Biology:Ranunculus
| Ranunculus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Eschscholtz's buttercup (Ranunculus eschscholtzii) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Plantae |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Tracheophytes |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Angiosperms |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Eudicots |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Ranunculales |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Ranunculaceae |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Ranunculoideae |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Ranunculeae |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Ranunculus L. |
| Diversity | |
| About 1,700 species | |
| Synonyms[1][2] | |
| |
Ranunculus /ræˈnʌŋkjʊləs/[3] is a large genus of about 1700 to more than 1800 species[1][2] of flowering plants in the family Ranunculaceae. Members of the genus are known as buttercups, spearworts and water crowfoots.
The genus is distributed in Europe, North America and South America.[2] The familiar and widespread buttercup of gardens throughout Northern Europe (and introduced elsewhere) is the creeping buttercup Ranunculus repens, which has extremely tough and tenacious roots. Two other species are also widespread, the bulbous buttercup Ranunculus bulbosus and the much taller meadow buttercup Ranunculus acris. In ornamental gardens, all three are often regarded as weeds.
Buttercups usually flower in the spring, but flowers may be found throughout the summer, especially where the plants are growing as opportunistic colonizers, as in the case of garden weeds.
The water crowfoots (Ranunculus subgenus Batrachium), which grow in still or running water, are sometimes treated in a separate genus Batrachium (from Greek βάτραχος bátrakhos, "frog"). They have two different leaf types, thread-like leaves underwater and broader floating leaves. In some species, such as R. aquatilis, a third, intermediate leaf type occurs.
Ranunculus species are used as food by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including the Hebrew character and small angle shades. Some species are popular ornamental flowers in horticulture, with many cultivars selected for large and brightly coloured flowers.
Description
Plant
Buttercups are mostly perennial, but occasionally annual or biennial, herbaceous, aquatic or terrestrial plants, often with leaves in a rosette at the base of the stem. In many perennial species runners are sent out that will develop new plants with roots and rosettes at the distanced nodes.
The leaves lack stipules, have petioles, are palmately veined, entire, more or less deeply incised, or compound, and leaflets or leaf segments may be very fine and linear in aquatic species.
Flowers
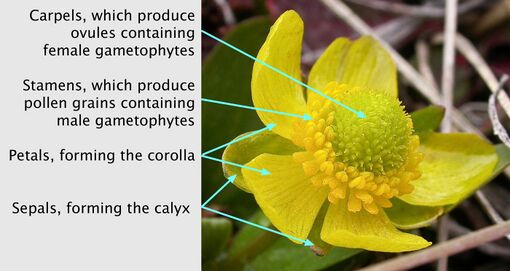
The hermaphrodite flowers are single or in a cyme, have usually five (but occasionally as few as three or as many as seven) sepals and usually, five yellow, greenish or white petals that are sometimes flushed with red, purple or pink (but the petals may be absent or have a different, sometimes much higher number).
At the base of each petal is usually one nectary gland that is naked or may be covered by a scale. Anthers may be few, but often many are arranged in a spiral, are yellow or sometimes white, and with yellow pollen. The sometimes few but mostly many green or yellow carpels are not fused and are also arranged in a spiral, mostly on a globe or dome-shaped receptacle.
Reflective petals
The petals of buttercups are often highly lustrous, especially in yellow species, owing to a special coloration mechanism: the petal's upper surface is very smooth causing a mirror-like reflection.[4][5] The flash aids in attracting pollinating insects and temperature regulation of the flower's reproductive organs.[4]
-
Glacier buttercup Ranunculus glacialis
-
Sagebrush buttercup (Ranunculus glaberrimus)
-
Creeping buttercup (Ranunculus repens)
-
Ranunculus asiaticus, a cultivated form
Fruit


.
The fruits (in this case called achenes) may be smooth or hairy, winged, nobby or have hooked spines.[6]
Naming
The genus name Ranunculus is Late Latin for "little frog", the diminutive of rana.[7] This probably refers to many species being found near water, like frogs.[6]
The common name buttercup may derive from a false belief that the plants give butter its characteristic yellow hue (in fact it is poisonous to cows and other livestock). A popular children's game involves holding a buttercup up to the chin; a yellow reflection is supposed to indicate a fondness for butter.[8] In ancient Rome, a species of buttercup was held to the skin by slaves attempting to remove forehead tattoos made by their owners.[9]: 106
In the interior of the Pacific Northwest of the United States, the buttercup is called "Coyote's eyes"—ʔiceyéeyenm sílu in Nez Perce[10] and spilyaynmí áčaš in Sahaptin.[11] In the legend, Coyote was tossing his eyes up in the air and catching them again when Eagle snatched them. Unable to see, Coyote made eyes from the buttercup.[citation needed]
Splitting of the genus
Molecular investigation of the genus has revealed that Ranunculus is not monophyletic with respect to a number of other recognized genera in the family—e.g. Ceratocephala, Halerpestes, Hamadryas, Laccopetalum, Myosurus, Oxygraphis, Paroxygraphis and Trautvetteria. A proposal to split Ranunculus into several genera has thus been published in a 2010 classification for the tribe Ranunculeae.[12] The split (and often re-recognized) genera include Arcteranthis Greene, Beckwithia Jeps., Callianthemoides Tamura, Coptidium (Prantl) Beurl. ex Rydb., Cyrtorhyncha Nutt. ex Torr. & A.Gray, Ficaria Guett., Krapfia DC., Kumlienia E. Greene and Peltocalathos Tamura. Not all taxonomists and users accept this splitting of the genus, and it can alternatively be treated in the broad sense.
