Biology:Northern snake-necked turtle
| Northern snake-necked turtle | |
|---|---|

| |
| Chelodina rugosa | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Pleurodira |
| Family: | Chelidae |
| Genus: | Chelodina |
| Subgenus: | Chelydera |
| Species: | C. rugosa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Chelodina rugosa Ogilby, J.D., 1890[2]
| |
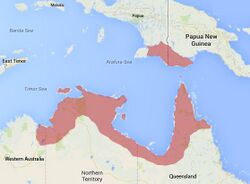
| |
| Distribution of C. (M) rugosa in Australia and New Guinea. | |
| Synonyms[6][7] | |
| |
The northern snake-necked turtle or northern long-necked turtle (Chelodina (Chelydera) rugosa) is a species of turtle in the family Chelidae or Austro-South American Side-necked Turtles. It is native to northern Australia and southern New Guinea.
The species was described in 1890 from material collected in Cape York of Queensland, Australia. The species has in recent years had several species of turtle synonymised with it,[7] the distribution includes northern Australia , Indonesia and Pitcairn. As a member of the sub-family Pleurodira this species is a side-necked turtle and also a snake-necked strike and gape predator. This carnivorous turtle will consume fish, tadpoles, hatchling turtles, worms, crickets, etc.
It is not an aggressive species with a biting defense. Individuals tend to flail to escape rather than bite. This species can be found not only in fresh water, but due to the proximity of the south New Guinea coast and close off shore islands, it also can be found in brackish water. Chelodina rugosa tends to hide under and between rocks and logs where possible or buries itself in the mud to act as an ambush predator to fish, amphibian, and invertebrate prey. Sexual dimorphism is quite evident in this species. Females can be easily recognized by the very short, stubby tail.
Taxonomic history
This species has had a rather convoluted taxonomic history. Initially described in 1841 by John Edward Gray[8] it was later synonymised (as senior synonym) with Chelodina colliei[9] and for many years northern and western Australia was believed to have a single species.[10][11] In 1967, the species was separated from the south-western Australian species but the name was incorrectly applied to that species with the name Chelodina siebenrocki applied to the northern form. Just eight years later it was found that the name Chelodina rugosa J. D. Ogilby 1890[2] had precedence over Chelodina siebenrocki and for many years after this that name was used for this species.[12] In 2000, it was found that the holotype of Chelodina oblonga was in fact a northern long-neck turtle and hence a petition was put in to conserve the now well established name of Chelodina rugosa.[11] This petition to the ICZN was ultimately overturned with the direction to use the Principal of Priority to determine the names, hence the name Chelodina oblonga is the correct name for this species.[13] More recently using mitagenomics of the types it was found that the specimen assumed to be the holotype of Chelodina oblonga, in all likelihood, could not be. It was clearly collected in northern Australia and described as such by Gray with characters that are true of the northern species.[6] However, its genomics suggest it is from Perth calling into question whether the unlabelled specimen figured in Gray 1841 was in fact the same as the specimen described. As such the name Chelodina rugosa has been resurrected for the species and Chelodina oblonga declared a nomen dubium, rendering it unusable.[6]
Subspecies are recognised by some for this species, basically geographic variants of doubtful significance. However, these are Chelodina (Chelydera) rugosa from Queensland and Chelodina (Chelydera) siebenrocki from New Guinea.[6][14]
Etymology
The specific name, siebenrocki, is in honor of Austrian herpetologist Friedrich Siebenrock.[15]
Reproduction
Like all turtles, the northern snake-necked turtle is oviparous. Unlike any other turtle, however, C. rugosa lays her eggs underwater. Aboriginal Australians have had knowledge of this reproductive behavior for many generations, but the first published report was by Kennett et al. in 1993.[16] Nests are excavated in soft substrate in billabongs and other ephemeral bodies of slow-moving fresh water toward the end of the wet season (austral summer, Dec-April). An average of 12 eggs are buried under 6–20 cm of sediment in shallow (<2 m) water. As the dry season progresses and the waters recede, the nests eventually dry out, and only then - when atmospheric oxygen is available[17] - do the embryos within the eggs resume growth. Exhibiting a reproductive strategy almost unique among reptiles, embryos of C. rugosa can survive at least 12 weeks of submersion. The hatchlings emerge approximately 70 days after resumption of development.[16]
Gallery
References
- ↑ Tortoise & Freshwater Turtle Specialist Group (1996). "Chelodina oblonga". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 1996: e.T4607A11032585. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.1996.RLTS.T4607A11032585.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/4607/11032585. Retrieved March 28, 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Ogilby, J. D. (1890). "Description of a new Australian tortoise". Records of the Australian Museum 1 (3): 56–59. doi:10.3853/j.0067-1975.1.1890.1226. http://www.carettochelys.com/pdf-library/ogilby_1890.pdf.
