Art Gallery, where it was misidentified as a plaster cast. In 2008, Dean Lomax, from the University of Manchester, recognised it as genuine and worked with Judy Massare, of the State University of New York, to establish it as a new species.[15]
Description
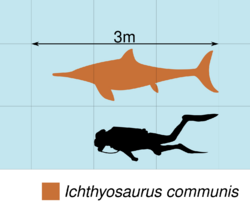
Ichthyosaurus was smaller than most of its relatives, with the largest specimen of I. somersetensis measuring up to 3–3.3 m (9.8–10.8 ft) in length.[17] In comparison, other species were much smaller, with the I. communis reaching up to 2 metres (6.6 ft) in length, I. larkini probably up to 2.5 metres (8.2 ft), I. anningae up to 1.8 metres (5.9 ft), I. breviceps up to 1.9 metres (6.2 ft), and I. conybeari up to 1.5 metres (4.9 ft).[18][8] Many Ichthyosaurus fossils are well-preserved and fully articulated. Some fossils still had baby specimens inside them, indicating that Ichthyosaurus was viviparous. Similar finds in the related Stenopterygius also show this.[19][20] Jurassic ichthyosaurs had a fleshy dorsal fin on their back as well as a large caudal fin. Icthyosaurus is distinguished from other ichthyosaurs by having a wide forefin with 5 or more digits with an anterior digital bifurcation, but the morphology of the humerus and coracoids are also distinct from that of other Lower Jurassic ichthyosaurs, as is the arrangement of the dermal bones, though the suture lines used to diagnose these are not always visible.[14]
Classification


This cladogram below follows the topology from a 2010 analysis by Patrick S. Druckenmiller and Erin E. Maxwell.[21]
| Thunnosauria |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Palaeobiology

Ichthyosaurus is suggested to have been a ram feeder, with the morphology of its hyobranchial apparatus suggesting that it was incapable of suction feeding,[23] using the jaws and teeth alone to capture prey. Ichthyosaurus is thought to have been a pursuit predator that was capable of sustained swift swimming via thunniform locomotion.[24] Stomach contents of Ichthyosaurus anningae indicate that it fed on cephalopods (likely belemnites) and fish.[25] Like other ichthyosaurs, it likely relied on its sense of sight, possibly in combination with olfaction.[26]
It was initially believed that Ichthyosaurus laid eggs on land, but fossil evidence shows that in fact the females gave birth to live young. As such, they were well-adapted to life as fully pelagic organisms (i.e. they never came onto land). Three pregnant females are known, all of the subspecies I. somersetensis. Although none of the fetuses show a clear birth orientation it is likely they exited tail-first, a common feature in highly aquatic vertebrates.[19]
Cultural significance

