Biology:Rhynchostegium
| Rhynchostegium | |
|---|---|

| |
| Rhynchostegium murale | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Bryophyta |
| Class: | Bryopsida |
| Subclass: | Bryidae |
| Order: | Hypnales |
| Family: | Brachytheciaceae |
| Genus: | Rhynchostegium Bruch & Schimp. 1852[1] |
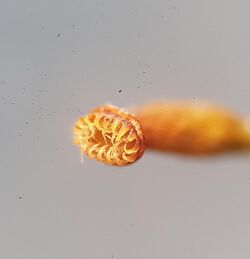
Rhynchostegium is a genus of pleurocarpous mosses belonging to the family Brachytheciaceae.[2] The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution across different climatological regions except the polar regions, mostly in tropic to north temperate regions.[2][1] The genus contains both aquatic and terrestrial species.[1][3] The genus was named for their rostrate opercula.[1] The type species of this genus is Rhynchostegium confertum (Dicks.) Schimp.[1]
Etymology
The genus name comes from the Greek rhyncho- (beaked) and stegos (a lid), which refers to the rostrate operculum of the sporophyte.[1]
History
The genus was first described by Bruch and Wilhelm Philippe Schimper in 1852.[2][1]
Habitats
Terrestrial species of Rhynchostegium live in moist to wet or shaded habitats, on rock, soil, tree base, tree stem, and logs.[1][4][5]
Aquatic species live by or in running water, including streams, springs, rivers, beds of waterfalls, and seepy cliffs.[3][6]
Morphology
Gametophyte
Rhynchostegium are small to large mosses that form either loose tuft or extensive mats on the substrate, with irregular or regular branching.[1][3] The younger plants are generally deep green or light green; aging plants could become whitish, brownish, or paler green.[1][3] Stems are creeping and lack hyaloderm, with acute to acuminate pseudoparaphyllia.[3] Stem leaves are erectopatent or erect.[1][3] Branch leaves are similar in morphology to stem leaves but smaller and sometimes narrower.[3] Leaves are commonly straightly to homomallously arranged; subimbricate, subcomplanate, or complanate arrangement are sometimes seen, especially in branch leaves.[1] Leaf base, decurrent or not, varies from ovate to ovate-cordate, occasionally lanceolate, and the narrowing from gradual to abrupt, towards a short- or long-acuminate apex, where sometimes a differentiated long acumen or apiculus is present.[1] The leaves have a single costa that generally smoothly ends 35-75% up the leaf, and more often in branch leaves in an abaxial spine.[1] Leaf surfaces vary from flat to slightly concave and not to strongly longitudinally plicate, with little to some pores and linear laminal cells.[1][3] Leaf margins are serrate to serrulate.[1][3] Axillary hairs constitute of 3-7 cells,[3] with 1-3 upper cells.[1] Alar cells are slightly enlarged, and either undifferentiated or quadrate to elongate-rectangular.[1][3]
Sporophyte
Rhynchostegium are autoicous.[3] Covered by a naked calyptra is a rostrate to long-rostrate operculum attached to a red-brown to brown, oblong-cylindric, weakly curved capsule, which is inclined or horizontal to a red-brown, smooth seta that has abruptly contracted perichaetial leaves at the base, with acumen straight to reflexed.[1][3] An annulus separates the operculum.[3] The peristome is xerochastic and perfect, which the red to orange-red exostomes have reduced trabeculae and cross-striolae at the base of the teeth; in rare cases the exostomes are narrow and yellow.[1][3] The broadly or narrowly perforated endostomes and developed to vestigial cilia are supported by a low or high basal membrane.[1] Spore diameters range between 9-16 µm.[3]
Biochemistry
Allelopathy
Allelopathy has been studied on Rhynchostegium pallidifolium, which usually form pure colonies in their natural habitat.[7][8] Methanol extract of R.pallidifolium represses the seedling of cress, alfalfa, lettuce, ryegrass, timothy,and Digitaria sanguinalis in a concentration-dependent manner.[7] A combination of ESI-MS and 1H NMR analyses identified the inhibitory chemical as 3-hydroxy-β-ionone.[7] Further study showed a minimal 3-hydroxy-β-ionone concentration of 1 µM for the inhibition of cress hypocotyl growth, and 3 µM for cress root growth, while the endogenous concentration.[8] The presence of 3-hydroxy-β-ionone in their natural substrate and the growing medium suggested secretion to the environment, which may imply an important role of 3-hydroxy-β-ionone in competition with other plants and the forming of pure colonies.[8]
Antibacterial
Acetone extract of Rhynchostegium riparioides showed antibiotic activity on some Gram-negative bacteria, including Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Entero-bacter cloacae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.[9]
Ethanolic extract of Rhynchostegium vagans showed similar effect on some Gram-negative bacteria and fungi, with performance superior to chloramphenicol and fluconazole.[10]
Applications
Freshwater monitoring
Rhynchostegium riparioides is used in monitoring of heavy metals concentration in freshwater in multiple regions around the world,[11][12][13] such as copper,[14][15] zinc.[16] R. riparioides as a neutrophilous species has been used in monitoring water acidification.[17]
List of species
The World Flora Online lists 221 species of Rhynchostegium.[18]
- Rhynchostegium acanthophyllum (Mont.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium acicula (Broth.) Broth.