Pharmacological activity
The most common uses of Ranunculus species in traditional medicines are as an antirheumatic, as a rubefacient, and to treat intermittent fever. The findings in some Ranunculus species of, for example, protoanemonin, anemonin, may justify the uses of these species against fever, rheumatism and rubefacient in Asian traditional medicines.[13]
Toxicity
All Ranunculus (buttercup) species are poisonous when eaten fresh, but their acrid taste and the blistering of the mouth caused by their poison means they are usually left uneaten. Poisoning in livestock can occur where buttercups are abundant in overgrazed fields where little other edible plant growth is left, and the animals eat them out of desperation. Symptoms of poisoning include bloody diarrhea, excessive salivation, colic, and severe blistering of the mouth, mucous membranes and gastrointestinal tract. When Ranunculus plants are handled, naturally occurring ranunculin is broken down to form protoanemonin, which is known to cause contact dermatitis in humans and care should therefore be exercised in extensive handling of the plants.[14] The toxins are degraded by drying, so hay containing dried buttercups is safe.[15]
Fossil record
Ranunculus gailensis and Ranunculus tanaiticus seed fossils have been described from the Pliocene Borsoni Formation in the Rhön Mountains, central Germany .[16] Achenes labelled Ranunculus cf. tachiroei is known from the Pliocene of the Hengduan Mountains of China.[17] Indeterminate achenes have been found from Neogene strata in the Transantarctic Mountains.[18]
Species
References
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Ranunculus L., Sp. Pl. : 548 (1753)". Plants of the World Online. Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 2022. https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:30002060-2#synonyms.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Ranunculus L.". World Flora Online Consortium. 2022. http://www.worldfloraonline.org/taxon/wfo-4000032540.
- ↑ Sunset Western Garden Book. 1995. pp. 606–607.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Van der Kooi, Casper; Elzenga, Theo; Dijksterhuis, Jan; Stavenga, Doekele (2017). "Functional optics of glossy buttercup flowers". Journal of the Royal Society Interface 14 (127): 20160933. doi:10.1098/rsif.2016.0933. PMID 28228540.
- ↑ "Buttercups focus light to heat their flowers and attract insects". New Scientist. 25 February 2017. https://www.newscientist.com/article/mg23331142-400-buttercups-focus-light-to-heat-their-flowers-and-attract-insects/.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Lehnebach, C.A. (2008), Phylogenetic Affinities, Species Delimitation and Adaptive Radiation of New Zealand Ranunculus, Palmerston North, New Zealand: Massey University, http://mro.massey.ac.nz/bitstream/handle/10179/787/02whole.pdf?sequence=2
- ↑ Lewis, Charlton T.; Short, Charles (1879). "rānuncŭlus". rānuncŭlus. Perseus Digital Library. https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0059:entry=ranunculus.
- ↑ Edsall, Marian S. (1985). Roadside Plants and Flowers: A Traveler's Guide to the Midwest and Great Lakes Area: With a Few Familiar Off-Road Wildflowers. North Coast Books. University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 0299097048. https://archive.org/details/roadsideplantsfl0000edsa.
- ↑ Kamen, Deborah (2010). "A corpus of inscriptions: Representing slave marks in antiquity". Memoirs of the American Academy in Rome 55: 95–110. ISSN 0065-6801. https://www.jstor.org/stable/41419689.
- ↑ Aoki, Haruo (1994). Nez Perce dictionary. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. pp. 641, 1007. ISBN 9780520097636.
- ↑ Rude, Noel (2014). Umatilla dictionary. Seattle, WA: University of Washington Press. pp. 54, 275. ISBN 9780295994284.
- ↑ Emadzade, K.; Lehnebach, C.; Lockhart, P.; Hörandl, E. (2010). "A molecular phylogeny, morphology and classification of genera of Ranunculeae (Ranunculaceae)". Taxon 59 (3): 809–828. doi:10.1002/tax.593011.
- ↑ Aslam, M.S.; Choudhari, B.S.; Uzair, M.; Ijaz, A.S. (2012). "The genus Ranunculus: A phytochemical and ethnopharmacological review". International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences 4 (5): 15–22.
- ↑ "Ranunculus". Botanical Dermatology Database. http://www.botanical-dermatology-database.info/BotDermFolder/RANU.html#Ranunculus.
- ↑ Bateman, Stephanie (May 25, 2021). "Are buttercups poisonous to horses? We ask the experts…". https://www.horseandhound.co.uk/features/are-buttercups-poisonous-to-horses-648261.
- ↑ Mai, Dieter Hans (2007). "The floral change in the tertiary of the Rhön mountains (Germany)". Acta Paleobotanica 47 (1): 135–143.
- ↑ Huang, Yong‐Jiang; Zhu, Hai; Su, Tao; Spicer, Robert A.; Hu, Jin‐Jin; Jia, Lin‐Bo; Zhou, Zhe‐Kun (September 2022). "Rise of herbaceous diversity at the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: First insight from fossils" (in en). Journal of Systematics and Evolution 60 (5): 1109–1123. doi:10.1111/jse.12755. ISSN 1674-4918. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jse.12755.
- ↑ Ashworth, A; Cantrill, D (2004-10-07). "Neogene vegetation of the Meyer Desert Formation (Sirius Group) Transantarctic Mountains, Antarctica" (in en). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 213 (1–2): 65–82. doi:10.1016/S0031-0182(04)00359-1. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0031018204003591.
General sources
- "GRIN Species Records of Ranunculus". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Beltsville Area. http://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/npgs/html/splist.pl?10248.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ranunculus. |
Wikidata ☰ Q146130 entry
 |




