Biology:Mozambique spitting cobra
| Mozambique spitting cobra | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Family: | Elapidae |
| Genus: | Naja |
| Species: | N. mossambica
|
| Binomial name | |
| Naja mossambica Peters, 1854[2]
| |
| <mapframe height="200" frameless="1" width="300">{"properties":{"stroke-width":6,"stroke":"#ff0000","title":"Mozambique spitting cobra"},"type":"ExternalData","title":"Mozambique spitting cobra range.map","service":"page"}</mapframe> | |
| Mozambique spitting cobra IUCN distribution
Extant (resident)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Naja nigricollis mossambica Peters, 1854 | |
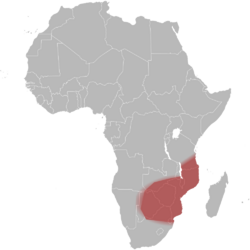
The Mozambique spitting cobra (Naja mossambica) is a highly venomous species of spitting cobra native to Africa. It is largely found in Angola, Botswana, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa , Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
Taxonomy
German naturalist Wilhelm Peters described this species in 1854.
Description
In colour, the snake is slate to blue, olive or tawny black above, with some or all scales having black edging. Below, it is salmon pink to purple yellowish, with black bars across the neck and ventrals speckled or edged with brown or black; young specimens sometimes have pink or yellow bars on the throat.[3][4]
The average length of adults is between 90 cm and 105 cm (3–3½ feet), but the largest specimen measured was a male 154 cm (5 feet) long in Durban, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.[4]
Distribution
This species is the most common cobra of the savanna regions of tropical and subtropical Africa. The distribution includes all of Mozambique; KwaZulu-Natal, as far south as Durban; Mpumalanga's lowveld region; southeastern Tanzania and Pemba Island; and west to far southeastern Angola and northeastern Namibia. Younger specimens are much more frequently encountered in the open at daytime. Unlike the Egyptian Cobra, this species prefers localities near water, to which it will readily take when disturbed.[4]
Toxicology
The snake is considered one of the most dangerous in Africa. Its venom is about as toxic as the American Mojave rattlesnake, considered the world's most venomous rattlesnake. Like the rinkhals, it can spit its venom. Its bite causes severe local tissue destruction (similar to that of the puff adder). Venom to the eyes can also cause impaired vision or blindness.[4] The venom of this species contains postsynaptic neurotoxin and cytotoxin. There have been only a few fatalities resulting from bites of this species, and survivors are mostly disfigured.[5]
A polyvalent antivenom is currently being developed by the Universidad de Costa Rica's Instituto Clodomiro Picado.[6]
Diet
The cobra's diet mainly consists of amphibians, other snakes, birds, eggs, small mammals, and occasionally even insects.[4] This cobra has been reported to scavenge and eat carcasses in an advanced stage of decomposition.[7] It has been documented feeding on venomous snakes such as black mamba and has developed immunity to its venom.[8]
Habits
The snake is nervous and temperamental. When confronted at close quarters, it can rear up as much as two-thirds of its length and spread its long narrow hood, and will readily spit in defense, usually from a reared-up position. The venom can be propelled 2–3 metres (6½–10 feet), with great accuracy. This species also can spit its venom without rearing up and flare out its neck into a hood, as well as spit from very tight spaces. The spitting cobra might bite instead of spitting depending on its circumstances, and like the rinkhals, it may feign death to avoid further molestation.[3]
Reproduction
The eggs average 10 to 22 in number; hatchlings measure 230–250 mm.
References
- ↑ Verburgt, L., Pietersen, D., Farooq, H., Chapeta, Y., Wagner, P., Safari, I. & Chenga, J. (2020). Naja mossambica. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T20878771A20878776.en
- ↑ "Naja mossambica". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=700631. Retrieved 11 January 2014.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Carruthers, Vincent (2005). The Wildlife of Southern Africa: A Field Guide to the Animals and Plants of the Region?. Struik. p. 100. ISBN 978-1-86872-451-2.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Branch, Bill (1998). Field Guide to the Snakes and Other Reptiles of Southern Africa. Ralph Curtis Publishing. p. 109. ISBN 9780883590423.
- ↑ Venomous Snakes of the world by Mark O'Shea, Page number 72
- ↑ Sánchez, Andrés (2017). "Expanding the neutralization scope of the EchiTAb-plus-ICP antivenom to include venoms of elapids from Southern Africa". Toxicon 125: 59–64. doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.11.259. PMID 27890775.
- ↑ Canning, G; Davidson, S; Phillips; Myram, P (April 2017). "Mozambique spitting cobra". African Herp News. p. 28. http://africanherpetology.org/wp/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/AHN-64-2017.pdf. Retrieved 1 April 2020.
- ↑ "Mozambique spitting cobra makes a meal of a black mamba". Earth Touch News. https://www.earthtouchnews.com/natural-world/predator-vs-prey/mozambique-spitting-cobra-makes-a-meal-of-a-black-mamba/.
Wikidata ☰ Q183062 entry
 |