- ↑ Werner, Franz (1901). "Ueber Reptilien und Batrachier aus Ecuador und Neu-Guinea". Verhandlungen der Kaiserlich-Königlichen Zoologisch-Botanischen Gesellschaft in Wien 51: 593–614. doi:10.5962/bhl.part.4586.
- ↑ Fry, Dene B. (1915). "On a new Chelodina from Australia, with a key to the genus". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Queensland 27 (1): 88–90. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/13910500.
- ↑ Wells, Richard W.; Wellington, C. Ross (1985). "A classification of the Amphibia and Reptilia of Australia". Australian Journal of Herpetology, Supplemental Series 1: 1–61. https://iucn-tftsg.org/wp-content/uploads/file/Articles/Wells_and_Wellington_1985.pdf.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Kehlmaier, Christian; Zhang, Xiuwen; Georges, Arthur; Campbell, Patrick D.; Thomson, Scott; Fritz, Uwe (2019). "Mitogenomics of historical type specimens of Australasian turtles: clarification of taxonomic confusion and old mitochondrial introgression". Scientific Reports 9 (1): 5841. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-42310-x. PMID 30967590.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Georges, Arthur; Thomson, Scott (2010). "Diversity of Australasian freshwater turtles, with an annotated synonymy and keys to species". Zootaxa 2496 (1): 137. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.2496.1.1. http://www.mapress.com/zootaxa/2010/f/zt02496p037.pdf.
- ↑ Gray, John Edward. (1841). A catalogue of the species of reptiles and amphibia hitherto described as inhabiting Australia, with a description of some new species from Western Australia, and some remarks on their geographical distribution. In: Grey, G. Journals of Two Expeditions of Discovery in Northwest and Western Australia. London: T. and W. Boone, Vol. 2. Appendix E, pp. 422–449.
- ↑ Boulenger, G.A. 1889. Catalogue of the Chelonians, Rhynchocephalians, and Crocodiles in the British Museum (Natural History) London: Trustees of the Museum, 311pp.
- ↑ Thomson, S. (2000). "The identification of the holotype of Chelodina oblonga (Testudines: Chelidae) with a discussion of taxonomic implications". Chelonian Conservation and Biology 3 (4): 745–748.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Thomson, S. A. (2006). "Chelodina rugosa Ogilby, 1890 (currently Macrochelodina rugosa; Reptilia, Testudines): proposed precedence over Chelodina oblonga Gray, 1841". Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature 63 (3): 187–193. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/34353079.
- ↑ Cogger, H.G., Cameron, E.E. and Cogger, H.M. (1983). Zoological Catalogue of Australia. Volume 1. Amphibia and Reptilia. Australian Government Printing Service, Canberra. 313pp.
- ↑ International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (2013). "Opinion 2315 (Case 3351) Chelodina rugosa Ogilby, 1890 (currently Macrochelodina rugosa; Reptilia, Testudines): precedence not granted over Chelodina oblonga Gray, 1841". Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature 70 (1): 57–60. doi:10.21805/bzn.v70i1.a12.
- ↑ Shea, G., Thomson, S. & Georges, A. 2020. The identity of Chelodina oblonga Gray 1841 (Testudines: Chelidae) reassessed. Zootaxa 4779(3): 419–437. DOI: 10.11646/zootaxa.4779.3.9. PDF
- ↑ Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. ISBN:978-1-4214-0135-5. (Chelodina siebenrocki, p. 243).
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Kennett, R., Christian, K. & Pritchard, D. 1993. Underwater nesting by the tropical freshwater turtle, Chelodina rugosa (Testudinata: Chelidae). Australian Journal of Zoology 41:47-52. doi:10.1071/zo9930047
- ↑ Kennett, R., Georges, A. & Palmer-Allen, M. 1993. Early developmental arrest during immersion of eggs of a tropical freshwater turtle, Chelodina rugosa (Testudinata: Chelidae), from Northern Australia. Australian Journal of Zoology 41:37-45. doi:10.1071/zo9930037
External links
- Asian Turtle Trade Working Group (2000). "Chelodina rugosa ssp. siebenrocki". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2000: e.T39622A10252168. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2000.RLTS.T39622A10252168.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/39622/10252168. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- Testudines.org catalog project (2015). 'Chelodina oblonga. 2016 >Turtles and tortoise Catalog. Readed 18 December 2016.
- Video of a Northern Snake-necked Turtle in the wild on Youtube
Wikidata ☰ Q2697599 entry
 |