Biology:Microcotyle sebastis
| Microcotyle sebastis | |
|---|---|
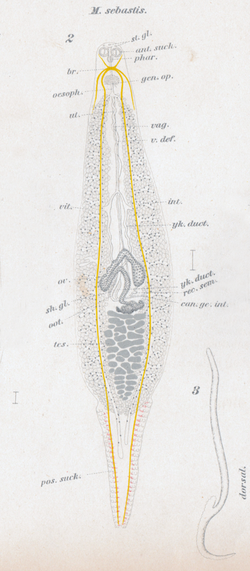
| |
| Microcotyle sebastis, drawing from original description | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Platyhelminthes |
| Class: | Monogenea |
| Order: | Mazocraeidea |
| Family: | Microcotylidae |
| Genus: | Microcotyle |
| Species: | M. sebastis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Microcotyle sebastis Goto, 1894 [1]
| |
Microcotyle sebastis is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.[1]
Studies dealing with Microcotyle sebastis
Microcotyle sebastis was first described by Goto in 1894, based on specimens obtained from the gills of rockfish, Sebastes sp.[1] In the original description, the author also illustrated the various stages of spermatogenesis of the species.[1] Bychowsky (1957) provided a brief description of the oncomiracidium; his study was completed by Thoney who described the post-larval growth and morphological changes during development.[2] It has been subsequently recorded on several host species, mostly from the genus Sebastes.[2] Bonham & Guberlet (1937) redescribed this species based on ten mature specimens from Sebastodes spp collected from Puget Sound, United States .[3]
Yamaguti redescribed Microcotyle sebastis based on two specimens from the gills of Sebastes schlegelii from Mutsu Bay, Japan.[4] Yamaguti noted that the framework of the posterior clamps differed from Goto's representation, and that his specimens had lateral branches from the oesophagus, not mentioned by Goto. Bonham & Guberlet noted that their specimens were rather intermediate in both characters.[3] Yoon et al. studied the seasonality and the microhabitat of Microcotyle sebastis from the gills of farmed Sebastes schlegeli. [5]
Radujkovic & Euzet reported one specimen of M. sebastis from the gills of Helicolenus dactylopterus.[6] Ayadi et al. suggested that the species of Microcotyle collected from Helicolenus dactylopterus from off Montenegro and identified as M. sebastis by Radujkovic & Euzet was probably a different species, based on extremely geographically distant localities (Pacific Ocean vs Mediterranean Sea), absence of detailed morphological evidences of identity, and absence of molecular information.[7]
Ayadi et al., suggested that species of Microcotyle from scorpaeniform fish on the Eastern side of the Pacific (USA coast) might be the same as M. sebastis (for which the type-locality is off Japan) and emphasised the need for a detailed morphological and molecular study of specimens from different localities and hosts.[7]
Morphology
Microcotyle sebastis has the general morphology of all species of Microcotyle, with a slender symmetrical body. The body comprises an anterior part which contains most organs and a posterior part called the haptor. The haptor bears 58 clamps, arranged as two rows (29 on each side). The clamps of the haptor attach the animal to the gill of the fish. There are also two buccal septate suckers at the anterior extremity. The digestive organs include an anterior, terminal mouth, a pharynx, and a posterior intestine with two branches provided with only a few short branches towards the median side, the left branch is longer than the right, and both branches extends for a certain distance into the haptor. Each adult contains male and female reproductive organs. The reproductive organs include a genital atrium opening a little in front of the point of bifurcation of the alimentary canal, armed with conical slightly curved spines, unarmed vagina opening middorsally behind the common genital opening, a single ovary, with an anterior portion shaped as in inversed V and a posterior portion somewhat S-shaped, about 40 small testes posterior to the ovary and occupying a little less than one-fifth the whole length of the body.[1] Information on the surface topography of Microcotyle sebastis is available in the study of Alyousif (1986).[8]
Post-larval growth
