Biology:Caatinga antwren
| Caatinga antwren | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male Caatinga antwren seen in Crato, Ceará | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Thamnophilidae |
| Genus: | Radinopsyche Whitney et al., 2021 |
| Species: | R. sellowi
|
| Binomial name | |
| Radinopsyche sellowi (Whitney & Pacheco, 2000)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Herpsilochmus sellowi Whitney, Pacheco, Buzzetti & Parrini, 2000 | |
The Caatinga antwren (Radinopsyche sellowi) is a species of bird in the family Thamnophilidae. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Radinopsyche. Prior to 2022, it was classified in the genus Herpsilochmus, but was reclassified into Radinopsyche by the International Ornithological Congress following a 2021 phylogenetic study.[2][3]
It is endemic to Brazil . Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forests and dry savanna. It is threatened by habitat loss.
Taxonomy
The Caatinga antwren is the only member of the genus Radinopsyche. When originally described, it was placed in the genus Herpsilochmus as the pileated antwren. In 2000, a study showed that the southeastern population of the pileated antwren varied from the larger population in terms of morphology and vocalizations.[4] A split was proposed between the two, with the Bahia antwren representing the smaller southeastern population, and the Caatinga antwren the rest. Mitochondrial DNA studies in 2021 showed that the Caatinga antwren was more closely related to the white-bearded antshrike (Biatas nigropectus), prompting it to be placed in a new monotypic genus.[3]
Description
The Caatinga antwren is a small bird, averaging 10.5–11.5 centimetres (4.1–4.5 in) long, and 6.5–8 grams (0.23–0.28 oz) in weight.[5] Both sexes have a black crown and nape, with a dark eyeband. The wings are dark near the shoulder, with white bands across and black feather tips. The tail is largely black with white tips and white outer feathers. The male is overall a dusky grey with lighter underparts. The female has a grey back with buffy underparts.[6]
Distribution and habitat
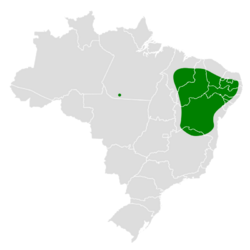
The Caatinga antwren is endemic to Brazil. It is found in the north-central and eastern regions of the country. It is found from Maranhão in the east to the Rio Grande do Norte in the west, and from Minas Gerais in the north to Bahia in the south.[7]
As its name suggests, it is found primarily in the Caatinga, a type of semi-arid tropical vegetation found in northeastern Brazil. It is most abundant in semi-deciduous forest between 300–900 metres (980–2,950 ft) in elevation.[8]
Feeding and diet
Similar to other antbirds, Caatinga antwren's diet consists primarily of arthropods, including grasshoppers, crickets, and moths.[9] Few studies have been done on the particulars of the Caatinga antwren's diet.
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Herpsilochmus sellowi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22701558A93836378. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22701558A93836378.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22701558/93836378. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ "IOC World Bird List 12.1" (in en-US). doi:10.14344/ioc.ml.12.1. https://doi.org/10.14344/IOC.ML.12.1.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bravo, Gustavo A; Whitney, Bret M; Belmonte-Lopes, Ricardo; Bornschein, Marcos R; Aristizábal, Natalia; Beco, Renata; Battilana, Jaqueline; Naka, Luciano N et al. (2021-05-08). "Phylogenomic analyses reveal non-monophyly of the antbird genera Herpsilochmus and Sakesphorus (Thamnophilidae), with description of a new genus for Herpsilochmus sellowi". Ornithology 138 (3). doi:10.1093/ornithology/ukab025. ISSN 0004-8038. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ornithology/ukab025.
- ↑ Whitney, B. M.; Pacheco, J. F.; Buzzetti, D. R. C.; Parrini, R. (2000). "Systematic revision and biogeography of the Herpsilochmus pileatus complex, with description of a new species from northeastern Brazil". Auk 117 (4): 869–891. doi:10.1093/auk/117.4.869.
- ↑ Olmos, F.; Albano, C. (2012). "As aves da região do Parque Nacional Serra da Capivara (Piauí, Brasil)" (in Portuguese). Revista Brasileira de Ornitologia 20 (3): 173–187.
- ↑ Taylor, J; Gilroy, J; Butchart, S. "Caatinga Antwren Herpsilochmus sellowi". http://datazone.birdlife.org/species/factsheet/caatinga-antwren-herpsilochmus-sellowi/text.
- ↑ Pacheco, J. F.; Olmos, F. (2005). "Birds of a latitudinal transect in the Tapajós-Xingu Interfluvium, eastern Brazilian Amazonia". Ararajuba 13 (1): 29–46.
- ↑ Olmos, Fábio (March 1993). "Birds of Serra da Capivara National Park, in the "caatinga" of north-eastern Brazil". Bird Conservation International 3 (1): 21–36. doi:10.1017/S0959270900000769.
- ↑ Zimmer, K.J.; Isler, M.L. (2004). Handbook of the Birds of the World. Vol. 8: Broadbills to Tapaculos. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. pp. 448–531. ISBN 978-84-87334-50-4.
Wikidata ☰ Q1267674 entry
 |