- Rhynchostegium acutifolium (Hook. f. & Wilson) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium alboviridum R.S. Williams
- Rhynchostegium algirianum (Brid. ex P. Beauv.) Lindb.
- Rhynchostegium alopecuroides (Brid.) A.J.E. Sm.
- Rhynchostegium altisetum Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium ambiguum (Schwägr.) W.R. Buck
- Rhynchostegium anceps (Bosch & Sande Lac.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium aneuron Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium angustifolium Renauld & Cardot
- Rhynchostegium apophysatum (Hornsch.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium aquaticum A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium arcticum (I. Hagen) Ignatov & Huttunen
- Rhynchostegium asperisetum (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium assumptionis Besch.
- Rhynchostegium bello-intricatum (Broth.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium bequaertii Thér. & Naveau
- Rhynchostegium berteroanum (Mont.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium beskeanum (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium bifariellum (Kindb.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium brachypterum (Hornsch.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium brachypyxis Renauld & Cardot
- Rhynchostegium brachythecioides Dixon & P. de la Varde
- Rhynchostegium brandegei (Austin) Renauld & Cardot
- Rhynchostegium brevicuspis Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium brevinerve Huttunen & Ignatov
- Rhynchostegium brevirete Broth.
- Rhynchostegium buluense (Broth.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium cacticola (Müll. Hal.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium calderi Vohra
- Rhynchostegium caloosiense (Austin) Renauld & Cardot
- Rhynchostegium campylocarpum (Müll. Hal.) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium campylocladulum Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium cataractarum Thér. & P. de la Varde
- Rhynchostegium celebicum (Sande Lac.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium chrysophylloides A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium circinatum (Brid.) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium cirrosum (Schwägr.) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium collatum (Hook. & Wilson) Broth. & Watts
- Rhynchostegium comorae (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium complanum (Mitt.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium compridense (Müll. Hal. ex Broth.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium conchophyllum (Taylor) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium confertum (Dicks.) Schimp.
- Rhynchostegium confusum Cezón, J. Muñoz, Hedenäs & Huttunen[4]
- Rhynchostegium congruens (Hampe) Mitt.
- Rhynchostegium conostomus (Mont.) Huttunen & Ignatov
- Rhynchostegium contortulum Tixier
- Rhynchostegium contractum Cardot
- Rhynchostegium crassinervium (Taylor) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium cylindritheca Dixon
- Rhynchostegium dasyphyllum Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium delicatulum James
- Rhynchostegium demissum (Wilson) Schimp.
- Rhynchostegium dentiferum (Hampe) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium deplanatum (Bruch & Schimp. ex Sull.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium depressum (Brid.) Schimp.
- Rhynchostegium distans Besch.
- Rhynchostegium distratum (Hampe) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium drepanocladioides (Müll. Hal.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium duthiei Müll. Hal. ex Dixon
- Rhynchostegium elusum (Mitt.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium erythropodium (Hampe) Mitt.
- Rhynchostegium esquirolii Cardot & Thér.
- Rhynchostegium exiguum (Blandow) Brockm.
- Rhynchostegium exilissimum (Sull.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium fabroniadelphus (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium fauriei Cardot
- Rhynchostegium finitimum (Hampe) Ångström
- Rhynchostegium fissidens (Müll. Hal.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium fissidentellum Besch.
- Rhynchostegium fragilicuspis Dixon
- Rhynchostegium fuegianum (Cardot) Huttunen & Ignatov
- Rhynchostegium funckii (Schimp.) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium gaudichaudii (Mont.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium georgianum Dixon & Grout
- Rhynchostegium glaucovirescens (Müll. Hal.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium globipyxis (Müll. Hal.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium gracilipes Thér.
