Biology:Shrewlike rat
| Shrewlike rat | |
|---|---|

| |
| Rhynchomys soricoides (lower animal) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Rodentia |
| Family: | Muridae |
| Tribe: | Hydromyini |
| Genus: | Rhynchomys Thomas, 1895 |
| Type species | |
| R. soricoides | |
| Species | |
|
Rhynchomys banahao | |
| |
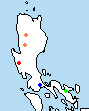
| Distribution of shrewlike rats on Luzon Island. Orange = R. soricoides, red = R. tapulao, blue = R. banahao, and green = R. isarogensis. | |
The shrewlike rats, genus Rhynchomys, also known as the tweezer-beaked rats are a group of unusual Old World rats found only on the island of Luzon in the Philippines . They look a great deal like shrews and are an example of convergent evolution. Shrewlike rats evolved to be vermivores and insectivores feeding on soft-bodied invertebrates associated with leaf litter.
Characteristics
The snout and rostrum are very long. Eyes are small. Head and body is 18.8–21.5 cm with a tail 10.5–14.6 cm.[1] Only two molars are present on each side of the upper and lower jaws; these are small and peg-like. Incisors are described as needle-like and mandibles as delicate.[1][2] Their characteristic method of locomotion has given rise to the epithet "hopping rats," describing their method of pouncing on an earthworm prey before it can slide back into its hole.[3]
Distribution
Shrewlike rats are found at elevations of 1,100 to 2,460 meters.[1][2] They are restricted to moist, mossy highland regions with ample rainfall and large populations of earthworms. Populations appear to be very isolated, restricted to "sky islands" of Luzon. Specimens have been collected from Mt. Bali-it and Mt. Data of the Central Cordillera (R. soricoides), Mt. Tapulao of the Zambales Mountains (R. tapulao),[2] Mount Banahao (R. banahao),[2] Mount Isarog (R. isarogensis), Mt. Labo of the Bicol Peninsula (R. labo)[4] and Mt. Mingan of the Sierra Madre (R. mingan).[4]
Relationships
Rhynchomys is an old endemic of the Philippines.[5] The genus is distinct enough to give it its own group distinct from all other old endemics.[5] It was classified as part of the Chrotomys division along with Apomys, Archboldomys, and Chrotomys.[6] Within this division, Rhynchomys is most closely related to the other Philippine shrew-rats in the genera Archboldomys and Chrotomys.[7]
Species
From 1895 until 1981, Rhynchomys was only known from a few specimens taken from near the type locality of R. soricoides. In 1981, this was expanded by one species with the discovery and description of R. isarogensis. In 2007, two species, R. banahao and R. tapulao, were described from Mt. Banahao and Mt. Tapulao, respectively.[2] In 2019, two additional species were described, R. labo and R. mingan from Mt. Labo and Mt. Mingan, respectively.[8][4]
- Banahao shrew-rat (Rhynchomys banahao) Balete et al., 2007
- Isarog shrew-rat, (Rhynchomys isarogensis) Musser and Freeman, 1981
- Labo shrew-rat (Rhynchomys labo) Rickart et al., 2019
- Mingan shrew-rat (Rhynchomys mingan) Rickart et al., 2019
- Mount Data shrew-rat (Rhynchomys soricoides) Thomas, 1895
- Tapulao shrew-rat (Rhynchomys tapulao) Balete et al., 2007
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Nowak, R. M.; Walker, E. P. (1999). Walker's Mammals of the World. JHU Press. ISBN 978-0801857898. https://archive.org/details/walkersmammalsof0001nowa.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Balete, D. S.; Rickart, E. A.; Rosell-Ambal, R.G.B.; Jansa, S.; Heaney, L. R. (2007). "Descriptions of Two New Species of Rhynchomys Thomas (Rodentia: Muridae: Murinae) from Luzon Island, Philippines". Journal of Mammalogy 88 (2): 287–301. doi:10.1644/06-MAMM-A-090R.1.
- ↑ "3 Questions with a Scientist: Hopping Rats". Field Museum of Natural History. June 6, 2019. https://www.fieldmuseum.org/blog/3-questions-scientist-hopping-rats.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Rickart, E. A; Balete, D. S; Timm, R. M; Alviola, P. A; Esselstyn, J. A; Heaney, L. R (2019). "Two new species of shrew-rats (Rhynchomys: Muridae: Rodentia) from Luzon Island, Philippines". Journal of Mammalogy. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz066.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Musser, G. G.; L. R. Heaney (2006). "Philippine rodents: Definitions of Tarsomys and Limnomys plus a preliminary assessment of phylogenetic patterns among native Philippine murines (Murinae, Muridae)". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 211: 1–138.
- ↑ Musser, G.G.; Carleton, M.D. (2005). "Genus Rhynchomys". in Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 1497–1498. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494. http://www.departments.bucknell.edu/biology/resources/msw3/browse.asp?id=13001799.
- ↑ Jansa, S.; Barker, F. K.; Heaney, L. R. (2006). "The pattern and timing of diversification of Philippine endemic rodents: evidence from mitochondrial and nuclear gene sequences". Systematic Biology 55 (1): 73–88. doi:10.1080/10635150500431254. PMID 16507525.
- ↑ Lanese, M. (6 June 2019). "Worms lure two new species of hopping rats out of obscurity". https://www.sciencenews.org/article/two-new-species-hopping-rats-discovered-worms.
Wikidata ☰ Q1189626 entry
 |
