Biology:Linshcosteus
| Linshcosteus | |
|---|---|
| |
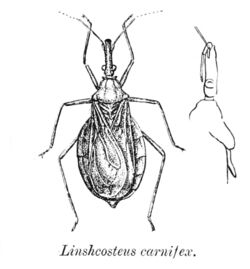
| L. carnifex | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hemiptera |
| Suborder: | Heteroptera |
| Family: | Reduviidae |
| Subfamily: | Triatominae |
| Genus: | Linshcosteus Distant, 1904 |
| Type species | |
| L. carnifex | |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
Linshcosteus is a genus of assassin bugs in the subfamily Triatominae (the kissing bugs). It is the only genus of Triatomines restricted to the Old World within the mostly Neotropical subfamily Triatominae (a few Triatoma species are known from the Old World and one New World species Triatoma rubrofasciata has been spread by humans across the tropics) and consists of six species restricted to peninsular India. Within the Triatominae, the genus is differentiated by the lack of a prosternal stridulatory furrow and a short rostrum that does not reach the prosternum.[1] Adults feed on vertebrate blood.[2]
The head is cylindrical and as long as the pronotum and scutellum combined. The is a sinuate constriction behind the eye. The portion in front of the head is nearly three times the length of the portion behind. The antennae are closer to the tip than to the eye and the first joint of the antenna reaches just short of the tip of the head while the second segment is as long as the head portion in front of the eye.[3]
Many species are found under rocks or in cavities inside tree. New World triatomines are found in sheltered locations where vertebrate hosts like bats or rodents may be easily found.[4] L. carnifex is found only in northern India in moist forest while L. confumus and L. costalis are associated with deciduous forest in Peninsular India. L. kali is known from near the Coimbatore region while L. karupus is found further south in Tamil Nadu.[5][6][7] The peculiar distribution of this genus restricted to the Old World while all other triatomines are restricted to the New World has led to questions on the phylogeny and placement.[8] It has been speculated that species in the genus may be involved in the transmission of leprosy.[9]
Species list
The following species have been described in the genus:
- L. carnifex Distant , 1904 - Bellary (possibly also Kanpur)
- L. confumus Ghauri, 1976 - Bangalore (Kodigehalli)
- L. chota Lent & Wygodzinsky, 1979 - "South India"
- L. costalis Ghauri, 1976 - Bangalore (Kodigehalli)
- L. kali Lent & Wygodzinsky, 1979 - Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu
- L. karupus Galvão, Patterson, Rocha & Jurberg, 2002 - Kalakkadu, Tamil Nadu
References
- ↑ "A new species of Triatominae from Tamil Nadu, India". Medical and Veterinary Entomology 16 (1): 75–82. March 2002. doi:10.1046/j.0269-283x.2002.00351.x. PMID 11963984.
- ↑ "The status of Linshcosteus in the Triatominae (Hemiptera: Reduviidae)". Journal of Medical Entomology 38 (6): 862–7. November 2001. doi:10.1603/0022-2585-38.6.862. PMID 11761385.
- ↑ The Fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Rhynchota.. II. London: Taylor and Francis. 1904. p. 287. https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/12704234.
- ↑ "Biosystematics of Old World Triatominae". Acta Tropica 63 (2–3): 127–40. February 1997. doi:10.1016/s0001-706x(97)87188-4. PMID 9088426.
- ↑ "The Indian triatomine genus Linshcosteus (Reduviidae)". Systematic Entomology 1 (3): 183–187. 1976. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3113.1976.tb00037.x.
- ↑ "Evolution, Systematics, and Biogeography of the Triatominae". Advances in Parasitology. Volume 99. Academic Press. 2018. pp. 265–325.
- ↑ "Description of Eggs and Nymphs of Linshcosteus karupus (Hemiptera: Reduviidae: Triatominae)". Annals of the Entomological Society of America 98 (6): 861–872. 2005-11-01. doi:10.1603/0013-8746(2005)098[0861:DOEANO2.0.CO;2].
- ↑ "The status of Linshcosteus in the Triatominae (Hemiptera: Reduviidae)". Journal of Medical Entomology 38 (6): 862–7. November 2001. doi:10.1603/0022-2585-38.6.862. PMID 11761385.
- ↑ "Triatomines: Trypanosomatids, Bacteria, and Viruses Potential Vectors?". Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 8: 405. 2018-11-16. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2018.00405. PMID 30505806.
Wikidata ☰ Q21222002 entry
 |