- Rhynchostegium graminicolor (Brid.) A.L. Andrews
- Rhynchostegium herbaceum (Mitt.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium hians (Hedw.) Delogne
- Rhynchostegium homaliocaulon (Müll. Hal.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium hookeri A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium hopfferi (Welw. & Duby) A. Gepp
- Rhynchostegium horridum Broth.
- Rhynchostegium huitomalconum (Müll. Hal.) Besch.
- Rhynchostegium humillimum (Mitt.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium hunanense Ignatov & Huttunen
- Rhynchostegium huttonii (Hampe ex Beckett) Paris
- Rhynchostegium illecebrum (Schimp.) Delogne
- Rhynchostegium inaequale Dixon
- Rhynchostegium inclinatum (Mitt.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium inerme (Mitt.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium irriguum Dixon
- Rhynchostegium isopterygioides Cardot
- Rhynchostegium jamesii Sull.
- Rhynchostegium javanicum (Bél.) Besch.
- Rhynchostegium jovet-astiae Bizot
- Rhynchostegium laevisetum (Geh.) Mitt.
- Rhynchostegium lamasicum (Spruce ex Mitt.) Besch.
- Rhynchostegium laxatum (Mitt.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium laxirete Broth.
- Rhynchostegium leptoblastum (Müll. Hal.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium leptomerocarpum (Müll. Hal.) Besch.
- Rhynchostegium leptopteridium Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium leucodictyon Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium lindmanii (Broth.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium lusitanicum (Kindb.) Broth.
- Rhynchostegium luteonitens (Welw. & Duby) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium mac-owanianum Paris
- Rhynchostegium malmei (Broth.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium megapolitanum (Blandow ex F. Weber & D. Mohr) Schimp.
- Rhynchostegium membranaceum (Müll. Hal.) Broth.
- Rhynchostegium menadense (Sande Lac.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium meridionale (Schimp.) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium micans (Sw.) Austin
- Rhynchostegium microthamnioides Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium minutum Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium muelleri A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium murale (Hedw.) Schimp.
- Rhynchostegium muriculatum (Hook. f. & Wilson) Reichardt
- Rhynchostegium mutatum (Ochyra & Vanderp.) Huttunen & Ignatov
- Rhynchostegium myosuroides (Brid.) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium nanopennatum (Broth.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium nanothecium Müll. Hal. ex Dixon
- Rhynchostegium nervosum (Kiaer ex Renauld) Broth. ex Cardot
- Rhynchostegium nigrescens Besch.
- Rhynchostegium oblongifolium Broth. & Watts
- Rhynchostegium obtusatum Broth.
- Rhynchostegium obtusifolium (Mitt.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium occultum Larraín, Huttunen, Ignatova & Ignatov[5]
- Rhynchostegium omocrates W.R. Buck
- Rhynchostegium ovalfolium S. Okamura
- Rhynchostegium oxyodon (Welw. & Duby) A. Gepp
- Rhynchostegium pallidifolium (Mitt.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium pallidius (Hampe) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium pampae (Müll. Hal.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium parvulum Broth.
- Rhynchostegium patulifolium Cardot & Thér.
- Rhynchostegium patulum A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium pectinatum (Mitt.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium pellucidum Dixon
- Rhynchostegium pendulum (Brid.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium peruviense (R.S. Williams) Ochyra
- Rhynchostegium pervilleanum (Schimp.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium philippinense (Duby) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium piliferum (Hedw.) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium pinnicaule (Müll. Hal.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium plagiotheciella Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium planifolium Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium planiusculum (Mitt.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium praecox (Hedw.) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium praelongum (Hedw.) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium pringlei Cardot
- Rhynchostegium pseudoconfertum (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium pseudodistans Cardot
- Rhynchostegium pseudomurale (Hampe) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium pseudoserrulatum (Kindb.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium psilopodium Ignatov & Huttunen
- Rhynchostegium pulchellum (Hedw.) H. Rob.
- Rhynchostegium pumilum (Wilson) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium raphidorrhynchum (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium recurvans (Michx.) Besch.
- Rhynchostegium revelstokense (Kindb.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium riparioides (Hedw.) Cardot
- Rhynchostegium rivale (Hampe) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium robustum W.R. Buck
- Rhynchostegium rotundifolium (Scop. ex Brid.) Schimp.
- Rhynchostegium royae (Austin) Renauld & Cardot
- Rhynchostegium ruvenzorense (Broth.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium santaiense (Broth. & Paris) Broth.
