Biology:Meridiolestida
| Meridiolestida | |
|---|---|
| |
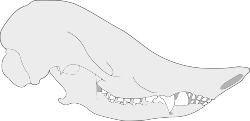
| Skull of Necrolestes | |
| |
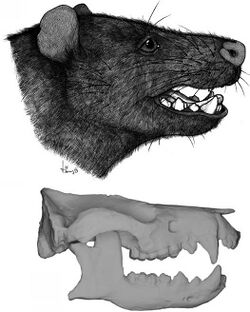
| Life restoration and skull and jaws of Peligrotherium | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Clade: | Cladotheria |
| Clade: | †Meridiolestida Rougier, 2011 |
| Subgroups | |
|
See text | |
Meridiolestida is an extinct clade of mammals known from the Cretaceous and Cenozoic of South America and possibly Antarctica. They represented the dominant group of mammals in South America during the Late Cretaceous.[1] Meridiolestidans were morphologically diverse, containing both small insectivores such as the "sabretooth-squirrel" Cronopio,[2] as well as the clade Mesungulatoidea/Mesungulatomorpha, which ranged in size from the shrew-sized Reigitherium to the dog-sized Peligrotherium. Mesungulatoideans had highly modified dentition with bunodont (low and rounded) teeth, and were likely herbivores/omnivores.[3] Meridiolestidans are generally classified within Cladotheria, more closely related to living marsupials and placental mammals (Theria) than to monotremes, barring one study recovering them as the sister taxa to spalacotheriid "symmetrodonts".[4] However, more recent studies have stuck to the cladotherian interpretation.[5][6] Within Cladotheria, they have often been placed in a group called Dryolestoidea together with Dryolestida, a group of mammals primarily known from the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of the Northern Hemisphere. However, some analyses have found this group to be paraphyletic, with the meridiolestidans being more or less closely related to therian mammals than other dryolestidans are.[6][7] Meridiolestidans differed from northern dryolestoids in the absence of a parastylar hook on the molariform teeth and the lack of a Meckelian groove.
Lakotalestes from the Early Cretaceous of North America, originally identified as a dryolestid, was noted in one paper to have a tooth morphology closer to that of meridiolestidans.[8] A possible meridiolestidan is known from a tooth fragment, now lost, found in the La Meseta Formation from the Eocene of the Antarctic Peninsula.[9] The latest surviving meridiolestidan was the mole-like burrowing insectivore Necrolestes from the Miocene of Patagonia.[6]
Taxa
- †Amarillodon[10]
- †Austrotriconodon
- †Bondesius[11]
- †Casamiquelia[11]
- †Lakotalestes?[8]
- †Paraungulatum[11]
- †Quirogatherium[11]
- †Cronopioidea[11][12]
- †Mesungulatoidea[12]
- †Peligrotherium
- †Reigitherium
- †Coloniatherium
- †Mesungulatum
- †Orretherium
References
- ↑ Defler, Thomas (2019), "Ancient Mammals of Gondwanan South America", History of Terrestrial Mammals in South America, Topics in Geobiology (Cham: Springer International Publishing) 42: pp. 29–44, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-98449-0_2, ISBN 978-3-319-98448-3, http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-319-98449-0_2, retrieved 2022-01-15
- ↑ Guillermo W. Rougier; Sebastián Apesteguía; Leandro C. Gaetano (2011). "Highly specialized mammalian skulls from the Late Cretaceous of South America". Nature 479 (7371): 98–102. doi:10.1038/nature10591. PMID 22051679. Bibcode: 2011Natur.479...98R, supplementary information.
- ↑ Harper, Tony; Adkins, Caleb; Rougier, Guillermo (2022). "Reconstructed masticatory biomechanics of Peligrotherium tropicalis, a non-therian mammal from the Paleocene of Argentina". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 67. doi:10.4202/app.00912.2021. ISSN 0567-7920. http://dx.doi.org/10.4202/app.00912.2021.
- ↑ Averianov, Alexander O.; Martin, Thomas; Lopatin, Alexey V. (2013). "A new phylogeny for basal Trechnotheria and Cladotheria and affinities of South American endemic Late Cretaceous mammals". Naturwissenschaften 100 (4): 311–326. doi:10.1007/s00114-013-1028-3. PMID 23494201. Bibcode: 2013NW....100..311A.
- ↑ Martinelli, Agustin; Chornogubsky, Laura; Abello, María; I. Goin, Francisco; Reguero, Marcelo (2014). "The first non-therian dryolestoid from Antarctica". 2014 SCAR Open Science Conference. Auckland, New Zealand. doi:10.13140/2.1.2770.8805. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265293378.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 O’Meara, Rachel N.; Thompson, Richard S. (2014). "Were There Miocene Meridiolestidans? Assessing the Phylogenetic Placement of Necrolestes patagonensis and the Presence of a 40 Million Year Meridiolestidan Ghost Lineage". Journal of Mammalian Evolution 21 (3): 271–284. doi:10.1007/s10914-013-9252-3.
- ↑ Lasseron, Maxime; Martin, Thomas; Allain, Ronana; Haddoumi, Hamid; Jalil, Nour-Eddine; Zouhri, Samir; Gheerbrant, Emmanuel (2022). "An African Radiation of 'Dryolestoidea' (Donodontidae, Cladotheria) and its Significance for Mammalian Evolution". Journal of Mammalian Evolution 29 (4): 733–761. doi:10.1007/s10914-022-09613-9. https://hal-mnhn.archives-ouvertes.fr/mnhn-03693015/file/Lasseron%20et%20al%202022_Donodontidae%20Ksar%20Metlili_d%C3%A9p%C3%B4t%20HAL.pdf.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Martin, Thomas; Averianov, Alexander O.; Schultz, Julia A.; Schwermann, Achim H.; Wings, Oliver (2021). "A derived dryolestid mammal indicates possible insular endemism in the Late Jurassic of Germany". The Science of Nature 108 (3): Article number 23. doi:10.1007/s00114-021-01719-z. PMID 33993371. Bibcode: 2021SciNa.108...23M.
- ↑ Gelfo, Javier N.; Goin, Francisco J.; Bauzá, Nicolás; Reguero, Marcelo (30 September 2019). "The fossil record of Antarctic land mammals: Commented review and hypotheses for future research". Advances in Polar Science: 274–292. doi:10.13679/j.advps.2019.0021. http://www.aps-polar.org/paper/2019/30/03/A190814000002/full.
- ↑ Martin, T.; Goin, F. J.; Schultz, J. A.; Gelfo, J. N. (2022). "Early Late Cretaceous mammals from southern Patagonia (Santa Cruz province, Argentina)". Cretaceous Research 133: 105127. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2021.105127.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 Rougier, G. W.; Martinelli, A. G.; Forasiepi, A. M. (2021). "Dryolestoids". Mesozoic Mammals from South America and Their Forerunners. Springer Earth System Sciences. pp. 201–260. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-63862-7_6. ISBN 978-3-030-63860-3.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Rougier, G. W.; Turazzinni, G. F.; Cardozo, M. S.; Harper, T.; Lires, A. I.; Canessa, L. A. (2021). "New Specimens of Reigitherium bunodontum from the Late Cretaceous La Colonia Formation, Patagonia, Argentina and Meridiolestidan Diversity in South America". Journal of Mammalian Evolution 28 (4): 1051–1081. doi:10.1007/s10914-021-09585-2.
Wikidata ☰ Q15991176 entry
 |
