Biology:Persoonia acerosa
| Needle geebung | |
|---|---|

| |
| Persoonia acerosa in the ANBG | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Proteaceae |
| Genus: | Persoonia |
| Species: | P. acerosa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Persoonia acerosa Sieber ex Schult. & Schult.f.[1]
| |
| |
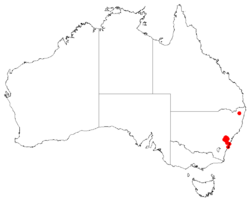
| Occurrence data downloaded from AVH | |
Persoonia acerosa, commonly known as needle geebung,[2] is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to a restricted area of New South Wales. It is a shrub with small, channelled, needle-like leaves, yellow tubular flowers and yellowish-green, pear-shaped fruit.
Description
Persoonia acerosa is an erect to spreading shrub that typically grows to a height of 0.5–2 m (1 ft 8 in–6 ft 7 in) and has smooth bark. The leaves are linear, 10–23 mm (0.39–0.91 in) long and 0.5 mm (0.020 in) wide and channelled on the upper surface. The flowers are arranged between the leaves on a branchlet that continues to grow after flowering, each flower on a pedicel 1–2 mm (0.039–0.079 in) long. The flowers are tube-shaped, 8–10 mm (0.31–0.39 in) long, glabrous, and mostly appear in summer. The fruit is a pear-shaped, yellowish-green drupe up to 14 mm (0.55 in) long.[2][3][4]
Taxonomy
Persoonia acerosa was first formally described in 1827 by Josef August and Julius Hermann Schultes in their book Mantissa in volumen primum [-tertium] :Systematis vegetabilium caroli a Linné from an unpublished description by Franz Sieber.[5][6]
Distribution and habitat
Needle geebung grows in heath, scrubby woodland and forest on sandstone on the Central Coast and from the central Blue Mountains to the Hill Top district in New South Wales at altitudes of 550–1,000 m (1,800–3,280 ft). It is mainly found in the upper Blue Mountains and is believed to be extinct at Hill Top.[2][4]
Conservation status
This geebung is listed as "vulnerable" under the Australian Government Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 and the New South Wales Government Biodiversity Conservation Act 2016. The main threats to the species are land clearing, burning for hazard reduction, weed invasion and disturbance by vehicles and rubbish dumping.[2]
References
- ↑ "Persoonia acerosa". Australian Plant Census. https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/111571.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Needle Geebung - profile". New South Wales Government Office of Environment and Heritage. https://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/threatenedSpeciesApp/profile.aspx?id=10591.
- ↑ Weston, Peter H.. "Persoonia acerosa". Royal Botanic Garden Sydney. https://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/NSWfl.pl?page=nswfl&lvl=sp&name=Persoonia~acerosa.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Weston, Peter H.. "Persoonia acerosa". Australian Biological Resources Study, Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment: Canberra. https://profiles.ala.org.au/opus/foa/profile/Persoonia%20acerosa.
- ↑ "Persoonia acerosa". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/544179.
- ↑ Schultes, Josef August; Schultes, Julius Hermann (1827). Mantissa in volumen primum [-tertium :Systematis vegetabilium caroli a Linné]. Stuttgart: Sumtibus J.G. Cottae. p. 269. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/10317#page/272/mode/1up. Retrieved 20 September 2020.
Wikidata ☰ Q7170704 entry
 |