- Rhynchostegium sarcoblastum Broth. & Paris
- Rhynchostegium savatieri Paris
- Rhynchostegium scariosum (Taylor) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium selaginellifolium Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium sellowii (Hornsch.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium semiscabrum (E.B. Bartram) H. Rob.
- Rhynchostegium semitortulum Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium semitortum A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium senodictyon (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium serpenticaule (Müll. Hal.) Broth.
- Rhynchostegium serrulatum (Hedw.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium shawii Hutsemekers & Vanderp.
- Rhynchostegium sinense (Broth. & Paris) Broth.
- Rhynchostegium sparsirameum (Geh. & Hampe) Paris
- Rhynchostegium stokesii (Turner) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium stramineoides (Sauerb.) Wijk & Margad.
- Rhynchostegium striatum (Schreb. ex Hedw.) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium strigosum (Hoffm. ex F. Weber & D. Mohr) De Not.
- Rhynchostegium strongylense (Bott.) W.R. Buck & Privitera
- Rhynchostegium styriacum (Limpr.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium subacutifolium (Müll. Hal. ex Geh.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium subbrachypterum Broth. & Bryhn
- Rhynchostegium subclavatum (Hampe) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium subconfertum (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium subenerve A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium submenadense Thér. & P. de la Varde
- Rhynchostegium subperspicuum (Müll. Hal.) Broth.
- Rhynchostegium subrectocarpum (Dixon) Vohra
- Rhynchostegium subrotundum (Hampe) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium subrusciforme (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium subserrulatum (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium subspeciosum (Müll. Hal.) Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium subtrachypterum Bryhn ex P. Syd.
- Rhynchostegium surrectum (Mitt.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium taphrophilum Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium tenellum (Dicks.) Schimp.
- Rhynchostegium tenuifolium (Hedw.) Reichardt
- Rhynchostegium tenuivagum (Broth.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium tocaremae (Hampe) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium trachynotum (Müll. Hal.) Kindb.
- Rhynchostegium trachypelma (Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium trieblingii Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium tubaronense Müll. Hal.
- Rhynchostegium ulicon (Taylor) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium validum (Herzog) Ochyra
- Rhynchostegium vitianum E.B. Bartram & Dixon
- Rhynchostegium volkensii (Broth.) Paris
- Rhynchostegium vriesei (Dozy & Molk.) A. Jaeger
- Rhynchostegium zeyheri (Spreng. ex Müll. Hal.) A. Jaeger
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 Hedenäs, Lars. "RHYNCHOSTEGIUM". https://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/Mosses_online/Brachytheciaceae_Rhynchostegium.pdf.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Rhynchostegium Bruch & Schimp." (in en). https://www.gbif.org/species/7441919.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 "Rhynchostegium in Flora of North America @ efloras.org". http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=128500.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Cezón, Katia; Muñoz, Jesús; Hedenäs, Lars; Huttunen, Sanna (2010-03-01). "Rhynchostegium confusum, a new species from the Iberian Peninsula and its relation to R. confertum based on morphological and molecular data". Journal of Bryology 32 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1179/037366810X12578498135832. ISSN 0373-6687. https://doi.org/10.1179/037366810X12578498135832.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 JUAN BERNARDO LARRAÍN; SANNA HUTTUNEN; ELENA IGNATOVA; MICHAEL IGNATOV (23 July 2020). "Rhynchostegium occultum (Brachytheciaceae), a new species from relict forests of central Chile". Phytotaxa 453 (3): 199–217. doi:10.11646/phytotaxa.453.3.3. https://www.biotaxa.org/Phytotaxa/article/view/phytotaxa.453.3.3. Retrieved 11 September 2023.
- ↑ Kelly, M. G.; Whitton, B. A. (December 1987). "Growth rate of the aquatic moss Rhynchostegium riparioidesin Northern England" (in en). Freshwater Biology 18 (3): 461–468. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2427.1987.tb01331.x. ISSN 0046-5070. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2427.1987.tb01331.x.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Kato-Noguchi, Hisashi; Seki, Takahiro; Shigemori, Hideyuki (2010-04-15). "Allelopathy and allelopathic substance in the moss Rhynchostegium pallidifolium" (in en). Journal of Plant Physiology 167 (6): 468–471. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2009.10.018. ISSN 0176-1617. PMID 20018404. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0176161709004672.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Hisashi Kato-Noguchi; Takahiro Seki (1 June 2010). "Allelopathy of the moss Rhynchostegium pallidifolium and 3-hydroxy-β-ionone" (in en). Plant Signaling & Behavior 5 (6): 702–704. doi:10.4161/psb.5.6.11642. PMID 20400848. PMC 3001564. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.5.6.11642. Retrieved 11 September 2023.
