Biology:Pleurosternon
| Pleurosternon | |
|---|---|
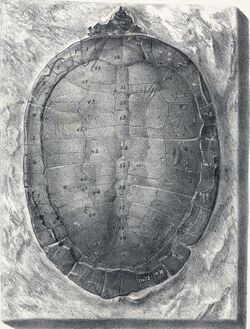
| |
| Pleurosternon (ovatum) bullockii fossil | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Animalia |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Chordata |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Reptilia |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Pantestudines |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Testudinata |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | †Paracryptodira |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | †Pleurosternidae |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | †Pleurosternon Owen, 1853 |
| Species | |
| |
Pleurosternon is an extinct genus of freshwater pleurosternid turtle from the latest Jurassic to earliest Cretaceous of Europe.[1] Its type species, P. bullockii was described by the paleontologist Richard Owen (noted for coining the word Dinosauria) in 1853. Since then, and throughout the late 19th century, many fossil turtles were incorrectly assigned to this genus, though only two are currently considered valid.
Taxonomy
Pleurosternon bullockii fossils were first described by Richard Owen in 1841 from specimens found in the earliest Cretaceous (Berriasian) aged Purbeck Group of the Isle of Purbeck, of Dorset in southern England, under the living genus Platemys.[2] It was not until 1853 however, that it was published under the name Pleurosternon in a paper Owen presented to the Palaeontographical Society.[3] P. portlandicum named by Richard Lydekker in 1889 from the latest Jurassic (Tithonian) aged Portland Stone of the Isle of Portland, Dorset, is now considered a junior synonym of the P. bullockii.[4] In 2021 a second valid species, Pleurosternon moncayensis, was named from the Ágreda locality of Tarazona y el Moncayo, Aragon, Spain, which spans the Tithonian-Berriasian transition.[5]
Description
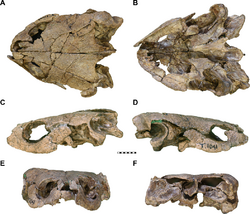
Pleurosternon has a very depressed carapace, much flatter than similar genera, such as the North American Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous Glyptops.[6][7] Adults show little or none of the nuchal emargination that is more visible in juveniles.[7] The Xiphiplastras also have a large, V-shaped notch near the back of the bone.[7] The skull of P. bullockii is similar to that of other pleurosternids, and is similar in some aspects to those of pleurodires.[8] The known shell specimens of P. bullockii exhibit a large amount of variability, and also exhibit sexual dimorphism.[9]
Distribution and habitat
In Europe, P. bullockii is best known from southeast England 's Purbeck Group and Portland stone, with over sixty carapaces known from the Purbeck Group alone.[9][10] Several areas within the formation became noted by some for producing Pleurosternon fossils. Among them were Swanage, Durlston Bay, Langton Matravers, and Herston.[7] P. bullockii is also known from disarticulated shell elements found in Tithonian aged deposits near Wimille in Pas-de-Calais in northern France.[4] As well as from numerous remains found in the Berriasian aged Angeac-Charente bonebed in western France, where it is the most abundant turtle.[11] The Purbeck Group, at the time was a coastal region with a complex system of shallow lagoons that slowly lost their salinity over time.[12] The Portland stone, however is a maritime deposit of slightly older age than the Purbeck, most bones found there are interpreted as having washed out to sea.
See also
- Glyptops
- Chengyuchelys
- Helochelys
References
- ↑ E. Schweizerbart. 1994. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie: Monatshefte, Issues 7-12.
- ↑ Owen, Richard. Report on British Fossil Reptilia. Report of the British Association for the Advancement of Science. P. p43- 126. 1841
- ↑ Owen, R. A Monograph of the Fossil Chelonian Reptiles of the Wealden Clays and Purbeck Limestones. Palaeontographical Society, Vol. VII, 1853
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Guerrero, A.; Pérez-García, A. (December 2020). "On the validity of the British Upper Jurassic turtle "Pleurosternon portlandicum" (Paracryptodira, Pleurosternidae)" (in en). Journal of Iberian Geology 46 (4): 419–429. doi:10.1007/s41513-020-00136-x. ISSN 1698-6180. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s41513-020-00136-x.
- ↑ Pérez-García, A.; Martín-Jiménez, M.; Aurell, M.; Canudo, J.I.; Castanera, D. (2021-04-12). "A new Iberian pleurosternid (Jurassic-Cretaceous transition, Spain) and first neuroanatomical study of this clade of stem turtles" (in en). Historical Biology 34 (2): 298–311. doi:10.1080/08912963.2021.1910818. ISSN 0891-2963. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/08912963.2021.1910818.
- ↑ Boule, Marcellin. Priviteau, Jean. Les Fossiles. Éléments De Paléontologie. Libraries de L'académie Médecine. Paris, 1935. P. 433
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Milner, Andrew R. (November 2004). "The turtles of the Purbeck Limestone Group of Dorset, southern England" (in en). Palaeontology 47 (6): 1441–1467. doi:10.1111/j.0031-0239.2004.00418.x. ISSN 0031-0239.
- ↑ Evers, Serjoscha W.; Rollot, Yann; Joyce, Walter G. (2020-06-30). "Cranial osteology of the Early Cretaceous turtle Pleurosternon bullockii (Paracryptodira: Pleurosternidae)" (in en). PeerJ 8: e9454. doi:10.7717/peerj.9454. ISSN 2167-8359. PMID 32655997.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Guerrero, A.; Pérez-García, A. (2021-09-01). "Morphological variability and shell characterization of the European uppermost Jurassic to lowermost Cretaceous stem turtle Pleurosternon bullockii (Paracryptodira, Pleurosternidae)" (in en). Cretaceous Research 125: 104872. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2021.104872. ISSN 0195-6671. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0195667121001191.
- ↑ Hay, Oliver Perry. 1908. Fossil Turtles of North America. Carnegie Institution of Washington. p. 45
- ↑ Ronan Allain, Romain Vullo, Lee Rozada, Jérémy Anquetin, Renaud Bourgeais, et al.. Vertebrate paleobiodiversity of the Early Cretaceous (Berriasian) Angeac-Charente Lagerstätte (southwestern France): implications for continental faunal turnover at the J/K boundary. Geodiversitas, Museum National d’Histoire Naturelle Paris, In press. ffhal-03264773f
- ↑ Radley, Jonathan D. Distribution and Environmental Significance of Molluscs in the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous Purbeck Formation of Dorset, Southern England: a Review. Life and Environments in Purbeck Times. (Special Papers in Palaeontology No. 68). p 48.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q7204816 entry
 |
