Biology:Pelophylax caralitanus
| Pelophylax caralitanus | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Ranidae |
| Genus: | Pelophylax |
| Species: | P. caralitanus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pelophylax caralitanus (Arikan, 1988)
| |
| |
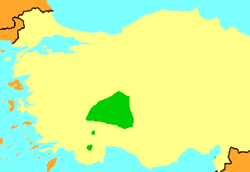
| Range of P. caralitanus in green | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Pelophylax caralitanus, commonly known as the Anatolian frog or Beyşehir frog,[2] is a species of frog in the family Ranidae. It is endemic to southern Turkey where it has a moderately large range and is considered near-threatened by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
Description
The dorsal surface of P. caralitanus is greenish-brown heavily blotched with dark brown. It is similar in appearance to the Levant water frog (Pelophylax bedriagae) and the marsh frog (Pelophylax ridibundus), the two other lowland species of frog found in Turkey, but differs in being rather larger and not having longitudinal brown stripes on the head and back. It can also be distinguished from them by having a pale neck and belly blotched with red, orange, or sometimes yellow.[2]
Distribution and habitat
Pelophylax caralitanus is endemic to the Turkish Lakes Region of southwestern Turkey where it is found from the Konya Plain to Denizli. It has been recorded in Lake Beyşehir, Lake Eğirdir, Lake Suğla, Çarşamba Creek (Konya), Lake Gölcük (Isparta), Lake Hotamiş, Ivriz (Ereğli/Konya), Işikli Lake in Çivril (Denizli), and Çardak (Denizli). It occupies lakes, reservoirs, ponds, pools, rivers, streams, ditches, springs and marshes. It is tolerant of disturbed habitats such as fish ponds.[1]
Ecology
This is an aqueous species of frog which spends the main part of its life in fresh water locations with plentiful vegetation. The tadpoles are herbivorous and feed on algae while the diet of the adult frog consists largely of insects and other aqueous invertebrates and their larvae; this is sometimes supplemented by the consumption of tadpoles.[2]
Status
This frog is the largest edible frog native to Turkey and is collected for food, being exported commercially to France, Italy and Switzerland.[1] It is also threatened by water extraction and loss of habitat, with several dams being planned to provide drinking water and crop irrigation. It is however present in two protected areas, Lake Kovada National Park and Lake Beyşehir National Park. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as being near-threatened.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Mehmet Ǒz, Yakup Kaska, Yusuf Kumlutaş, Uğur Kaya, Aziz Avci, Nazan Üzüm, Can Yeniyurt, Ferdi Akarsu, Max Kasparek (2009). "Pelophylax caralitanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2009: e.T135806A4203649. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2009.RLTS.T135806A4203649.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/135806/4203649. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Pelophylax caralitanus" (in Turkish). AdaMerOs Herptil Türkiye. http://www.turkherptil.org/IcerikDetay.asp?IcerikKatId=19&TurId=475.
Wikidata ☰ Q1186053 entry
 |