- ↑ A. Basile; M. L. Vuotto; M. T. L. Ielpo; V. Moscatiello; L. Ricciardi; S. Giordano; R. Castaldo Cobianchi (1998). "Antibacterial Activity inRhynchostegiumriparioides(Hedw.) Card. Extract (Bryophyta)". Phytotherapy Research 12 (S1): S146–S148. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-1573(1998)12:1+<S146::AID-PTR278>3.0.CO;2-4. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1573(1998)12:1+%3CS146::AID-PTR278%3E3.0.CO;2-4. Retrieved 11 September 2023.
- ↑ Negi, Kavita; Chaturvedi, Preeti (2016-01-01). "In vitro antimicrobial efficacy of Rhynchostegium vagans A. Jaeger (moss) against commonly occurring pathogenic microbes of Indian sub-tropics" (in en). Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease 6 (1): 10–14. doi:10.1016/S2222-1808(15)60977-X. ISSN 2222-1808.
- ↑ García-Álvaro, M. Angélica; Martínez-Abaigar, Javier; Núñez-Olivera, Encarnación; Beaucourt, Nathalie (September 2000). [0518:ECAERI2.0.CO;2.full "Element Concentrations and Enrichment Ratios in the Aquatic Moss Rhynchostegium riparioides along the River Iregua (La Rioja, Northern Spain)"]. The Bryologist 103 (3): 518–533. doi:10.1639/0007-2745(2000)103[0518:ECAERI2.0.CO;2]. ISSN 0007-2745. https://bioone.org/journals/the-bryologist/volume-103/issue-3/0007-2745_2000_103_0518_ECAERI_2.0.CO_2/Element-Concentrations-and-Enrichment-Ratios-in-the-Aquatic-Moss-Rhynchostegium/10.1639/0007-2745(2000)103[0518:ECAERI]2.0.CO;2.full.
- ↑ Wehr, J. D.; Whitton, B. A. (1983-01-01). "Accumulation of heavy metals by aquatic mosses. 2: Rhynchostegium riparioides" (in en). Hydrobiologia 100 (1): 261–284. doi:10.1007/BF00027433. ISSN 1573-5117. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00027433.
- ↑ Mouvet, Christophe; Claveri, Bruno (1999-02-01). "Localization of copper accumulated in Rhynchostegium riparioides using sequential chemical extraction" (in en). Aquatic Botany 63 (1): 1–10. doi:10.1016/S0304-3770(98)00110-7. ISSN 0304-3770. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304377098001107.
- ↑ Claveri, B.; Morhain, E.; Mouvet, C. (1994-06-01). "A methodology for the assessment of accidental copper pollution using the aquatic moss Rhynchostegium riparioides" (in en). Chemosphere 28 (11): 2001–2010. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(94)90150-3. ISSN 0045-6535. Bibcode: 1994Chmsp..28.2001C. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535%2894%2990150-3.
- ↑ Claveri, B.; Mouvet, C. (1995-04-01). "Temperature effects on copper uptake and CO2 assimilation by the aquatic moss Rhynchostegium riparioides" (in en). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 28 (3): 314–320. doi:10.1007/BF00213108. ISSN 1432-0703. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00213108.
- ↑ Wehr, J. D.; Kelly, M. G.; Whitton, B. A. (1987-12-01). "Factors affecting accumulation and loss of zinc by the aquatic moss Rhynchostegium riparioides (Hedw.) C. Jens." (in en). Aquatic Botany 29 (3): 261–274. doi:10.1016/0304-3770(87)90020-9. ISSN 0304-3770. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0304-3770%2887%2990020-9.
- ↑ Thiebaut, Gabrielle; Vanderpoorten, Alain; Guerold, François; Boudot, Jean-Pierre; Muller, Serge (1998-03-01). "Bryological patterns and streamwater acidification in the Vosges Mountains (N.E. France): An analysis tool for the survey of acidification processes" (in en). Chemosphere 36 (6): 1275–1289. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00373-1. ISSN 0045-6535. Bibcode: 1998Chmsp..36.1275T. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045653597003731.
- ↑ "Search". http://www.worldfloraonline.org/search?query=Rhynchostegium.
Wikidata ☰ Q13568749 entry
 |