During post-larval development of Microcotyle sebastis, the ciliated epidermal jacket, ocellus, and larval opisthaptor are lost, and the clamps and genitalia develop. Microcotyle sebastis is protandrous and the genital elements develop in a specific order, following that of M. mormyri.[2] The larval ciliated epidermal jacket and the four pairs of lateral hooks were shed by the "2 clamp-pair stage". The other hooks remain on the haptor and are lost between the 3 and 5 clamp-pair stage. As the clamps are then added, the genitalia develop and the intestinal branches extend. The 20 clamp-pair stage is reached within 12 days after hatching.[2]
Etymology
The specific epithet sebastis is derived from the generic name of the type-host Sebastes sp.[1]
Molecular information
Park et al. provided the complete mitochondrial genome of Microcotyle sebastis, which is 14,407 bp in size, and considered one of the largest flatworm mitochondrial genomes published[9] However, Ayadi et al. pointed that Park et al. did not indicate any deposition of material in a Museum collection.[7]
Hosts and localities





The type-host is Sebastes sp.[1] Microcotyle sebastis was also reported on several (Sebastidae); the Korean rockfish Sebastes schelegelii,[10][11][12] on the black rockfish Sebastes melanops,[2] Sebastodes caurinus ( currently synonymised with the Copper rockfish Sebastes caurinus), Sebastodes maliger ( currently synonymised with the Quillback Rockfish Sebastes maliger) [3] Sebastes oblongus [13] the Blackbelly rosefish Helicolenus dactylopterus,[6][14] and on the yellowtail rockfish Sebastes flavidus.[15]
Microcotyle sebastis was first described from fishes caught off Hakodate off Japan .[1] It was also reported from farms in Korea,[10][11][5][12][9] off California ,[2] Puget Sound,[3] off Japan ,[13] off Montenegro,[6] Southeast Atlantic,[14] and from the Pacific coast of North America.[15]
Note that Tongyoung is considered an endemic area of M. sebastis.[10] When Stanley & Lee investigated parasites of yellowtail rockfish, Sebastes flavidusfrom the Pacific coast of North America as potential biological tags for stock identification, they revealed that only Microcotyle sebastis showed a latitudinal cline with a prevalence increasing from 0- 10% in samples from central British Columbia, to 80 and 100% in those off and Oregon respectively.[15]
Pathology of fish and treatment
Microcotyle sebastis is a major parasitic disease agent for Sebastes schlegeli in Korea, responsible for a high mortality rate of juveniles in Summer.[10][11][5]
Ki Hong Kim & Eun Seok Choi evaluated the oral administration of mebendazole or bithionol for the control of Microcotyle sebastis and suggested that a single dose of 50 mg mebendazole/kg B.W., 100 mg bithionol/kg B.W. or 200 mg bithionol/kg B.W. significantly reduces the numbers of this monogenean on the gills of the host fish.[10]
Kim & Cho also suggested that feeding a praziquantel-adsorbed diet significantly reduces the abundance of M. sebastis infestation, and that bathing in 100 ppm praziquantel for 4 min is effective for controlling infestations in practical rockfish cultures.[11] Kim et al. investigated the influence of the temperature on the rate of egg production and on the embryonic development of Microcotyle sebastis to determine the precise time of a second treatment.[12] It was suggested that treatment of M. sebastis with medicated feed was more practical than bath treatment in netpen farms. However, the authors noted that these chemicals should be administered to only juveniles until pharmacokinetic characteristics of these compounds in fish are investigated.[10]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Goto, Seitaro. (1894). Studies on the ectoparasitic Trematodes of Japan. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.56506.

- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Thoney, Dennis A. (1986). "Post-Larval Growth of Microcotyle sebastis (Platyhelminthes: Monogenea), a Gill Parasite of the Black Rockfish". Transactions of the American Microscopical Society 105 (2): 170–181. doi:10.2307/3226389. ISSN 0003-0023.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Bonham, Kelshaw; Guberlet, John E. (1937). "Notes on Microcotyle sebastis Goto from Puget Sound". Journal of Parasitology 23 (3): 281. doi:10.2307/3272417. ISSN 0022-3395.
