Biology:Luebering–Rapoport pathway
In biochemistry, the Luebering–Rapoport pathway (also called the Luebering–Rapoport shunt) is a metabolic pathway in mature erythrocytes involving the formation of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG), which regulates oxygen release from hemoglobin and delivery to tissues. 2,3-BPG, the reaction product of the Luebering–Rapoport pathway was first described and isolated in 1925 by the Austrian biochemist Samuel Mitja Rapoport and his technical assistant Jane Luebering.[1][2]
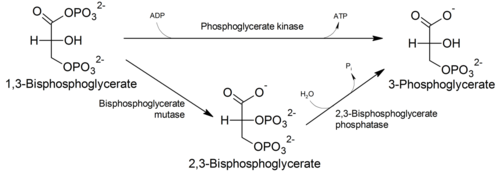
Through the Luebering–Rapoport pathway bisphosphoglycerate mutase catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from C1 to C2 of 1,3-BPG, giving 2,3-BPG. 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate, the most concentrated organophosphate in the erythrocyte, forms 3-PG by the action of bisphosphoglycerate phosphatase. The concentration of 2,3-BPG varies proportionately with the pH, since it is inhibitory to catalytic action of bisphosphoglyceromutase.
References
External links
- UniProt: Bisphosphoglycerate mutase - Homo sapiens (Human) UniProt-Information about bisphosphoglycerate mutase
- A live model of the effect of changing 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate on the oxyhaemoglobin saturation curve
 |