Biology:Red-lipped batfish
| Red-lipped batfish | |
|---|---|

| |
| Off the Galápagos Islands | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Lophiiformes |
| Family: | Ogcocephalidae |
| Genus: | Ogcocephalus |
| Species: | O. darwini
|
| Binomial name | |
| Ogcocephalus darwini C. L. Hubbs, 1958
| |
| <mapframe height="200" frameless="1" width="300">{"properties":{"stroke-width":6,"stroke":"#ff0000","title":"Red-lipped batfish"},"type":"ExternalData","title":"Galápagos batfish range.map","service":"page"}</mapframe> | |
| IUCN distribution
Extant (resident)
| |
The red-lipped batfish or Galápagos batfish (Ogcocephalus darwini) is a fish of unusual morphology found around the Galápagos Islands and off Peru at depths of 3 to 76 m (10 to 249 ft).[2] Red-lipped batfish are closely related to rosy-lipped batfish (Ogcocephalus porrectus), which are found near Cocos Island off the Pacific coast of Costa Rica. This fish is mainly known for its bright red lips. Batfish are not good swimmers; they use their highly adapted pectoral, pelvic and anal fins to "walk" on the ocean floor. When the batfish reaches maturity, its dorsal fin becomes a single spine-like projection (thought to function primarily as a lure for prey).
Diet
The species is a piscivore/invertivore, mainly feeding on other small fish and small invertebrates including shrimp, crabs, worms and mollusks.[3]
Description
The red-lipped batfish reaches up to 40 centimetres (16 in) in length.[2] Its body color is light brown and a greyish colour on its back (though not very visible in sea), with white countershading on the underside. On the top side of the batfish, there is usually a dark brown stripe starting at the head and going down the back to the tail. The snout and horn of the red-lipped batfish is a brownish color. As the name of the fish states, the batfish has bright, almost fluorescent, red lips. The color of the squamation of the red-lipped batfish is shagreen-like with a relatively smooth texture. The bucklers are concealed by a layer of fine spinules.
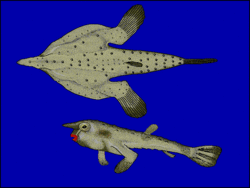
When compared to the porrectus, the red-lipped batfish has a shorter disk perimeter but a higher fibre pectoral fin ray count. Regarding the number of scales along the lateral line, there are four to nine subopercular scales, six to nine on the cheek, usually. The red-lipped batfish has around 19-20 vertebrae.[2]
On the top of the batfish's head there is a special body part that extends outward called an illicium. After the red-lipped batfish fully matures, its dorsal fin becomes a single spine-like projection that comes out of the top of the head. The batfish uses the illicium as a way to lure prey near them.[4][unreliable source?]
At the top of its illicium is an esca. The esca emits a bright light and since these fish dwell in deep waters, the light lures other fish to where the batfish is positioned.[5] The esca lures the prey to the batfish which then allows it to eat those small creatures which fall into its trap.
Red-lipped batfish have extremely bright red lips which allows people to distinguish them from other batfish. Marine biologists hypothesize that the bright red lips may enhance species recognition during spawning. [6]
Habitat
Red-lipped batfish can be found at depths of 3 to 76 m (10 to 249 ft) in the Pacific Ocean around the Galapagos Islands and off Peru.[2] It has been noted before that a few specimens of red-lipped batfish were found in fishnets in California, but all these types of sightings are extremely rare, and could very well be another type of batfish. They are bottom dwellers, so they are usually found within the sand or ocean floor. Although they are considered shallow-water forms, they occasionally come to the surface over deep water.[7] They tend to associate themselves with the edges of reefs up to about 120 m deep.[1]
Predators
The red-lipped batfish has no known direct threats. However, rising sea temperatures and coral bleaching could pose a threat, as it would alter the natural habitat and may cause a decline in the availability of a natural food source.[8]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Lea, B.; McCosker, J. (2010). "Ogcocephalus darwini". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010: e.T183821A8183039. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-3.RLTS.T183821A8183039.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/183821/8183039. Retrieved 25 March 2023.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2016). "Ogcocephalus darwini" in FishBase. January 2016 version.
- ↑ "Red-lipped batfish | Strange Animals". Strangeanimals.info. 2011-10-13. http://www.strangeanimals.info/2011/10/red-lipped-batfish.html.
- ↑ "Red-lipped Batfish". http://factspod.blogspot.com/2013/02/red-lipped-batfish.html.
- ↑ "Red-Lipped Batfish". Aboutfishonline.com. http://www.aboutfishonline.com/articles/redlipped.html.
- ↑ "Red-Lipped Batfish". Aboutfishonline.com. http://www.aboutfishonline.com/articles/redlipped.html.
- ↑ Hubbs, Carl L. (August 28, 1958). "Ogcocephalus darwini, a new batfish endemic at the Galápagos Islands". Copeia 1958 (3): 161-170. doi:10.2307/1440581.
- ↑ "Red-lipped Batfish". 2021. https://galapagosconservation.org.uk/wildlife/red-lipped-batfish/.
External links
- About fish online
- Photos of Red-lipped batfish on Sealife Collection
Wikidata ☰ Q2021885 entry
 |


