Biology:List of Hypericum nothospecies
From HandWiki
The genus Hypericum contains a number of nothospecies, or hybrids created directly from crossing two accepted species to create an intermediate organism that shares properties of both. Many of these hybrid species are used as ornamental or decorative plants.
Nothospecies
| Binomial | Common Name | Type | Distribution | Parentage | Image | CollapseReferences |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Section Adenosepalum | ||||||
| H. × joerstadii
Lid (1968) |
Intermediate shrub | 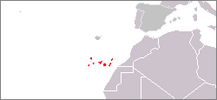
|
H. glandulosum × H. reflexum | 
|
[1][2][3][4][5] | |
| H. pubescens × tomentosum | 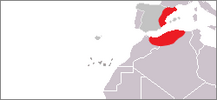
|
H. pubescens × H. tomentosum | 
|
[6][7][8] | ||
| Section Androsaemum | ||||||
| H. × inodorum
Mill. (1768) |
Tall Tutsan | Deciduous shrub | Corsica, France , Italy, Spain | [2][9][10][11][12] | ||
| Section Ascyreia | ||||||
| H. kouytchense × calycinum
D.Walker |
Shrub | Only in cultivation | H. kouytchense × H. calycinum | [1][13] | ||
| H. × cyathiflorum
N.Robson (1985) |
Shrub | Only in cultivation | H. addingtonii × H. hookerianum | 
|
[4][13][12][8] | |
| H. × dummeri
N.Robson (1985) |
Shrub | Only in cultivation | H. calycinum × H. forrestii | 
|
[4][14][8] | |
| H. × moserianum
André (1889) |
Shrub | Only in cultivation | 
|
[9][15][14][11][12] | ||
| Section Drosocarpium | ||||||
| H. × reinosae
A. Ramos (1983) |
Perennial herb | 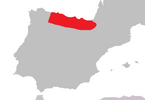
|
H. perforatum × H. richeri subsp. burseri | [1][13][8] | ||
| Section Graveolentia | ||||||
| H. × mitchellianum
Rydb. (1927) |
Blue Ridge St. John's Wort | Perennial herb | 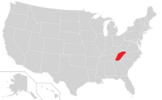
|
H. graveolens × H. punctatum | [16][17][18][19][20] | |
| Section Hypericum | ||||||
| H. × desetangsii
Lamotte (1874) |
Des Etang's St. John's Wort | 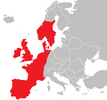
|
H. perforatum × H. maculatum | 
|
[10][3][21][22][23] | |
| H. × hyugamontanum
Y. Kimura |
Perennial herb | Japan (Kyushu) | [1][16] | |||
| H. × laschii
A.Fröhl. |
Scandinavia, France , Central Europe | [1][3][24][4][8] | ||||
| H. × medium
Peterm. |
Austria, Czech Republic, France, Germany , Romania | [1][24][3] | ||||
| Section Oligostema | ||||||
| H. × caesariense
Druce ex N.Robson |
Perennial herb | Scotland, England | H. linariifolium × H. humifusum | [2][8] | ||
| Section Trigynobrathys | ||||||
| H. × dissimulatum
E.P.Bicknell |
Disguised St. John's Wort | H. boreale × H. canadense | [25][9][19][20][26] | |||
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 "Hypericum Tourn. ex L.". https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:30002180-2.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 Zicha, Ondrej. "BioLib: Biological library" (in cs). https://www.biolib.cz/en/taxon/id1136485/.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Bulletin of the Natural History Museum. 2002. pp. Botany Series.
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 "Hypericum L". Global Biodiversity Information Facility. 2018-03-25. https://www.gbif.org/species/3189452.
- ↑ Nurk, Nicolai (2011). Phylogenetic analyses in St. John's wort (Hypericum): Inferring character evolution and historical biogeography (Dissertation). Berlin. pp. 32, 110. http://www.diss.fu-berlin.de/diss/servlets/MCRFileNodeServlet/FUDISS_derivate_000000010425/Dissertation_Nuerk_epub.pdf. Retrieved 2018-04-22.