- ↑ Yamaguti, S. (1934). "Studies on the helminth fauna of Japan. Part II. Trematodes of fishes, I". Japanese Journal of Zoology 5 (3): 249–541. NAID 10027668348.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Yoon, Gil Ha; Shinn, Andrew; Sommerville, Christina; Jo, Jae-Yoon (1997). "Seasonality and the microhabitat of Microcotyle sebastis Goto, 1894, a monogenean gill parasite of farmed rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli Hilgendorf 1880". Korean Journal of Aquaculture 10 (4): 387–394. https://dspace.stir.ac.uk/handle/1893/10235.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Branko M. Radujkovic, Louis Euzet, Parasites des poissons marins du Monténégro: Monogènes, in: B. M. Radujkovic, A. Raibaut (Eds.),Faune des parasites de poissons marins des côtes du Monténégro (Adriatique Sud), Acta Adriatica, 30, 51–135.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Ayadi, Zouhour El Mouna; Gey, Delphine; Justine, Jean-Lou; Tazerouti, Fadila (2017). "A new species of Microcotyle (Monogenea: Microcotylidae) from Scorpaena notata (Teleostei: Scorpaenidae) in the Mediterranean Sea". Parasitology International 66 (2): 37–42. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2016.11.004. ISSN 1383-5769. PMID 27840197. http://hal.upmc.fr/hal-01462207/file/El_Mouna_Ayadi_A_new_species_of.pdf.
- ↑ Alyousif M.S., 1986. Surface topography of Microcotyle sebastis (Trematoda Monogenea) by scanning électron microscopy. Annals of Zoology (Agra), 24, 1-18.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Park, Joong-Ki; Kim, Kyu-Heon; Kang, Seokha; Kim, Won; Eom, Keeseon S; Littlewood, DTJ (2 February 2007). "A common origin of complex life cycles in parasitic flatworms: evidence from the complete mitochondrial genome of Microcotyle sebastis (Monogenea: Platyhelminthes)". BMC Evolutionary Biology 7: 11. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-7-11. PMID 17270057.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 Kim, Ki Hong; Choi, Eun Seok (1998). "Treatment of Microcotyle sebastis (Monogenea) on the gills of cultured rockfish (Sebastes schelegeli) with oral administration of mebendazole and bithionol". Aquaculture 167 (1–2): 115–121. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(98)00300-7. ISSN 0044-8486.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Kim, KH; Cho, JB (2000). "Treatment of Microcotyle sebastis (Monogenea: Polyopisthocotylea) infestation with praziquantel in an experimental cage simulating commercial rockfish Sebastes schlegeli culture conditions". Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 40 (3): 229–231. doi:10.3354/dao040229. ISSN 0177-5103. PMID 10843562.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Kim, K. H., Choi, E. S., Cho, J. B., Hwang, Y. J., & Park, S. I. (1998). Influence of temperature on the egg production and hatching of Microcotyle sebastis (Monogenea: Microcotylidae), parasitic on Rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli. Journal of Fish Pathology, 11(2), 113-117. PDF

- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Machida, M., Araki, J., Kamiya, H. and Ohbayashi, M. (1972). Trematodes collected from sea fishes of the Hidaka District, Hokkaido. Memoirs of the National Science Museum 5: 1–9. [In Japanese with English abstract])
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 A.V. Gajevskaja, L.D. Aljoshkina, Fauna of monogenea of the south-east Atlantic, its ecological and geographical analysis, Zool. Zhurnal. 57 (3) (1988) 325–330Moscow.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Stanley, R. D.; Lee, D. L.; Whitaker, D. J. (1992). "Parasites of yellowtail rockfish, Sebastes flavidus (Ayres, 1862) (Pisces: Teleostei), from the Pacific coast of North America as potential biological tags for stock identification". Canadian Journal of Zoology 70 (6): 1086–1096. doi:10.1139/z92-152. ISSN 0008-4301.
Wikidata ☰ Q2497104 entry
 |
