Biology:Lophophora
| Lophophora | |
|---|---|

| |
| Lophophora williamsii cluster | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Cactaceae |
| Subfamily: | Cactoideae |
| Tribe: | Cacteae |
| Genus: | Lophophora J.M.Coult. |
| Species | |
| |
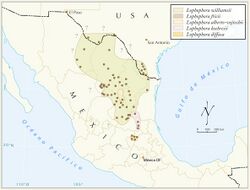
| Lophophora range | |
Lophophora (/ləˈfɒfərə/)[citation needed] is a genus of spineless, button-like cacti. Its area range covers southern through northeastern and north-central Mexico to Querétaro in central Mexico.[citation needed] The species are extremely slow growing, sometimes taking up to thirty years to reach flowering age (at the size of about a golf ball, excluding the root) in the wild.[citation needed] Cultivated specimens grow considerably faster, usually taking between three and ten years to reach from seedling to mature flowering adult.[citation needed] The slow rate of reproduction and over-harvesting by collectors render the species under threat in the wild.[citation needed]
Taxonomy
Lophophora means "crest-bearing", referring to the tufts of trichomes that adorn each tubercle. Lophophora has been reported to have two species, L. diffusa and L. williamsii. Another three species have been proposed[by whom?]: L. fricii, L. koehresii, and L. alberto-vojtechii.[1] Recent DNA sequencing studies (Butterworth et al. 2002) have shown that L. diffusa and L. williamsii indeed are distinct species. DNA evidence from the alleged species L. fricii and L. koehresii would allow for more accurate classification.[2]
Species
(As of November 2022), Plants of the World Online accepted four species:[3]
| Image | Scientific Name | Description | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lophophora alberto-vojtechii Bohata, Myšák & Šnicer | Mexico (San Luis Potosí) | ||
 |
Lophophora diffusa (Croizat) Bravo | The plants are yellow-green, usually lacking well-defined ribs and furrows. The podaria are rarely elevated, but are broad and flat. The tufts of hair are usually spread unequally on the prominent podaria. The flowers are commonly whitish to yellowish-white. This species contains zero to trace amounts of mescaline; pellotine is the principal alkaloid. | south end of the range of the genus in Querétaro state, Mexico |
| Lophophora fricii Haberm. | Mexico Northeast | ||
 |
Lophophora williamsii (Lemaire ex Salm-Dyck) J.M.Coult. | The plants are blue-green, usually with well-defined ribs and furrows. The tufts of hair are usually equally spaced on the ribs. The flowers are pinkish or rarely whitish. The mescaline content in dried "Peyote" can reach almost 7%.[citation needed] | the full range of the genus except in Querétaro state, Mexico |
Cultivation
Lophophora species easily adapt to cultivation, requiring warm conditions and a free-draining substrate, and to be kept dry in winter.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ Snicer, Jaroslav; Mysak, Vojtech; Bohata, Jaroslav (2005). "Lophophora Coulter". Kaktusy Special 2005/2 (41).
- ↑ C. A. Butterworth & J. H. Cota-Sanchez, & R. S. Wallace (2002), ”Molecular systematics of Tribe Cacteae (Cactaceae: Cactoideae): A phylogeny based on rpl16 intron sequence variation”, Systematic Botany 27 (2), 257-270.
- ↑ "Lophophora J.M.Coult. - Plants of the World Online". 2021-07-27. http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:5395-1.
- Edward F. Anderson, The Cactus Family (Timber Press, 2001) ISBN:0-88192-498-9, pp. 396–397
- Edward F. Anderson, Peyote: The Divine Cactus (University of Arizona Press; 2nd edition, 1996) ISBN:0-8165-1654-5
- Lyman Benson, Cacti of the United States and Canada (Stanford University Press, 1983) ISBN:0-8047-0863-0, pp. 680–683
- John M. Coulter, Preliminary revision of the North American species of Cactus, Anhalonium, and Lophophora (Contributions from the U. S. National Herbarium 3(2), 1894)
- Rudolf Grym, Rod/Die Gattung Lophophora (Vydavateľstvo Igor Dráb, 1997) ISBN:80-85441-11-X
External links
- Habitat photos of Lophophora
- Notes on growing Lophophora
- Cultivars photos of Lophophora
- lophophora collection video
Wikidata ☰ Q132102 entry
 |