- ↑ "Nomenclature | Hypericum online" (in en). http://hypericum.myspecies.info/taxonomy/term/484.
- ↑ Robson, Norman (1996). "Studies in the genus Hypericum L. (Guttiferae) 6. Sections 20. Myriandra to 28. Elodes". Bull. Br. Mus. (Nat. Hist.) Bot. 26: 75–271. http://hypericum.myspecies.info/node/855.
- ↑ Jump up to: 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 Barker, Christine. "The International Plant Names Index - home page". http://ipni.org/.
- ↑ Jump up to: 9.0 9.1 9.2 "Plants Profile for Hypericum". https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=HYPER.
- ↑ Jump up to: 10.0 10.1 Stace, C.A; Preston, C.D.; Pearman, D.A. (2015). Hybrid flora of the British isles. Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland.
- ↑ Jump up to: 11.0 11.1 "Hypericum". http://www.deeproot.co.uk/search_result.html?cx=partner-pub-6340217922483987%3A4469255120&cof=FORID%3A9&ie=UTF-8&q=Hypericum&sa=.
- ↑ Jump up to: 12.0 12.1 12.2 "Bean's Trees and Shrubs" (in en). http://www.beanstreesandshrubs.org/browse/hypericum/.
- ↑ Jump up to: 13.0 13.1 13.2 "Hypericum". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Missouri Botanical Garden. 2013. http://www.theplantlist.org/1.1/browse/A/Hypericaceae/Hypericum/.
- ↑ Jump up to: 14.0 14.1 "Hypericum: Royal Horticultural Society". https://www.rhs.org.uk/Plants/Search-Results?display=Grid&context=b%253D0%2526hf%253D12%2526l%253Den%2526q%253DHypericum%2526s%253Dasc%252528plant_botanical_sort%252529%2526sl%253Dplants&s=desc(plant_merged)&query=Hypericum&form-mode=true.
- ↑ "ITIS Standard Report Page: Hypericum". https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=21416#null.
- ↑ Jump up to: 16.0 16.1 Systematics and Biodiversity. 2006. pp. 4: 19–98.
- ↑ Bailey, C. (2015). Guide to the Vascular Plants of Tennessee. University of Tennessee press.
- ↑ Downs, RM (1972). "Hypericum mitchellianum in West Virginia". Castanea 37: 149.
- ↑ Jump up to: 19.0 19.1 "Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center". https://www.wildflower.org/plants/search.php?search_field=Hypericum&family=Clusiaceae&newsearch=true&demo=.
- ↑ Jump up to: 20.0 20.1 "Genus: Hypericum". 2009-02-02. http://explorer.natureserve.org/servlet/NatureServe#anchor_node.
- ↑ Crackles, FE (1990). "Hypericum x desetangsii Lamotte nm. desetangsii in Yorkshire, with special reference to its spread along railways". Watsonia 18: 63–67.
- ↑ "Plant Finder". https://www.brc.ac.uk/plantatlas/finder/plant/Hypericum.
- ↑ "Hypericum L. [Guttiferae-Hypericoideae"]. http://botanicalillustrations.org/taxa.php?id_taxon=4846&SID=0&lay_out=0&hd=0&group=1&size=0&mobile=0.
- ↑ Jump up to: 24.0 24.1 Stace, C.A. (1975). Hybridization and the Flora of the British Isles. London, New York, San Francisco: Academic Press.
- ↑ "Family: Clusiaceae, Genus: Hypericum" (in en). https://davesgarden.com/guides/pf/b/Clusiaceae/Hypericum/none/cultivar/0/.
- ↑ "Online Virtual Flora of Wisconsin - Hypericum". http://wisflora.herbarium.wisc.edu/taxa/index.php?taxon=873.
 |