Joseph Victor von Scheffels poem Der Ichthyosaurus describes its extinction in humouristic verses. A monument on Hohentwiel cites it as well.[27] The poem has been translated among others by Charles Godfrey Leland[28] Some of the stanzas: Template:Quote box2
See also
- List of ichthyosaurs
- Timeline of ichthyosaur research
References
- ↑ Dean R. Lomax (2010). "An Ichthyosaurus (Reptilia, Ichthyosauria) with gastric contents from Charmouth, England: First report of the genus from the Pliensbachian". Paludicola 8 (1): 22–36.
- ↑ Sousa, João; Mateus, Octávio (2021-09-09). "The southernmost occurrence of Ichthyosaurus from the Sinemurian of Portugal" (in English). Fossil Record 24 (2): 287–294. doi:10.5194/fr-24-287-2021. ISSN 2193-0066. Bibcode: 2021FossR..24..287S. https://fr.copernicus.org/articles/24/287/2021/.
- ↑ Lomax, D. R.; Porro, L. B.; Larkin, N. R. (2019). "Descriptive anatomy of the largest known specimen of Protoichthyosaurus prostaxalis (Reptilia: Ichthyosauria) including computed tomography and digital reconstruction of a three-dimensional skull". PeerJ 7. doi:10.7717/peerj.6112. PMID 30643690.
- ↑ Klug, C.; Sivgin, T.; Miedema, F.; Scheffold, B.; Reisdorf, A.G.; Stössel, I.; Maxwell, E.E.; Scheyer, T.M. (2024). "Swiss ichthyosaurs: a review". Swiss Journal of Palaeontology 143: 31. doi:10.1186/s13358-024-00327-4.
- ↑ Maisch MW, Matzke AT. 2000. The Ichthyosauria. Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde, Serie B (Geologie und Paläontologie) 298: 1-159
- ↑ McGowan C, Motani R. 2003. Ichthyopterygia. – In: Sues, H.-D. (ed.): Handbook of Paleoherpetology, Part 8, Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil, 175 pp., 101 figs., 19 plts; München
- ↑ Essesials of Anthropology 6th addition
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Judy A. Massare & Dean R. Lomax (2018). A taxonomic reassessment of Ichthyosaurus communis and I. intermedius and a revised diagnosis for the genus, Journal of Systematic Palaeontology, 16:3, 263-277, DOI: 10.1080/14772019.2017.129111
- ↑ Home, E. (1814). Some account of the fossil remains of an animal more nearly allied to fishes than any other classes of animals. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 101, 571–577.
- ↑ McGowan, C. (1974). A revision of the latipinnate ichthyosaurs of the Lower Jurassic of England (Reptilia: Ichthyosauria). Life Science Contributions of the Royal Ontario Museum 100:1–30
- ↑ De la Beche, H. T. & W. D. Conybeare. (1821). Notice of the discovery of a new fossil animal, forming a link between the Ichthyosaurus and crocodile, together with general remarks on the osteology of the Ichthyosaurus. Transactions of the Geological Society of London 5: 559–594.
- ↑ Conybeare, W. D. (1822). Additional notices on the fossil genera Ichthyosaurus and Plesiosaurus. Transactions of the Geological Society of London, 1, 103–123.
- ↑ Lomax, Dean R.; Massare, Judy A. (2022). "Rediscovery of two casts of the historically important ' Proteo-saurus ', the first complete ichthyosaur skeleton". Royal Society Open Science 9 (11). doi:10.1098/rsos.220966. PMID 36405641. Bibcode: 2022RSOS....920966L.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Lomax, Dean R.; Massare, Judy A. (2015). "A new species of Ichthyosaurusfrom the Lower Jurassic of West Dorset, England, U.K.". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 35 (2). doi:10.1080/02724634.2014.903260. ISSN 0272-4634. Bibcode: 2015JVPal..35E3260L. http://zoobank.org/urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:A5778FB5-A116-480A-93CA-AFC932ACAB55.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Gill, Victoria (19 February 2015). "BBC News - Forgotten fossil found to be new species of ichthyosaur". BBC Online. https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-31521719.
- ↑ "New species discovered in Doncaster". 19 February 2015. http://www.doncaster.gov.uk/db/enews/article.asp?Archive=&CatID=31&Art=6211.
- ↑ Lomax, D.R.; Sachs, S. (2017). "On the largest Ichthyosaurus: A new specimen of Ichthyosaurus somersetensis containing an embryo.". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 62. doi:10.4202/app.00376.2017. http://app.pan.pl/article/item/app003762017.html.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedLomax2019 - ↑ 19.0 19.1 Böttcher R. 1990. Neue Erkenntnisse über die Fortpflanzungsbiologie der Ichthyosaurier. Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde, Serie B (Geologie und Paläontologie) 164: 1-51
- ↑ Martill D.M. 1993. Soupy Substrates: A Medium for the Exceptional Preservation of Ichthyosaurs of the Posidonia Shale (Lower Jurassic) of Germany. Kaupia - Darmstädter Beiträge zur Naturgeschichte 2: 77-97
- ↑ Druckenmiller, P. M.; Maxwell, E. E. (2010). "A new Lower Cretaceous (lower Albian) ichthyosaur genus from the Clearwater Formation, Alberta, Canada". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 47 (8): 1037–1053. doi:10.1139/E10-028. Bibcode: 2010CaJES..47.1037D.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Arkhangel'sky, M. S., 1998, On the Ichthyosaurian Genus Platypterygius: Palaeontological Journal, v. 32, n. 6, p. 611-615.
- ↑ Motani, Ryosuke; Ji, Cheng; Tomita, Taketeru; Kelley, Neil; Maxwell, Erin; Jiang, Da-yong; Sander, Paul Martin (2013-12-11). Dodson, Peter. ed. "Absence of Suction Feeding Ichthyosaurs and Its Implications for Triassic Mesopelagic Paleoecology" (in en). PLOS ONE 8 (12). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066075. ISSN 1932-6203. PMID 24348983. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...866075M.
- ↑ Dick, Daniel G.; Maxwell, Erin E. (July 2015). "The evolution and extinction of the ichthyosaurs from the perspective of quantitative ecospace modelling" (in en). Biology Letters 11 (7). doi:10.1098/rsbl.2015.0339. ISSN 1744-9561. PMID 26156130.
- ↑ D.R. Lomax An Ichthyosaurus (Reptilia: Ichthyosauria) with gastric contents from Charmouth, England: first report of the genus from the Pliensbachian Paludicola, 8 (2010), pp. 23-36
- ↑ Müller, Johannes; Bickelmann, Constanze; Sobral, Gabriela (2018-05-30). "The Evolution and Fossil History of Sensory Perception in Amniote Vertebrates" (in en). Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 46 (1): 495–519. doi:10.1146/annurev-earth-082517-010120. ISSN 0084-6597. Bibcode: 2018AREPS..46..495M. https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/annurev-earth-082517-010120.
- ↑ Werkkatalog Sieckes (PDF; 7,7 MB)
- ↑ Charles Godfrey Leland, Gaudeamus! Humorous Poems by Joseph Viktor von Scheffel, Ebook-Nr. 35848 on gutenberg.org
Template:Ichthyosauria Wikidata ☰ Q131565 entry
 |
