Biology:Pterophorus furcatalis
| Pterophorus furcatalis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Lepidoptera |
| Family: | Pterophoridae |
| Genus: | Pterophorus |
| Species: | P. furcatalis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pterophorus furcatalis (Walker, 1864)[1]
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Pterophorus furcatalis, the Pittosporum plume moth, is a moth of the family Pterophoridae.[3] It was first described by Frances Walker and is endemic to New Zealand. This species can be found throughout the North, South and Stewart Islands. Its preferred habitat is dense native bush. Larval host plants include Pittosporum eugenioides and Pittosporum crassicaule. Adult moths are on the wing from November to March and are attracted to light.
Taxonomy
This species was first described by Frances Walker in 1864 and named Aciptilus furcatalis.[4] Walker used specimens from Colonel Bolton collected in Auckland and T.R. Oxley collected in Nelson.[4][2] In 1913 Edward Meyrick placed Aciptilus furcatalis into the genus Alucita.[5] In 1928 George Hudson followed Meyrick's placement discussing and illustrating this species in his 1928 publication The butterflies and moths of New Zealand.[6] In 1988 John S. Dugdale discussed this species under the name Pterophorus furcatalis.[2] In 1993 Cees Gielis discussed this species under the name Pterophorus furcatalis but placed it in a list where the species were regarded as having an uncertain status.[7] The lectotype specimen, collected by T. R. Oxley in Nelson, is held at the Natural History Museum, London.[2]
Description
In 1928 Hudson illustrated the egg of this species.[6] Hudson subsequently described the larva of this species as follows:
The length of the larva when full-grown is about 3⁄8 inch. Very stout, rapidly tapering posteriorly; segments well defined. General colour rather pale green, darker on the back; the edges of the darker dorsal band edged with whitish. Head pale brown on the sides. Each segment furnished with a row of long, very stout, blackish-brown bristles and tufts of short whitish hairs near ventral surface.[8]
In 1939 Hudson described the larvae of this species as follows:
The length of the larva when full-grown is about 3⁄8 inch. Very stout, rapidly tapering posteriorly; segments well defined. General colour rather pale green, darker on the back; the edges of the darker dorsal band edged with whitish. Head pale brown on the sides. Each segment furnished with a row of long, very stout, blackish-brown bristles and tufts of short whitish hairs near ventral surface.[8]
The larva prepares a large pad of silk on a support upon which the pupa is attached by the whole of its flattened ventral surface.[8] Hudson also described the pupa as follows:
The pupa is about 5⁄16 inch long, stout, rapidly tapering towards extremity. Colour uniform grass green; integument polished, slightly and irregularly striated, with a row of impressions on each side of abdominal segments; limbs very faintly sculptured; no hairs or bristles.[8]
Hudson described the adults of this species as follows:
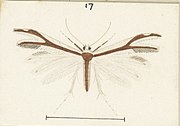
The expansion of the wings is about 7⁄8 inch. The fore-wings are brown with 2⁄3 of the costa broadly edged with white, and a small white mark near the middle of the first plume. The hindwings are snow white. The head is white and the dorsal surface of the thorax and abdomen brown. All the cilia are white except a brown patch near the extremity of the second plume on the fore-wings.[6]
Some species have markings that are a darker shade of brown.[6] This species can possibly be confused with the brown streak form of P. monospilalis.[9] P. furcatalis but can be distinguished as the second plume is brown where as with P. monospilalis that second plume is white.[9] P. furcatalis also has a brown streak down the dorsal side of its abdomen which is also a distinguishing feature.[6]
Distribution
This species is endemic to New Zealand.[1] It can be found throughout the country including in the North, South and Stewart Islands.[6]
Habitat and hosts
This species inhabits dense native forest.[6] The larval hosts of this species include Pittosporum eugenioides and Pittosporum crassicaule.[8][10] Larvae reared on P. crassicaule produce pupa strongly spotted with black.[10]
Behaviour
The larvae are slow moving and rest on the upper surface of the leaves of its food plants.[8] Adults of this species are on the wing from November to March.[6] They are attracted to light.[11]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Pterophorus furcatalis (Walker, 1864)". 2021. https://www.nzor.org.nz/names/607acce3-2b57-4866-bee5-add81c06167f.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 , pp. 132-133, Wikidata Q45083134
- ↑ , p. 463, Wikidata Q45922947
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 , pp. 950, Wikidata Q108264250
- ↑ , pp. 48, Wikidata Q113379622
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 , pp. 210, Wikidata Q58593286
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ , pp. 76, Wikidata Q93258703
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 , pp. 429, Wikidata Q109420935
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Hoare, Robert J. B. (2014). A photographic guide to moths & butterflies of New Zealand. Olivier Ball. Auckland. pp. 41. ISBN 978-1-86966-399-5. OCLC 891672034. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/891672034.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 , pp. 103-104, Wikidata Q107693053
- ↑ , Wikidata Q57483705
Wikidata ☰ Q7256854 entry
 |