Biology:Mycobacterial porin
| MspA | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | MspA | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF09203 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR015286 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1uun / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| TCDB | 1.B.24 | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 268 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1uun | ||||||||
| |||||||||
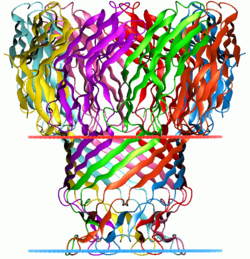
Mycobacterial porins are a group of transmembrane beta-barrel proteins produced by mycobacteria, which allow hydrophilic nutrients to enter the bacterium.[1][2] They are located in the impermeable mycobacterial outer membrane, or mycomembrane of fast-growing mycobacteria. The mycomembrane is unique and composed of very-long chain fatty acids, mycolic acids. These proteins are structurally different from the typical porins located in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. For example, the MspA protein forms a tightly interconnected octamer with eight-fold rotation symmetry that resembles a goblet and contains a central channel. Each protein subunit contains a beta-sandwich of immunoglobulin-like topology and a beta-ribbon arm that forms an oligomeric transmembrane beta-barrel.[3]
MspA has biotechnological applications, most notably in nanopore sequencing.
References
- ↑ "Mycobacterial outer membranes: in search of proteins". Trends in Microbiology 18 (3): 109–16. 2010. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2009.12.005. PMID 20060722.
- ↑ Niederweis, M. (2003). "Mycobacterial porins--new channel proteins in unique outer membranes". Molecular Microbiology 49 (5): 1167–1177. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03662.x. PMID 12940978. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12940978/.
- ↑ "The structure of a mycobacterial outer-membrane channel". Science 303 (5661): 1189–92. 2004. doi:10.1126/science.1094114. PMID 14976314. Bibcode: 2004Sci...303.1189F.
 |
